Flexible and Versatile as a Chameleon—Sophisticated Functions of microRNA-199a
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. miR-199a: One among Thousands
2.1. Regulation of miR-199a Expression
2.2. miR-199a in Tumorigenesis
2.2.1. Down-Regulation of miR-199a
2.2.2. Up-Regulation of miR-199a
2.2.3. Other Features of miR-199a in Cancer
2.4. miR-199a in Cardiogenesis
2.5. miR-199a in Osteogenesis, Chondrogenesis and Adipogenesis
2.6. miR-199a in Embryonic Stem Cells Differentiation and Embryo Development
2.7. Other Functions of miR-199a
3. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
References
- Lagos-Quintana, M.; Rauhut, R.; Meyer, J.; Borkhardt, A.; Tuschl, T. New micrornas from mouse and human. RNA 2003, 9, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. MiRbase: Integrating microrna annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 2011, 39, D152–D157. [Google Scholar]
- Krichevsky, A.M.; Gabriely, G. MiR-21: A small multi-faceted rna. J. Cell. Mol. Med 2009, 13, 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, L.P.; Glasner, M.E.; Yekta, S.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Vertebrate microrna genes. Science 2003, 299, 1540. [Google Scholar]
- Landgraf, P.; Rusu, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sewer, A.; Iovino, N.; Aravin, A.; Pfeffer, S.; Rice, A.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Landthaler, M.; et al. A mammalian microrna expression atlas based on small rna library sequencing. Cell 2007, 129, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.B.; Bantounas, I.; Lee, D.Y.; Phylactou, L.; Caldwell, M.A.; Uney, J.B. Twist-1 regulates the miR-199a/214 cluster during development. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, G.; Chen, R.; Alvero, A.B.; Fu, H.H.; Holmberg, J.; Glackin, C.; Rutherford, T.; Mor, G. Twisting stemness, inflammation and proliferation of epithelial ovarian cancer cells through miR199a2/214. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3545–3553. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, T.; Sato, T.; Amano, T.; Kawamura, Y.; Kawamura, N.; Kawaguchi, H.; Yamashita, N.; Kurihara, H.; Nakaoka, T. Dnm3os, a non-coding rna, is required for normal growth and skeletal development in mice. Dev. Dyn 2008, 237, 3738–3748. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Lee, U.J.; Kim, M.N.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Choung, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, Y.C. Microrna miR-199a* regulates the met proto-oncogene and the downstream extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (erk2). J. Biol. Chem 2008, 283, 18158–18166. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, S.; Iba, H. Putative promoter regions of miRna genes involved in evolutionarily conserved regulatory systems among vertebrates. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, H.H.; Lee, T.L.; Davis, A.J.; Taft, D.H.; Rennert, O.M.; Chan, W.Y. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling reveals novel epigenetically regulated genes and non-coding rnas in human testicular cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Mudduluru, G.; Ceppi, P.; Kumarswamy, R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Papotti, M.; Allgayer, H. Regulation of axl receptor tyrosine kinase expression by miR-34a and miR-199a/b in solid cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2888–2899. [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai, K.; Furukawa, C.; Haraguchi, T.; Inada, K.; Shiogama, K.; Tagawa, T.; Fujita, S.; Ueno, Y.; Ogata, A.; Ito, M.; et al. Micrornas miR-199a-5p and -3p target the brm subunit of swi/snf to generate a double-negative feedback loop in a variety of human cancers. Cancer Res 2011, 71, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar]
- Loebel, D.A.; Tsoi, B.; Wong, N.; Tam, P.P. A conserved noncoding intronic transcript at the mouse dnm3 locus. Genomics 2005, 85, 782–789. [Google Scholar]
- Wienholds, E.; Kloosterman, W.P.; Miska, E.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Berezikov, E.; de Bruijn, E.; Horvitz, H.R.; Kauppinen, S.; Plasterk, R.H. Microrna expression in zebrafish embryonic development. Science 2005, 309, 310–311. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, R.; O’Carroll, D.; Pasolli, H.A.; Zhang, Z.; Dietrich, F.S.; Tarakhovsky, A.; Fuchs, E. Morphogenesis in skin is governed by discrete sets of differentially expressed micrornas. Nat. Genet 2006, 38, 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- van Rooij, E.; Sutherland, L.B.; Liu, N.; Williams, A.H.; McAnally, J.; Gerard, R.D.; Richardson, J.A.; Olson, E.N. A signature pattern of stress-responsive micrornas that can evoke cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18255–18260. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, L.; Hummel, M.; Korfel, A.; Lenze, D.; Joehrens, K.; Thiel, E. Differential micro-rna expression in primary cns and nodal diffuse large b-cell lymphomas. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 13, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Santhakumar, D.; Forster, T.; Laqtom, N.N.; Fragkoudis, R.; Dickinson, P.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Manakov, S.A.; Choudhury, N.R.; Griffiths, S.J.; Vermeulen, A.; et al. Combined agonist-antagonist genome-wide functional screening identifies broadly active antiviral micrornas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13830–13835. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Lin, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Dong, Q.; Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Identification of miRnomes in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 232–243. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.G.; Kim, Y.W.; Kim, E.H.; Meng, Z.; Huang, W.; Hwang, S.J.; Kim, S.G. Farnesoid X receptor protects hepatocytes from injury by repressing miR-199a-3p, which increases levels of lkb1. Gastroenterology 2012, 142. [Google Scholar]
- Rane, S.; He, M.; Sayed, D.; Yan, L.; Vatner, D.; Abdellatif, M. An antagonism between the akt and beta-adrenergic signaling pathways mediated through their reciprocal effects on miR-199a-5p. Cell. Signal 2010, 22, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, D.; Abdellatif, M. Akt-ing via microrna. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3213–3217. [Google Scholar]
- Haghikia, A.; Missol-Kolka, E.; Tsikas, D.; Venturini, L.; Brundiers, S.; Castoldi, M.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Eder, M.; Stapel, B.; Thum, T.; et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-mediated regulation of miR-199a-5p links cardiomyocyte and endothelial cell function in the heart: A key role for ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. Eur. Heart J 2011, 32, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, E.A.; Kong, L.; Bai, X.H.; Luan, Y.; Liu, C.J. MiR-199a, a bone morphogenic protein 2-responsive microrna, regulates chondrogenesis via direct targeting to smad1. J. Biol. Chem 2009, 284, 11326–11335. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukigi, M.; Bilim, V.; Yuuki, K.; Ugolkov, A.; Naito, S.; Nagaoka, A.; Kato, T.; Motoyama, T.; Tomita, Y. Re-expression of miR-199a suppresses renal cancer cell proliferation and survival by targeting gsk-3beta. Cancer Lett 2012, 315, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.; Zeng, H.; Li, J.; Xiao, L.; He, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y. MiR-199a regulates the tumor suppressor mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 11 in gastric cancer. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2010, 33, 1822–1827. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, B.; Hoshen, M.B.; Purim, O.; David, M.B.; Ashkenazi, K.; Marshak, G.; Kundel, Y.; Brenner, R.; Morgenstern, S.; Halpern, M.; et al. Micrornas as a potential prognostic factor in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol 2011, 17, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, T.; Volinia, S.; Okumura, H.; Shimizu, M.; Taccioli, C.; Rossi, S.; Alder, H.; Liu, C.G.; Oue, N.; Yasui, W.; et al. Relation between microrna expression and progression and prognosis of gastric cancer: A microrna expression analysis. Lancet Oncol 2010, 11, 136–146. [Google Scholar]
- Shigehara, K.; Yokomuro, S.; Ishibashi, O.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Arima, Y.; Kawahigashi, Y.; Kanda, T.; Akagi, I.; Tajiri, T.; Yoshida, H.; et al. Real-time pcr-based analysis of the human bile micrornaome identifies miR-9 as a potential diagnostic biomarker for biliary tract cancer. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23584. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Gusev, Y.; Aderca, I.; Mettler, T.A.; Nagorney, D.M.; Brackett, D.J.; Roberts, L.R.; Schmittgen, T.D. Association of microrna expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin. Cancer Res 2008, 14, 419–427. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.Q.; Cheng, H.Q.; Qian, X.; Bian, C.X.; Shi, Z.M.; Zhang, J.P.; Jiang, B.H.; Feng, Z.Q. Lentivirus-mediated overexpression of microrna-199a inhibits cell proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem. Biophys 2012, 62, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, J.C.; Park, J.K.; Jiang, J.; Kim, J.H.; Nagorney, D.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Banerjee, S.; Schmittgen, T.D. MiR-199a-3p targets CD44 and reduces proliferation of CD44 positive hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2010, 403, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Q.; Cicinnati, V.R.; Zhang, X.; Iacob, S.; Weber, F.; Sotiropoulos, G.C.; Radtke, A.; Lu, M.; Paul, A.; Gerken, G.; Beckebaum, S. Role of microrna-199a-5p and discoidin domain receptor 1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma invasion. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 227. [Google Scholar]
- Fornari, F.; Milazzo, M.; Chieco, P.; Negrini, M.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Pollutri, D.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; Gramantieri, L. MiR-199a-3p regulates mtor and c-met to influence the doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 5184–5193. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, K.Z.; Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Afdhal, N.H.; Albitar, M. Circulating micrornas as biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Gastroenterol 2011, 45, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Magrelli, A.; Azzalin, G.; Salvatore, M.; Viganotti, M.; Tosto, F.; Colombo, T.; Devito, R.; Di Masi, A.; Antoccia, A.; Lorenzetti, S.; et al. Altered microrna expression patterns in hepatoblastoma patients. Transl. Oncol 2009, 2, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Choy, E.; Harmon, D.; Liu, X.; Susa, M.; Mankin, H.; Hornicek, F. Microrna-199a-3p is downregulated in human osteosarcoma and regulates cell proliferation and migration. Mol. Cancer Ther 2011, 10, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Feber, A.; Xi, L.; Pennathur, A.; Gooding, W.E.; Bandla, S.; Wu, M.; Luketich, J.D.; Godfrey, T.E.; Litle, V.R. Microrna prognostic signature for nodal metastases and survival in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Ann. Thorac. Surg 2011, 91, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, H.H.; Davis, A.J.; Lee, T.L.; Pang, A.L.; Nagrani, S.; Rennert, O.M.; Chan, W.Y. Methylation of an intronic region regulates miR-199a in testicular tumor malignancy. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3404–3415. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zheng, Z.; Guo, J.; Ding, X. Correlation and quantitation of microrna aberrant expression in tissues and sera from patients with breast tumor. Gynecol. Oncol 2010, 119, 586–593. [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio, E.; Mitchell, T.; van Kester, M.S.; Taylor, S.; Dunlop, H.M.; Chi, J.; Tosi, I.; Vermeer, M.H.; Tramonti, D.; Saunders, N.J.; et al. Microrna expression in sezary syndrome: Identification, function, and diagnostic potential. Blood 2010, 116, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Iorio, M.V.; Visone, R.; di Leva, G.; Donati, V.; Petrocca, F.; Casalini, P.; Taccioli, C.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.G.; Alder, H.; et al. Microrna signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 8699–8707. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, E.J.; Yoon, H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.T.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, S. Microrna expression profiles in serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res 2008, 14, 2690–2695. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Kong, W.; He, L.; Zhao, J.J.; O’Donnell, J.D.; Wang, J.; Wenham, R.M.; Coppola, D.; Kruk, P.A.; Nicosia, S.V.; et al. Microrna expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting pten. Cancer Res 2008, 68, 425–433. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Alvero, A.B.; Silasi, D.A.; Kelly, M.G.; Fest, S.; Visintin, I.; Leiser, A.; Schwartz, P.E.; Rutherford, T.; Mor, G. Regulation of ikkbeta by miR-199a affects nf-kappab activity in ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4712–4723. [Google Scholar]
- Jukic, D.M.; Rao, U.N.; Kelly, L.; Skaf, J.S.; Drogowski, L.M.; Kirkwood, J.M.; Panelli, M.C. Microrna profiling analysis of differences between the melanoma of young adults and older adults. J. Transl. Med 2010, 8, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Worley, L.A.; Long, M.D.; Onken, M.D.; Harbour, J.W. Micrornas associated with metastasis in uveal melanoma identified by multiplexed microarray profiling. Melanoma Res 2008, 18, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Ichimi, T.; Enokida, H.; Okuno, Y.; Kunimoto, R.; Chiyomaru, T.; Kawamoto, K.; Kawahara, K.; Toki, K.; Kawakami, K.; Nishiyama, K.; et al. Identification of novel microrna targets based on microrna signatures in bladder cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 345–352. [Google Scholar]
- Mascaux, C.; Laes, J.F.; Anthoine, G.; Haller, A.; Ninane, V.; Burny, A.; Sculier, J.P. Evolution of microrna expression during human bronchial squamous carcinogenesis. Eur. Respir. J 2009, 33, 352–359. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Choi, C.H.; Choi, J.J.; Park, Y.A.; Kim, S.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, W.Y.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, B.G.; Bae, D.S. Altered microrna expression in cervical carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res 2008, 14, 2535–2542. [Google Scholar]
- Garzon, R.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.G.; Fernandez-Cymering, C.; Palumbo, T.; Pichiorri, F.; Fabbri, M.; Coombes, K.; Alder, H.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Microrna signatures associated with cytogenetics and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 3183–3189. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xie, P.; Fan, H. Genomic profiling of micrornas and proteomics reveals an early molecular alteration associated with tumorigenesis induced by MC-LR in mice. Environ. Sci. Technol 2012, 46, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Bockmeyer, C.L.; Christgen, M.; Muller, M.; Fischer, S.; Ahrens, P.; Langer, F.; Kreipe, H.; Lehmann, U. Microrna profiles of healthy basal and luminal mammary epithelial cells are distinct and reflected in different breast cancer subtypes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat 2011, 130, 735–745. [Google Scholar]
- Shatseva, T.; Lee, D.Y.; Deng, Z.; Yang, B.B. Microrna miR-199a-3p regulates cell proliferation and survival by targeting caveolin-2. J. Cell Sci 2011, 124, 2826–2836. [Google Scholar]
- Migliore, C.; Petrelli, A.; Ghiso, E.; Corso, S.; Capparuccia, L.; Eramo, A.; Comoglio, P.M.; Giordano, S. Micrornas impair met-mediated invasive growth. Cancer Res 2008, 68, 10128–10136. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, A.; Luo, M.; Yuan, G.; Yu, J.; Deng, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Mitchelson, K.; Cheng, J. Complementary analysis of microrna and mrna expression during phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (TPA)-induced differentiation of hl-60 cells. Biotechnol. Lett 2008, 30, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.G.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, S.G. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha inhibition by a pyrrolopyrazine metabolite of oltipraz as a consequence of micrornas 199a-5p and 20a induction. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 661–669. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Wang, X.Y.; Gong, R.G.; Li, A.; Yang, S.; Cao, Y.T.; Wen, Y.M.; Wang, C.M.; Yi, X.Z. The expression profile of micrornas in a model of 7,12-dimethyl-benz[a]anthrance-induced oral carcinogenesis in syrian hamster. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res 2009, 28, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Burnside, J.; Ouyang, M.; Anderson, A.; Bernberg, E.; Lu, C.; Meyers, B.C.; Green, P.J.; Markis, M.; Isaacs, G.; Huang, E.; Morgan, R.W. Deep sequencing of chicken micrornas. BMC Genomics 2008, 9, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Detloff, M.R.; Miller, K.N.; Santi, L.; Houle, J.D. Exercise modulates micrornas that affect the pten/mtor pathway in rats after spinal cord injury. Exp. Neurol 2012, 233, 447–456. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, T.; Enomoto, M.; Fujii, H.; Sekiya, Y.; Yoshizato, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawada, N. Microrna-221/222 upregulation indicates the activation of stellate cells and the progression of liver fibrosis. Gut 2012. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, Y.; Aly, H.H.; Tajima, A.; Inoue, I.; Shimotohno, K. Regulation of the hepatitis c virus genome replication by miR-199a. J. Hepatol 2009, 50, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.L.; Li, Y.X.; Zheng, S.Q.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. Suppression of hepatitis b virus replication by microrna-199a-3p and microrna-210. Antivir. Res 2010, 88, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Dolganiuc, A.; Petrasek, J.; Kodys, K.; Catalano, D.; Mandrekar, P.; Velayudham, A.; Szabo, G. Microrna expression profile in lieber-decarli diet-induced alcoholic and methionine choline deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis models in mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res 2009, 33, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Rane, S.; He, M.; Sayed, D.; Vashistha, H.; Malhotra, A.; Sadoshima, J.; Vatner, D.E.; Vatner, S.F.; Abdellatif, M. Downregulation of MiR-199a derepresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and sirtuin 1 and recapitulates hypoxia preconditioning in cardiac myocytes. Circ. Res 2009, 104, 879–886. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.W.; Li, Q.; Lin, L.; Wang, X.C.; Li, D.F.; Wang, G.K.; Ren, A.J.; Wang, Y.R.; Qin, Y.W.; Yuan, W.J.; Jing, Q. Micrornas are dynamically regulated in hypertrophic hearts, and MiR-199a is essential for the maintenance of cell size in cardiomyocytes. J. Cell. Physiol 2010, 225, 437–443. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, M.; Andersen, D.C.; Silahtaroglu, A.; Lyngbaek, S.; Kauppinen, S.; Hansen, J.L.; Sheikh, S.P. Cell-specific detection of microrna expression during cardiomyogenesis by combined in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. J. Mol. Histol 2011, 42, 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Gonsalves, C.S.; Kalra, V.K. Hypoxia-mediated expression of 5-lipoxygenase-activating protein involves HIF-1alpha and NF-kappab and micrornas 135a and 199a-5p. J. Immunol 2010, 184, 3878–3888. [Google Scholar]
- Suomi, S.; Taipaleenmaki, H.; Seppanen, A.; Ripatti, T.; Vaananen, K.; Hentunen, T.; Saamanen, A.M.; Laitala-Leinonen, T. Micrornas regulate osteogenesis and chondrogenesis of mouse bone marrow stromal cells. Gene Regul. Syst. Biol 2008, 2, 177–191. [Google Scholar]
- Oskowitz, A.Z.; Lu, J.; Penfornis, P.; Ylostalo, J.; McBride, J.; Flemington, E.K.; Prockop, D.J.; Pochampally, R. Human multipotent stromal cells from bone marrow and microrna: Regulation of differentiation and leukemia inhibitory factor expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18372–18377. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, N.; Haqqi, T.M. Microrna-199a* regulates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human chondrocytes. Ann. Rheum. Dis 2012, 71, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.H.; Kao, A.P.; Singh, S.; Yu, S.L.; Kao, L.P.; Tsai, Z.Y.; Lin, S.D.; Li, S.S. Comparative expression profiles of mrnas and micrornas among human mesenchymal stem cells derived from breast, face, and abdominal adipose tissues. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci 2010, 26, 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Alt, E.U.; Senst, C.; Murthy, S.N.; Slakey, D.P.; Dupin, C.L.; Chaffin, A.E.; Kadowitz, P.J.; Izadpanah, R. Aging alters tissue resident mesenchymal stem cell properties. Stem Cell Res 2012, 8, 215–225. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.Z.; Yu, S.L.; Singh, S.; Kao, L.P.; Tsai, Z.Y.; Yang, P.C.; Chen, B.H.; Shoei-Lung Li, S. Identification of micrornas expressed highly in pancreatic islet-like cell clusters differentiated from human embryonic stem cells. Cell Biol. Int 2011, 35, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty, A.; Tranguch, S.; Daikoku, T.; Jensen, K.; Furneaux, H.; Dey, S.K. Microrna regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 during embryo implantation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15144–15149. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ami, O.; Pencovich, N.; Lotem, J.; Levanon, D.; Groner, Y. A regulatory interplay between MiR-27a and runx1 during megakaryopoiesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.Y.; Shatseva, T.; Jeyapalan, Z.; Du, W.W.; Deng, Z.; Yang, B.B. A 3′-untranslated region (3′UTR) induces organ adhesion by regulating MiR-199a* functions. PLoS One 2009, 4, e4527. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.Y.; Jeyapalan, Z.; Fang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yee, A.Y.; Li, M.; Du, W.W.; Shatseva, T.; Yang, B.B. Expression of versican 3′-untranslated region modulates endogenous microrna functions. PLoS One 2010, 5, e13599. [Google Scholar]
- Kanda, T.; Ishibashi, O.; Kawahigashi, Y.; Mishima, T.; Kosuge, T.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Arima, Y.; Yokomuro, S.; Yoshida, H.; et al. Identification of obstructive jaundice-related micrornas in mouse liver. Hepato-Gastroenterology 2010, 57, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Gu, L.; Di, W. MiR-199a attenuates endometrial stromal cell invasiveness through suppression of the IKKβ/NF-kappab pathway and reduced interleukin-8 expression. Mol. Hum. Reprod 2012, 18, 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Gu, L.Y.; Zhu, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Ji, F.; Di, W. Regulation of microrna-199a on adhesion, migration and invasion ability of human endometrial stromal cells. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 2011, 46, 817–821. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.G.; Zhang, S.M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wu, H.B.; Xu, X.P. Micrornas are dynamically regulated and play an important role in lps-induced lung injury. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol 2012, 90, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.H.; Gao, Y.; Ren, A.J.; Zhao, S.H.; Zhong, M.; Peng, Y.J.; Shen, W.; Jing, M.; Liu, L. Altered microrna expression profiles in retinas with diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmic Res 2011, 47, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.H.; Yao, X.Y.; Yu, H.J.; Huang, J.W.; Cui, L.Y. Downregulation of MiR-199a may play a role in 3-nitropropionic acid induced ischemic tolerance in rat brain. Brain Res 2012, 1429, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.S.; Oh, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Choi, M.S.; Park, S.M.; Kang, S.J.; Oh, M.J.; Kim, S.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Yoon, S. MiRna regulation of cytotoxic effects in mouse sertoli cells exposed to nonylphenol. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol 2011, 9, 126. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.A.; Kubicki, N.; Gnyawali, S.; Chan, Y.C.; Roy, S.; Khanna, S.; Sen, C.K. Natural vitamin E alpha-tocotrienol protects against ischemic stroke by induction of multidrug resistance-associated protein 1. Stroke 2011, 42, 2308–2314. [Google Scholar]
- Godwin, J.G.; Ge, X.; Stephan, K.; Jurisch, A.; Tullius, S.G.; Iacomini, J. Identification of a microrna signature of renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14339–14344. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.H.; Wu, M.Z.; Chiou, S.H.; Chen, P.M.; Chang, S.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Teng, S.C.; Wu, K.J. Direct regulation of twist by hif-1alpha promotes metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol 2008, 10, 295–305. [Google Scholar]
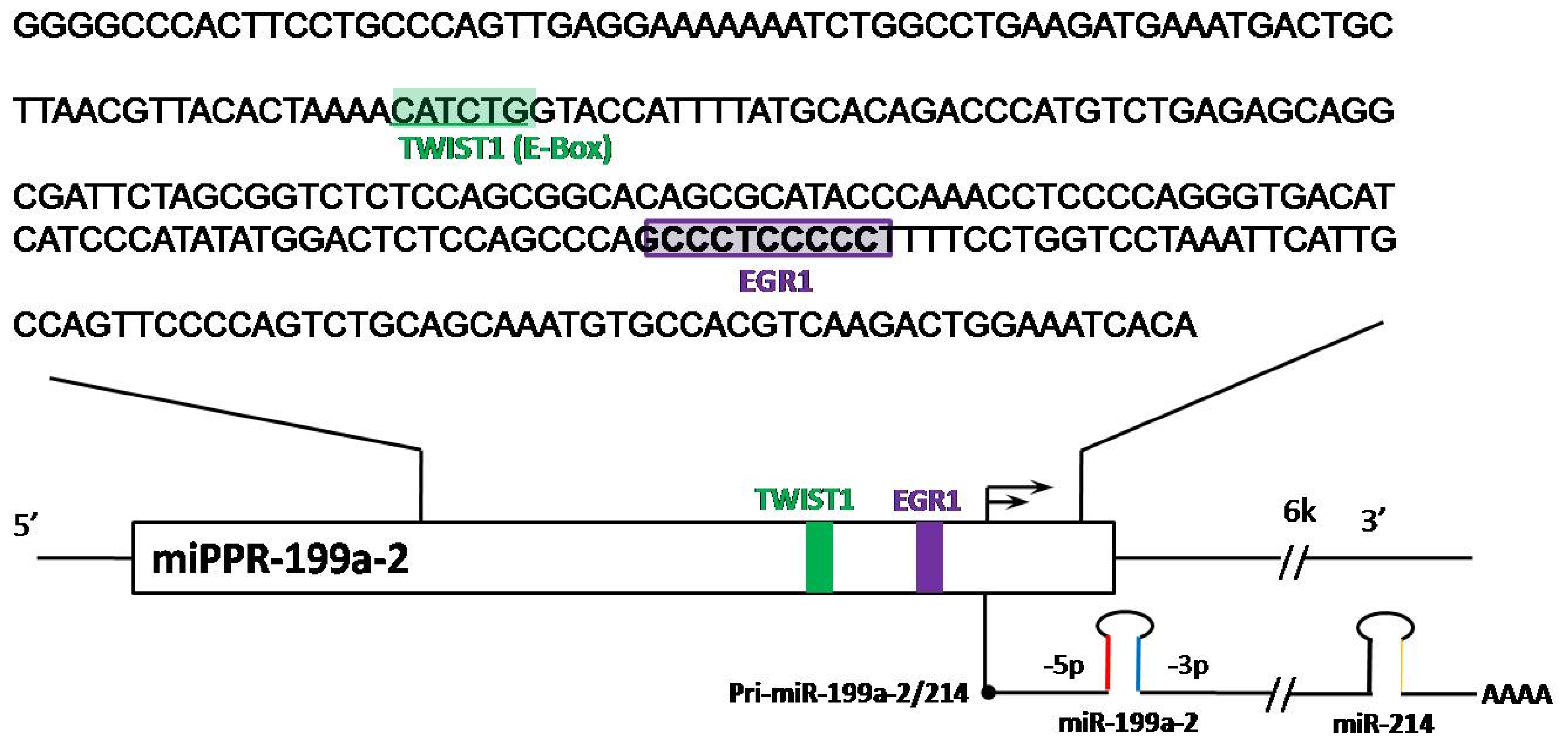
 ” arrows indicate inhibitory effects, while “→” arrows indicate activate effects.
” arrows indicate inhibitory effects, while “→” arrows indicate activate effects.
 ” arrows indicate inhibitory effects, while “→” arrows indicate activate effects.
” arrows indicate inhibitory effects, while “→” arrows indicate activate effects.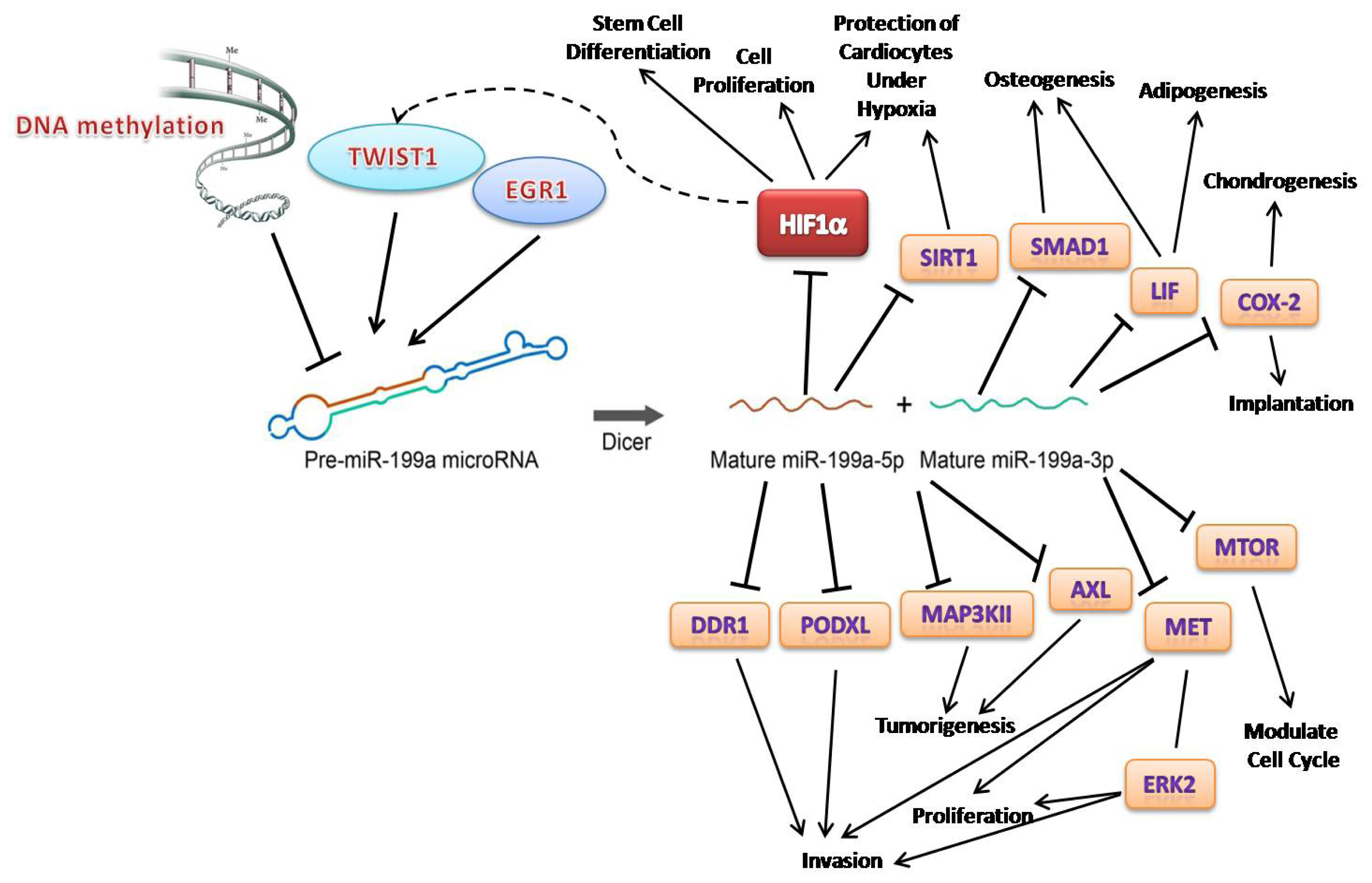
| Cancer | miR-199a Expression | miR-199a Involved Biological Processes | Validated Targets # | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renal cell cancer (RCC) | Down-regulated in RCC cells and tissues | GSK-3β (protein only) | [26] | |
| Gastric cancer * | miR-199a-3p up-regulated in patients with recurrence, miR-199a up-regulated in gastric cancer/metastatic tissues/Japanese gastric cancer tissues | Promotes proliferation and metastasis, progression-related | MAP3K11 (protein only) | [27–29] |
| Biliary tract cancer | miR-199a-3p up-regulated during malignancy | [30] | ||
| Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) | miR-199a down-regulated | Anti-proliferation, anti-growth of HCC, PAK4/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway, anti-invasion modulator of cell cycle | HIF-1α (protein), PAK4 (protein), CD44 (mRNA), DDR1(mRNA), mTOR (mRNA) | [20,31–36] |
| Hepatoblastoma | miR-199a up-regulated | [37] | ||
| Osteosarcoma | miR-199a down-regulated in cells and tissues | Anti-proliferation, anti-migration and affect cell cycle | MET? mTOR? STAT3? | [38] |
| Esophageal adenocarcinoma | miR-199a-3p and -5p up-regulated in worse survival patients | [39] | ||
| Testicular germ cell tumors | miR-199a-3p and -5p down-regulated in cells and tissues | anti-invasion, anti-migration, anti-proliferation | PODXL (mRNA) | [40] |
| Breast Cancer | miR-199a down-regulated in tissues | [41] | ||
| Sezary Syndrom (T-cell lymphoma) | miR-199a-3p up-regulated | Anti-apoptosis | EVL (host gene of miR-342) | [42] |
| Ovarian cancer * | miR-199a-2 up-regulated in ovarian cancer stem cells; miR-199a down-regulated in serous ovarian cancer tissues | IKKβ/NFκB pathway, Poor prognosis related, tumor progression related, anti-tumor progression and chemoresistance | IKKβ (protein) | [7,43–46] |
| Melanoma | miR-199a up-regulated in older adults (>60) | TLR-MyD88-NFκB pathway | [47] | |
| Uveal melanoma | miR-199a-3p and -5p up-regulated during metastasis | [48] | ||
| Bladder cancer | miR-199a-3p down-regulated in cells and tissues | Tumor suppressive | KRT7 (mRNA) | [49] |
| Bronchial squamous cancer | miR-199a up-regulated at a specific stage | [50] | ||
| Cervical Cancer | miR-199a up-regulated | Pro-proliferation of cells | [51] | |
| Acute myeloid leukemia | miR-199a up-regulation in worse survival | [52] |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, S.; Chan, W.-Y. Flexible and Versatile as a Chameleon—Sophisticated Functions of microRNA-199a. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8449-8466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078449
Gu S, Chan W-Y. Flexible and Versatile as a Chameleon—Sophisticated Functions of microRNA-199a. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(7):8449-8466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078449
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Shen, and Wai-Yee Chan. 2012. "Flexible and Versatile as a Chameleon—Sophisticated Functions of microRNA-199a" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 7: 8449-8466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078449
APA StyleGu, S., & Chan, W. -Y. (2012). Flexible and Versatile as a Chameleon—Sophisticated Functions of microRNA-199a. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(7), 8449-8466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078449




