Automated Ultrafiltration Device for Environmental Nanoparticle Research and Implications: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
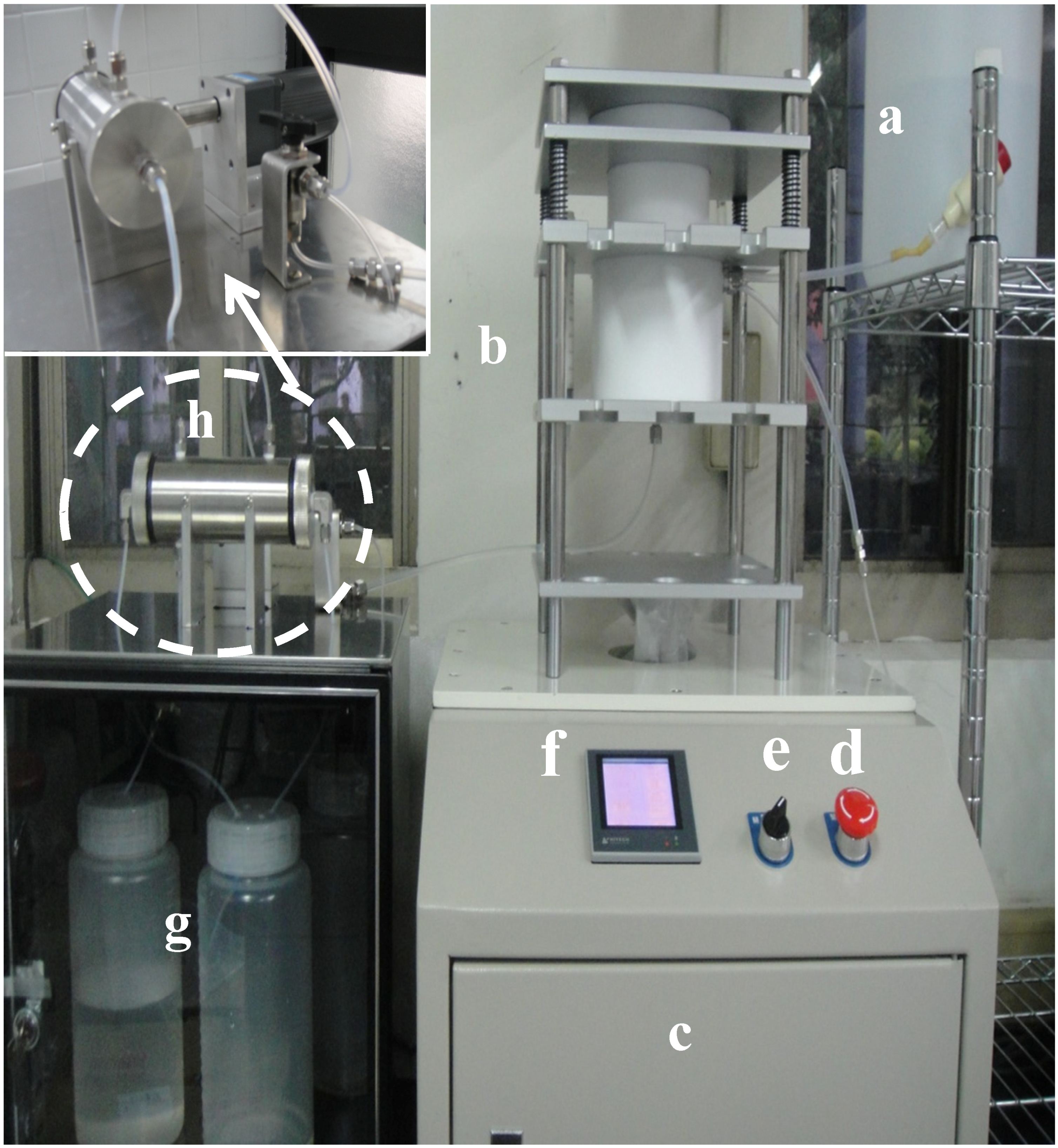
2. Description of the Automated Ultrafiltration Device (AUD)
2.1. First-Generation AUD Apparatus
2.2. Second-Generation AUD Apparatus
3. Efficiency Collection of the AUD Apparatus
3.1. Efficiency of the AUD Apparatus and Conventional Syringe Methods


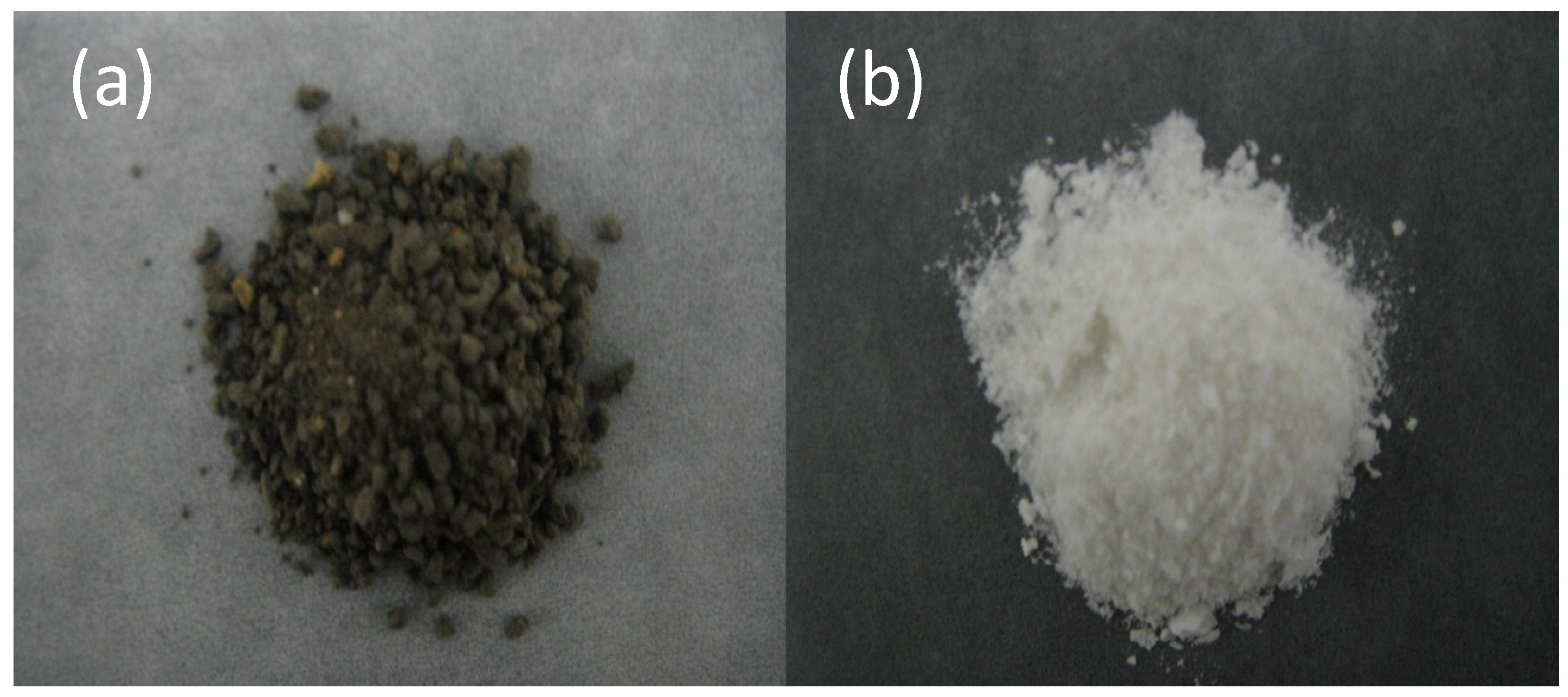
3.2. Collecting Large Quantities of Nanoparticles
4. The AUD Apparatus in Applications of Different Scientific Field
4.1. Separation and Physicochemical Properties of Zeolite Nanoparticles
| Size (nm) | Atom per unit cell † | Si/Al | Surface area | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | Na | Al | Si | O | ratio | (m2 g−1) | |
| 1–25 | 3.7 | 0.2 | 3.9 | 20.1 | 48 | 5.2 | 514 |
| 25–100 | 4.2 | 0.3 | 4.5 | 19.5 | 48 | 4.3 | 120 |
| 100–450 | 6.2 | 0.3 | 6.5 | 17.5 | 48 | 2.7 | 75 |
| 450–2000 | 7.4 | 0.4 | 7.8 | 16.2 | 48 | 2.1 | 46 |
| <2000 | 7.5 | 1.0 | 8.5 | 15.5 | 48 | 1.8 | 24 |
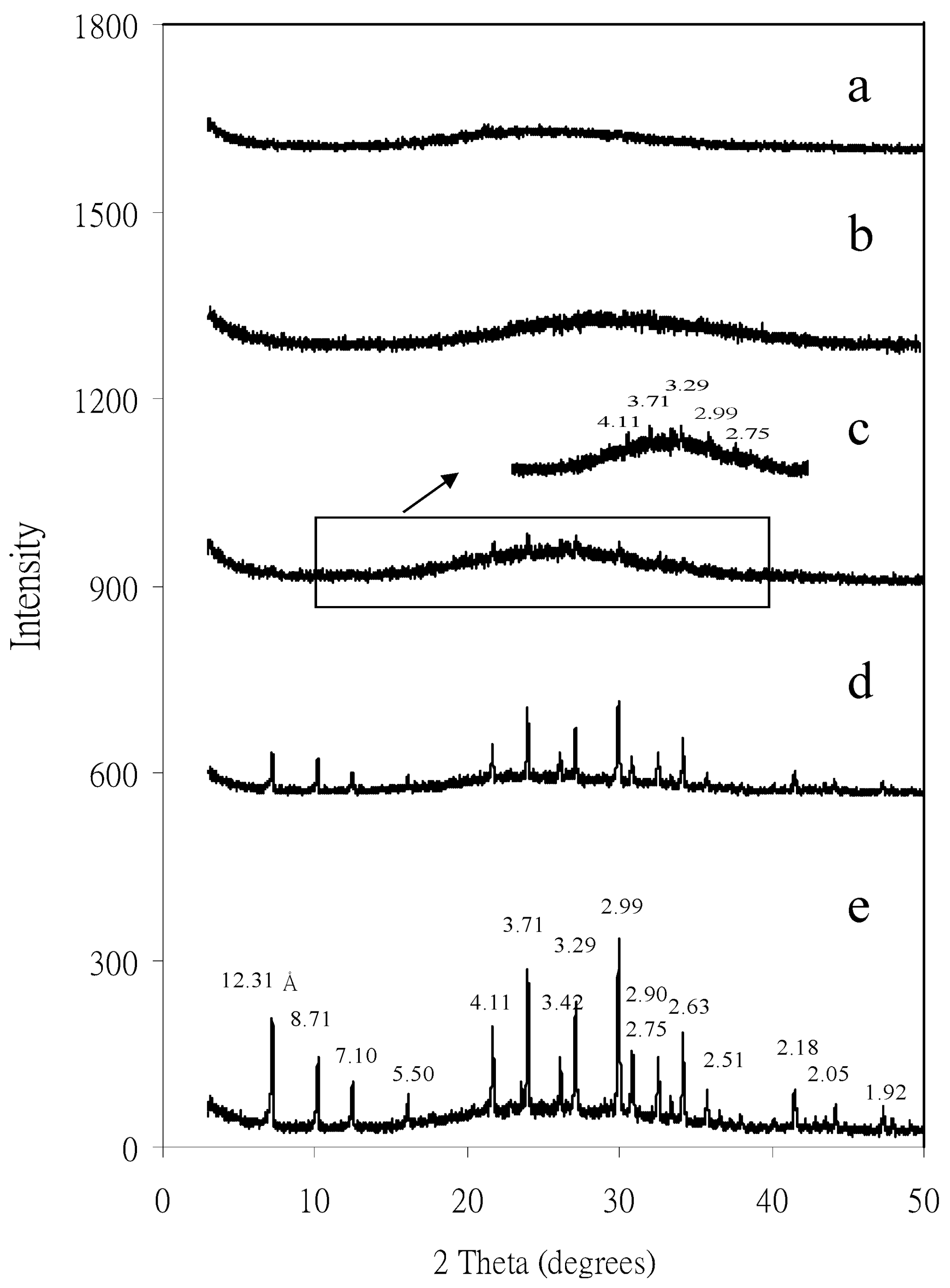
4.2. Mineral Nanoparticles in Red Soils
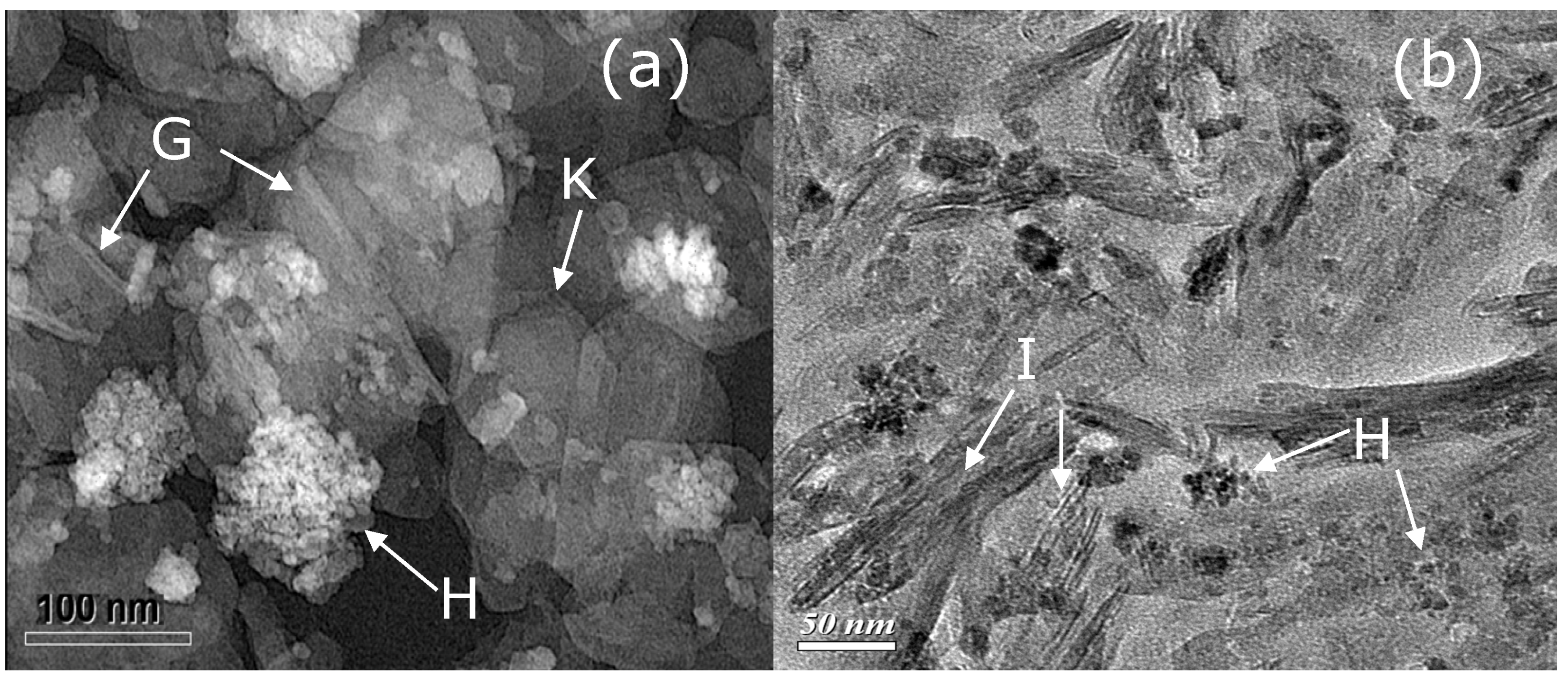

4.3. Smectite Nanoparticles in Black Soil

4.4. Quartz Nanoparticles in the Gouge of Fault of Chi-Chi Earthquake
5. Implications
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Zielinski, P.A.; van Neste, A.; Akolekar, D.B.; Kaliaguine, S. Effect of high-energy ball milling on the structural stability, surface and catalytic properties of small-, medium- and large-pore zeolites. Microporous Mater. 1995, 5, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiang, C.H.; Goddard, W.A.; Salem, R.J.R.; Bethune, D.S. Catalytic effects of heavy metals on the growth of carbon nanotubes and nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1996, 57, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskel, S.; Chapais, G.; Schlichte, K. Synthesis, characterization, and catalytic properties of high-surface-area aluminum silicon nitride based materials. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, A.A.; Klabunde, K.J. Chemical and catalytic activity of copper nanoparticles prepared via metal vapor synthesis. J. Mol. Catal. A 2005, 225, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawkataly, O.B.; Jothiramalingam, R.; Adam, F.; Radhika, T.; Tsao, T.M.; Wang, M.K. Ru-nanoparticle deposition on naturally available clay and rice husk biomass materials—Benzene hydrogenation catalysis and synthetic strategies for green catalyst development. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, G.; Lo, I.M.C. Removal and recovery of Cr (VI) from wastewater by naghemite nanoparticles. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4528–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göppert, T.M.; Müller, R.H. Adsorption kinetics of plasma plasma proteins on solid lipid nanoparticles for drug targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 302, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, B.; Denkwitz, Y.; Plzak, V.; Kinne, M.; Behm, R.J. Kinetics, mechanism, and the influence of H2 on the oxidation reaction on an Au/TiO2 catalyst. J. Catal. 2004, 224, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levdansky, V.V.; Smolik, J.; Moravec, P. Influence of size effect and foreign gases on formation of nanoparticles. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 33, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, J.T.; Yavuz, C.; Yean, S.; Cong, L.; Shipley, H.; Yu, W.; Falkner, J.; Kan, A.; Tomson, M.; Colvin, V.L. The effect of nanocrystalline magnetite size on arsenic removal. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2007, 8, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochella, M.F., Jr.; Lower, S.K.; Mauice, P.A.; Penn, R.L.; Sahai, N.; Sparks, D.L.; Twining, B.S. Nanominerals, mineral nanoparticles, and earth systems. Science 2008, 319, 1631–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, T.M.; Wang, M.K.; Huang, P.M. Structural transformation and physicochemical properties of environmental nanoparticles by comparison of various particle-size fractions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, S.J.; Sing, K.S.W. Adsorption, Specific Surface Area and Porosity; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, P.A.; Orr, C. Analytical Methods in Fine Particle Technology; Micromeritics Instrument Corp: Norcross, GA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- George, S.; Steinberg, S.M.; Hodge, V. The concentration, apparent molecular weight and chemical reactivity of silica from groundwater in southern Nevada. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassellöv, M.; Buesseler, K.O.; Pike, S.M.; Dai, M. Application of cross-flow ultrafi ltration for the determination of colloidal abundances in suboxic ferrous-rich ground waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 372, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, P.M.; Wilkinson, A.E.; Tipping, E.; Jones, M.N. Determination of molecular weights of humic substances by analytical (UV scanning) ultracentrifugation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadyen, P.; Fairhurst, D. High-resolution particle size analysis from nanometers to microns. Clay Miner. 1993, 28, 531–537. [Google Scholar]
- Crespo, J.G.; Boddeker, K.W. Membrane Processes in Separation and Purification; Kulwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Grzenia, D.L.; Carlson, J.O.; Czermak, P.; Han, B.; Specht, R.K.; Wickramasinghe, S.R. Purification of densonucleosis virus by tangential flow ultrafiltration. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Sikdar, S.K.; Grosse, D.; Rogut, I. Membrane technologies for remediating contaminated soils: A critical review. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 151, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K. Handbook of Industrial Membranes; Elsevier Advanced Technology Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chceryan, M. Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration Handbook, 2nd ed; Technomic Publishing Co.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schafer, A.I.; Mauch, R.; Waite, Y.D.; Fane, A.G. Charge effects in the fractionation of natural organics using ultrafiltration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2572–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, L. Mechanisms and parameters affecting flux decline in cross-flow microfiltration and ultrafiltration of colloids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3767–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bandow, S.; Rao, A.M.; Williams, K.A.; Thess, A.; Smalley, R.E.; Eklund, P.C. Purification of single-wall carbon nanotubes by microfiltration. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 8839–8842. [Google Scholar]
- Kyllönen, H.M.; Pirkonen, P.; Nystrom, M. Membrane filtration enhanced by ultrasound: A review. Desalination 2005, 181, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhalma, M.; de Pinho, M.N. Flocculation/flotation/ultrafiltration integrated process for the treatment of cork processing wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4916–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, T.M.; Wang, M.K.; Huang, P.M. Automated ultrafiltration device for efficient collection of environmental nanoparticles from aqueous suspensions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, T.M.; Wang, M.K.; Huang, P.M. An Apparatus for Collecting Nanoparticles. U.S. Patent 7501063 B2, 10 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Napper, D.H. Polymeric Stabilization of Colloidal Dispersions; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Kendall, K. Aggregate formation in colloidal dispersions. Colloids Surf. A 1998, 131, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.H.; Yue, P.L.; Mujumdar, A.S. Sludge dewatering and drying. Drying Technol. 2002, 20, 883–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffle, J.; Perret, D.; Newman, M. The use of filtration and ultrafiltration for size fractionation of aquatic particles, colloids, and macromolecules. In Environmental Particles, IUPAC Series on Environmental Analytical and Physical Chemistry; Buffle, J., van Leeuwen, H.P., Eds.; Lewis Publishers: Chelsea, MI, USA, 1992; Volume 1, pp. 171–230. [Google Scholar]
- Matthew, A.M.; Benoit, G. Environmental filtration artifacts caused by overloading membrane filters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3774–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, C.B.; Jackson, M.L. Nomographs of sedimentation times for soil particles under gravity or centrifugal acceleration. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1947, 12, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.W.; Kensal, E.; van Holde, K.E.; Baldwin, R.L.; Fujita, H. The theory of sedimentation analysis. Chem. Rev. 1958, 58, 715–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis: Advanced Course, 2nd ed; University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Hiemenz, P.C. Principles of Colloid and Surface Chemistry, 2nd ed; Polytehnic University Press: Pomona, CA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Laidlaw, I.; Steinmetz, M. Introduction to differential sedimentation. In Analytical Ultracentrifugation: Techniques and Methods; Scott, D.J., Harding, S.E., Rowe, A.J., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 270–290. [Google Scholar]
- Breck, D.W. Zeolite Molecular Sieves; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, E.C.J.; Baren, F.A.; van Schuylenborg, J. Tropical Soils: A Comprehensive Study of Their Genesis, 3rd ed; Monton-Ichitor: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, P. Properties and Management of Soils in the Tropics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Buol, S.W.; Sanchez, P.A. Red Soils in the Americas: Morphology, Classification and Management. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Red Soil; Academia Sinica Institute of Soil Science, Ed.; China Science: Beijing, China, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Eswaran, H.; Ikawa, H.; Kimble, J.M. Oxisols of the World. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Red Soil; Academia Sinica Institute of Soil Science, Ed.; China Science: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 90–123. [Google Scholar]
- China Soil Survey Office, China Soils; China Science: Beijing, China, 1987; (in Chinese with English abstract).
- IUSS Working Group WRB, World Reference Base for Soil Resources World Soil Resources Reports No. 103; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006.
- Wan, H.M.; Chen, S.H. The relationship between laterization, chemical and mineralogical characterizations, and weathering of gravels in Linkuo terrace. Ti Chih. 1988, 8, 27–47, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tsao, T.M.; Chen, Y.M.; Sheu, H.S.; Zhuang, S.Y.; Shao, P.H.; Chen, H.W.; Shea, K.S.; Wang, M.K.; Shau, Y.H.; Chiang, K.Y.J. Red soil chemistry and mineralogy reflect uniform weathering environments in fluvial sediments, Taiwan. J. Soils Sediments 2012, 12, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertmann, U.; Taylor, R.M. Iron Oxides. In Minerals in Soil Environments, 2nd; Dixon, J.B., Weed, S.B., Eds.; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1989; pp. 379–438. [Google Scholar]
- Ranville, J.F.; Chittleborough, D.J.; Beckett, R. Particle-size and element distributions of soil colloids: Implication for colloid transport. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, C.W.; Wang, M.K.; Wang, W.M.; Houng, K.H. Smectites in iron rich calcareous soil and black soils of Taiwan. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 389–398. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff, Key to Soil Tanonomy, 6th edUS Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Graham, R.C.; Southard, A.R. Genesis of a vertisol and an associated mollisol in Northern Utah. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1983, 47, 552–559. [Google Scholar]
- International Committee on Vertisols, Draft Keys; USDA-SMSS: Washington, DC, USA, 1990.
- Ma, K.F.; Lee, C.T.; Tsai, Y.B.; Shin, T.C.; Mori, J. The Chi-Chi, Taiwan earthquake: Large surface displacements on an inland thrust fault. Eos Trans. AGU 1999, 80, 605–611. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.C.; Chu, H.T.; Angelier, J.; Chan, Y.C.; Hu, J.C.; Lu, C.Y.; Rau, R.J.J. Geometry and structure of northern surface ruptures of the 1999 Mw = 7.6 Chi-Chi Taiwan earthquake: Influence from inherited fold belt structures. J. Struct. Geol. 2002, 24, 173–192. [Google Scholar]
- Angelier, J.; Lee, J.C.; Hu, J.C.; Chu, H.T.J. Three-dimensional deformation along the rupture trace of the September 21st, 1999, Taiwan earthquake: A case study in the Kuangfu school. In J. Struct. Geol.; 2003; Volume 25, pp. 351–370. [Google Scholar]
- Heaton, T.H. Evidence for and implications of self-healing pulses of slip in earthquake rupture. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1990, 64, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Dewers, T.; Reches, Z.E.; Brune, J. Particle size and energetics of gouge from earthquake rupture zones. Nature 2005, 434, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, J.S.; Chester, F.M.; Kronenberg, A.K. Fracture surface energy of the Punchbowl fault, San Andreas system. Nature 2005, 437, 133–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.-F.; Tanaka, H.; Song, S.-R.; Wang, C.-Y.; Hung, J.-H.; Tsai, Y.-B.; Mori, J.; Song, Y.-F.; Yeh, E.-C.; Soh, W.; et al. Slip zone and energetics of a large earthquake from the Taiwan Chelungpu-fault Drilling. Nature 2006, 444, 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, Y.M.; Tsao, T.M.; Song, S.R.; Yeh, E.C.; Wang, M.K.; Lin, C.S.; Lee, T.Q.; Chen, H.F. Preliminary Results of Nano-particle Analysis of Chelungpu-Fault Gouge in Wu-Feng, Central Taiwan; American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, R.J. The geochemistry of the amazon river system: Part I. The factors that control the salinity and the composition and concentration of the suspended solids. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1967, 78, 1203–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Forssberg, E. Production of carbonate and silica nano-particles in stirred bead milling. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 81, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Heilbronner, R.; Keulen, N. Grain size and grain shape analysis of fault rocks. Tectonophysics 2006, 427, 199–216. [Google Scholar]
- Sammis, C.G.; King, G.C.P. Mechanical origin of power law scaling in fault zone rock. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L04312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsao, T.M.; Wang, Y.N.; Chen, Y.M.; Chou, Y.M.; Wang, M.K. Automated Ultrafiltration Device for Environmental Nanoparticle Research and Implications: A Review. Micromachines 2013, 4, 215-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi4020215
Tsao TM, Wang YN, Chen YM, Chou YM, Wang MK. Automated Ultrafiltration Device for Environmental Nanoparticle Research and Implications: A Review. Micromachines. 2013; 4(2):215-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi4020215
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsao, Tsung M., Ya N. Wang, Yue M. Chen, Yu M. Chou, and Ming K. Wang. 2013. "Automated Ultrafiltration Device for Environmental Nanoparticle Research and Implications: A Review" Micromachines 4, no. 2: 215-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi4020215
APA StyleTsao, T. M., Wang, Y. N., Chen, Y. M., Chou, Y. M., & Wang, M. K. (2013). Automated Ultrafiltration Device for Environmental Nanoparticle Research and Implications: A Review. Micromachines, 4(2), 215-231. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi4020215




