Influence of Electric Motor Manufacturing Tolerances on End-of-Line Testing: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Manufacturing Process of an E-Motor
3. Necessity and Drawbacks of EOL Testing Methods
3.1. Necessity
- Active tests involve operating the e-motors in various modes, encompassing both monitored and unmonitored conditions, including parameters like current, voltage, torque, and winding temperature.
- Passive tests entail connecting the electric motor to an external motor and operating it as a generator. The same parameters as those in active tests can be examined during passive tests.
- Static tests involve disconnecting the motor from the power supply or an external motor to evaluate its static characteristics.
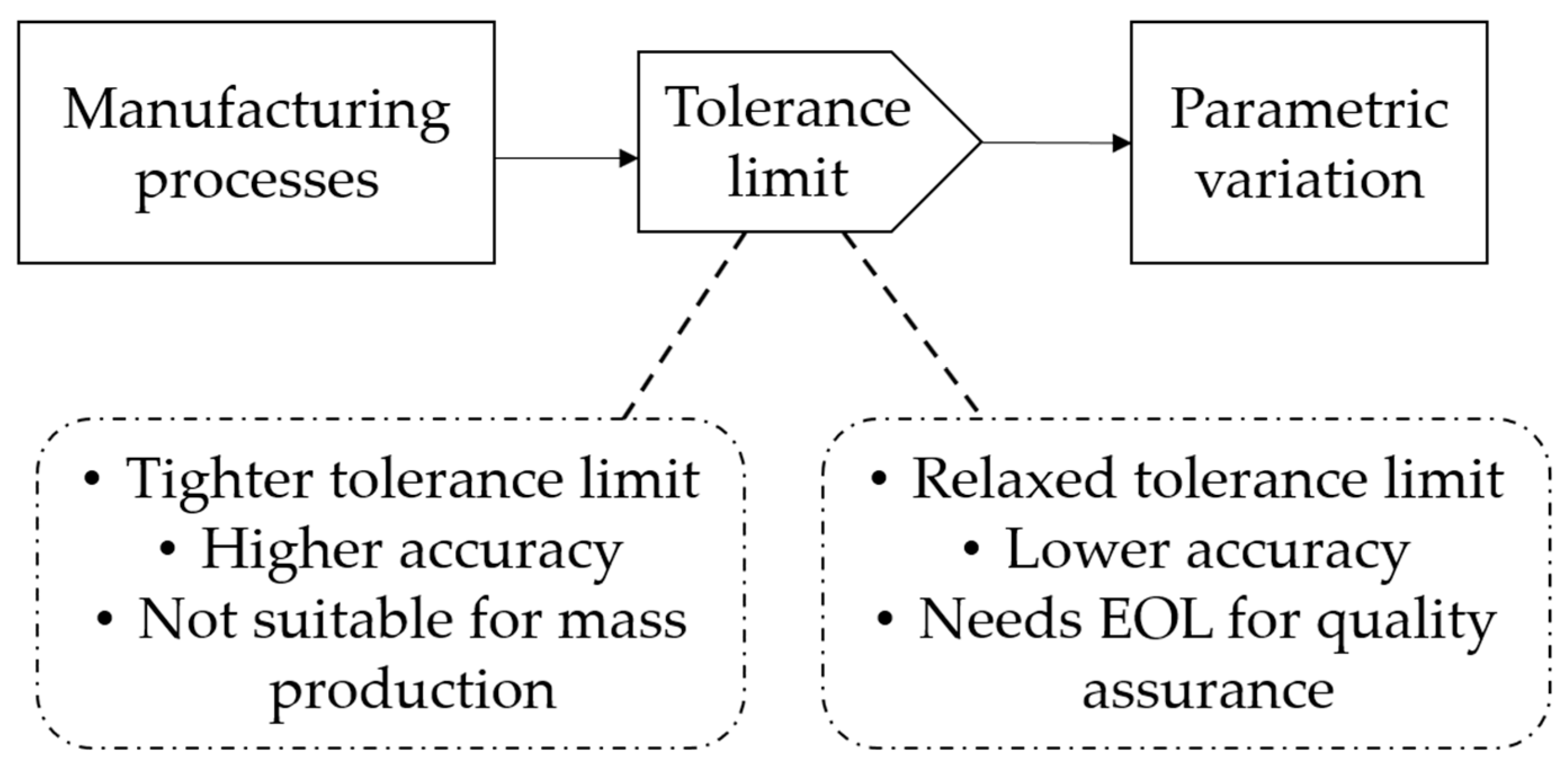
3.2. Drawbacks
4. Tolerances of Key E-Motor Parameters
4.1. Air Gap
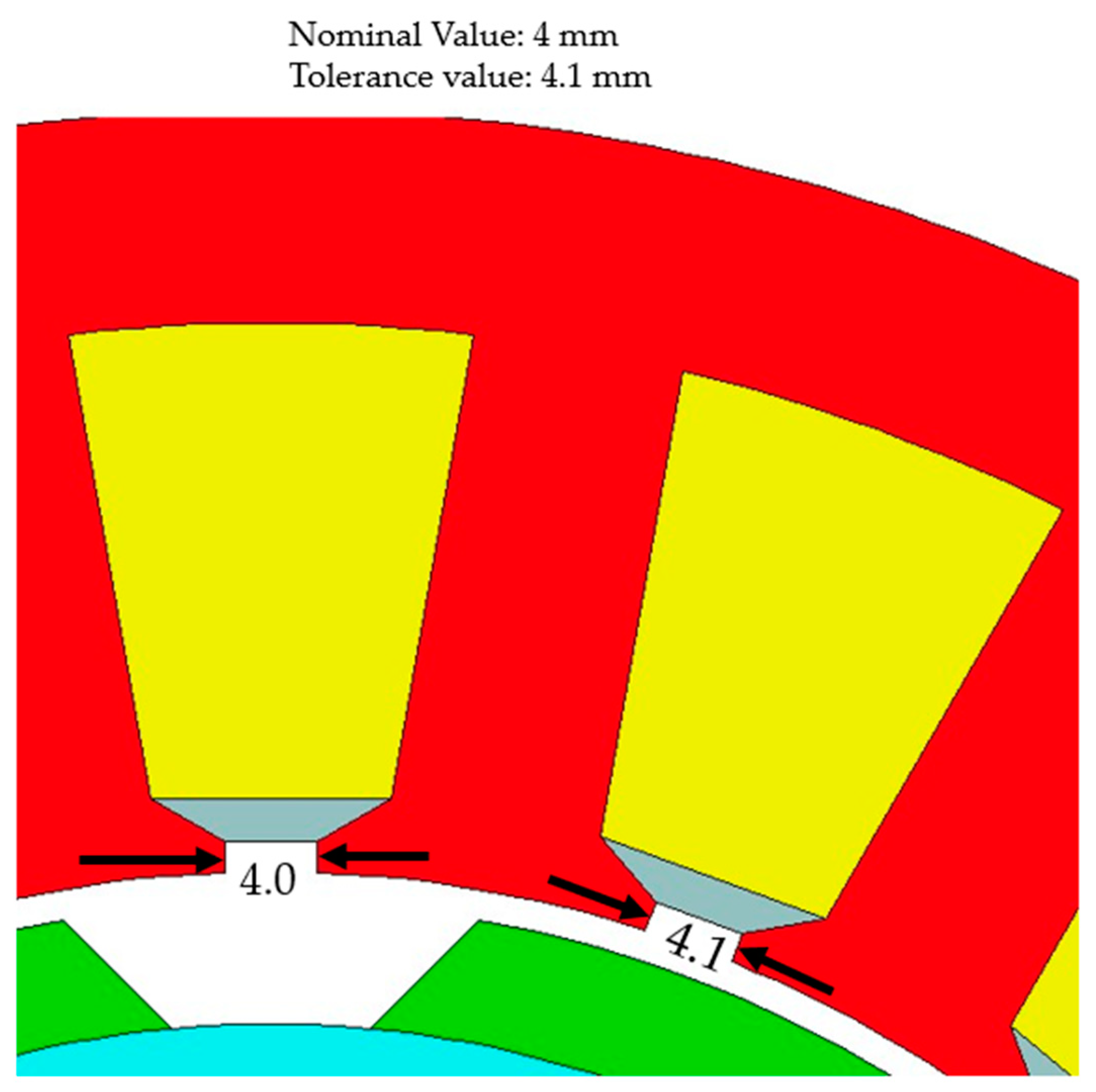
4.2. Stator Inner Diameter
4.3. Rotor Magnet Parameters
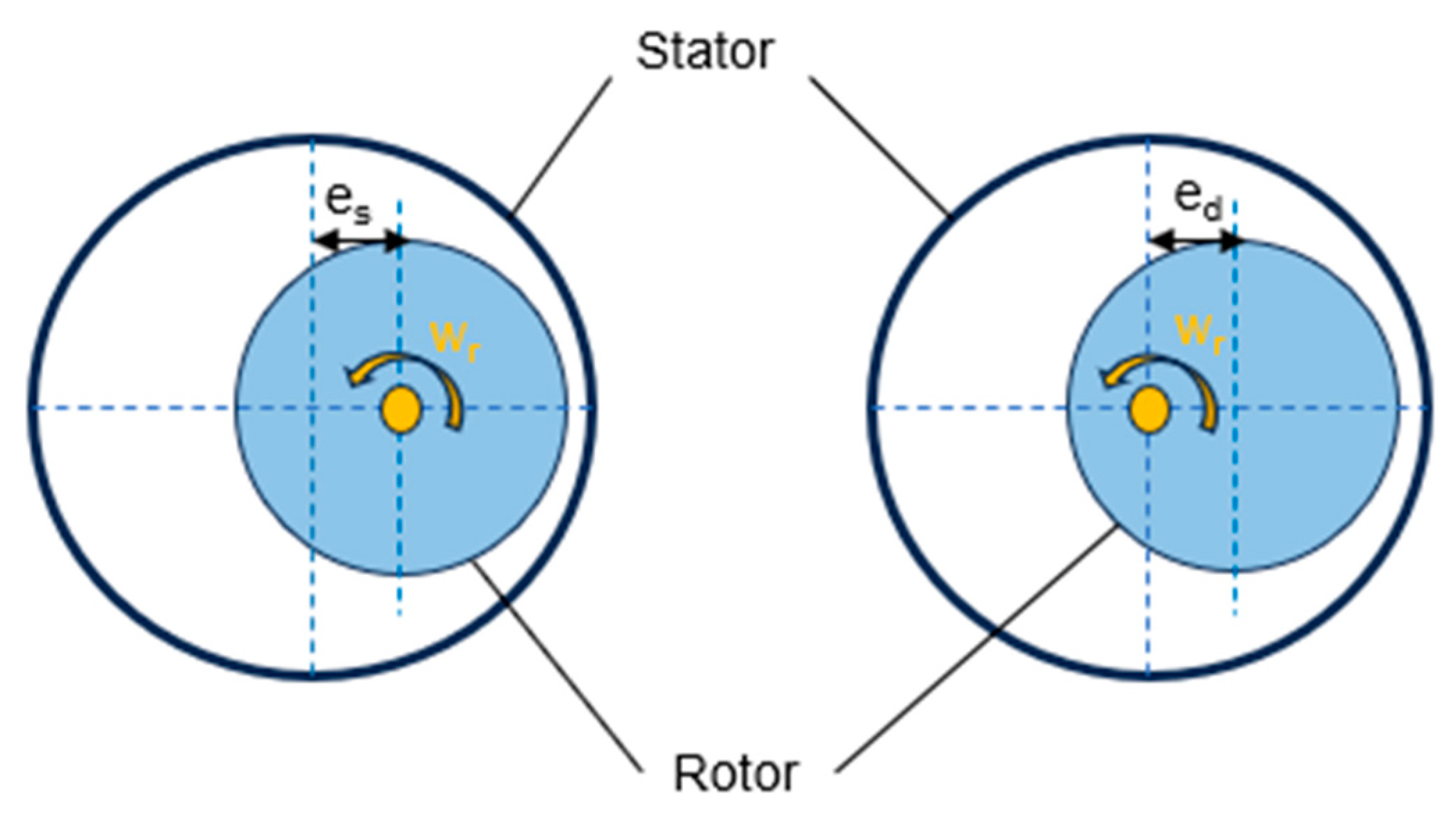
4.4. Rotor Eccentricity
4.5. Sensitivity Analysis to Identify Critical Parameters
4.5.1. Methodology
4.5.2. Results
5. Solutions to Mitigate the Drawbacks of EOL Testing
5.1. In-Process Monitoring during Manufacturing Processes
5.2. Designing Tolerance-Insensitive E-Motor Components
5.3. Prioritizing the Monitoring of Critical Parameters
5.4. Automated Inspection Techniques
5.5. Materials and Fabrication
5.6. Holistic Design
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flach, A.; Draeger, F.; Ayeb, M.; Brabetz, L. A New Approach to Diagnostics for Permanent-Magnet Motors in Automotive Powertrain Systems. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics & Drives, Bologna, Italy, 5–8 September 2011; pp. 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fan, W.; Zuo, Q.; Jiang, Y. Optimization Design of Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive System for Electric Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Sustainable Power and Energy Conference (iSPEC), Nanjing, China, 23–25 December 2021; pp. 3417–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Halima, N.; Ben Hadj, N.; Krichen, M.; Neji, R. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Performance Study Dedicated to Parallel Hybrid Electric Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 21st International Conference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering (STA), Sousse, Tunisia, 19–21 December 2022; pp. 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.-S.; Kwon, B.-I.; Kwon, O. Tolerance Sensitivity Analysis and Robust Optimal Design Method of a Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Motor by Using a Hybrid Response Surface Method Considering Manufacturing Tolerances. Energies 2018, 11, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mülder, C.; Franck, M.; Schröder, M.; Balluff, M.; Wanke, A.; Hameyer, K. Impact Study of Isolated and Correlated Manufacturing Tolerances of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine for Traction Drives. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 May 2019; pp. 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierczak, L.; Klimczyk, P.; Hennies, D.; Denke, P.; Siebert, S. Influence of Manufacturing Processes on Magnetic Properties of Stator Cores. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–26 August 2020; pp. 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaria, R.; Lehikoinen, A.; Arkkio, A.; Belahcen, A. Effects of Manufacturing Processes on Core Losses of Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Sempere, V.; Burgos-Payán, M.; Cerquides-Bueno, J.-R. Influence of Manufacturing Tolerances on the Electromotive Force in Permanent-Magnet Motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 5522–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coupek, D.; Verl, A.; Aichele, J.; Colledani, M. Proactive Quality Control System for Defect Reduction in the Production of Electric Drives. In Proceedings of the 2013 3rd International Electric Drives Production Conference (EDPC), Nuremberg, Germany, 29–30 October 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butov, A.; Verl, A. Comparison of End of Line Tests for Serial Production of Electric Motors in Hybrid Truck Applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 4th International Electric Drives Production Conference (EDPC), Nuremberg, Germany, 30 September–1 October 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Farnsworth, M.; Zhang, Z.; Jewell, G.W.; Tiwari, A. In-Process Monitoring in Electrical Machine Manufacturing: A Review of State of the Art and Future Directions. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2021, 235, 2035–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zhu, Z.Q. Sensitivity of Manufacturing Tolerances on Cogging Torque in Interior Permanent Magnet Machines with Different Slot/Pole Number Combinations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 3557–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Mir, S.; Sebastian, T. Issues in reducing the cogging torque of mass-produced permanent-magnet brushless DC motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 40, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.-P.; Choi, S.-K.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-Y. Effect of Manufacturing Tolerances on Cogging Torque of Spoke-type Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. In Proceedings of the 2021 24th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 10–13 October 2021; pp. 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taran, N.; Rallabandi, V.; Ionel, D.M.; Zhou, P.; Thiele, M.; Heins, G. A Systematic Study on the Effects of Dimensional and Materials Tolerances on Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Based on the IEEE Std 1812. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 1360–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madariaga, C.; Jara, W.; Riquelme, D.; Bramerdorfer, G.; Tapia, J.A.; Riedemann, J. Impact of Tolerances on the Cogging Torque of Tooth-Coil-Winding PMSMs with Modular Stator Core by Means of Efficient Superposition Technique. Electronics 2020, 9, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, C.; Herrmann, F.; Butov, A.; Verl, A. Economic Evaluation of a Modular Production System for Electric Traction Motors. In Proceedings of the 2015 5th International Electric Drives Production Conference (EDPC), Nuremberg, Germany, 15–16 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandekar, A.; Ugale, R.T. Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Traction Motor for Electric Vehicle (EV) Application Over Wide Speed Range. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems (PEDES), Jaipur, India, 14–17 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breban, S.; Dranca, M.; Chirca, M.; Pacuraru, A.-M.; Teodosescu, P.-D.; Oprea, C.-A. Experimental Tests on a Spoke-Type Permanent Magnets Synchronous Machine for Light Electric Vehicle Application. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, U.-J.; Chun, Y.-D.; Choi, J.-H.; Han, P.-W.; Koo, D.-H.; Lee, J. A Technique of Torque Ripple Reduction in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 3240–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarres, M.; Vahedi, A.; Ghazanchaei, M. Effect of Air Gap Variation on Characteristics of an Axial Flux Hysteresis Motor. In Proceedings of the 2010 1st Power Electronic & Drive Systems & Technologies Conference (PEDSTC), Tehran, Iran, 17–18 February 2010; pp. 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, W.A.M.; Hebala, A.; Ashour, H.A. Sensitivity Analysis of Parameters Affecting the Performance of Radial Flux Low-Speed PMSG. In Proceedings of the 2018 XIII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.T. Electric Vehicle Machines and Drives: Design, Analysis and Application; Wiley-IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 69–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Parsapour, A.; Yang, Z.; Caicedo-Narvaez, C.; Moallem, M.; Fahimi, B. Optimization of Air-Gap Profile in Interior Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors for Torque Ripple Mitigation. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2019, 5, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Meng, T. A New Design Concept of PMSM for Flux Weakening Operation. In Proceedings of the 2016 19th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Chiba, Japan, 13–16 November 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.-S.; Cho, H.-W.; Choi, J.-Y.; Jang, S.-M.; Lee, S.-H. Optimum Design of Stator and Rotor Shape for Cogging Torque Re-duction in Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. J. Power Electron. 2013, 13, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Luo, L.; Chai, Y.; Song, J.; Jiang, F.; Shao, Y. Optimization Design of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Torque Ripple Based on Stator Tooth Crown Slotting Method. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 32nd International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Helsinki, Finland, 19–21 June 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-M.; Yoon, M.-H.; Hong, J.-P.; Kim, S.-I. Analysis of Cogging Torque Caused by Manufacturing Tolerances of Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Electric Power Steering. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2016, 10, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, R.; Mellor, P.H.; Holliday, D. Thermal Modeling of a Segmented Stator Winding Design. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, A.; Sánchez, G.; Jara, W.; Madariaga, C.; Tapia, J.A.; Riedemann, J.; Reyes, E. Impact of Manufacturing Tolerances on Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Machines with Ironless Rotor Core: A Statistical Approach. Machines 2023, 11, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villén, M.T.; Cañete, M.G.; Martín, E.; Comech, M.P.; Lozano, C. Manufacturing Tolerances Influence on Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator (PMSG) Performance. 2016. Available online: https://windeurope.org/summit2016/conference/allfiles2/262_WindEurope2016presentation.pdf (accessed on 13 April 2024).
- Ma, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, L. Robust optimization design of permanent magnet synchronous motors for a solar airplane based on a lightweight structure. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Zhu, Z.Q. Influence of Manufacturing Tolerances on Cogging Torque in Interior Permanent Magnet Machines with Eccentric and Sinusoidal Rotor Contours. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 3568–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, A.; Sánchez, G.; Jara, W.; Madariaga, C.; Tapia, J.; Degano, M.; Riedemann, J. Statistical Analysis of Manufacturing Tolerances Effect on Axial-Flux Permanent Magnet Machines Cogging Torque. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–14 October 2021; pp. 4342–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Yang, G.; Yang, Y. Analysis of Cogging Torque of Permanent Magnet Motors under Mixed-Eccentricity and Manufacturing Tolerances. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 6672–6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparin, L.; Cernigoj, A.; Markic, S.; Fiser, R. Additional Cogging Torque Components in Permanent-Magnet Motors Due to Manufacturing Imperfections. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Jia, Y.; Soong, W.L. Comparison of Five Topologies for an Interior Permanent-Magnet Machine for a Hybrid Electric Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 3606–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Ge, B.; Tao, D.; Pan, B.; Wang, Y. Rotor Strength Analysis of FeCo-Based Permanent Magnet High Speed Motor. Machines 2022, 10, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Zuo, S.; Deng, W. Impact of Rotor Eccentricity on Electromagnetic Vibration and Noise of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. J. Vibroeng. 2018, 20, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, N.; Dasara, S.; Liang, J.; Al-Ani, D.; Emadi, A.; Bilgin, B. Study on the Effect of Dynamic Eccentricity on Acoustic Noise of an Interior Permanent Magnet Traction Motor. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo (ITEC), Chicago, IL, USA, 23–26 June 2020; pp. 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galfarsoro, U.; McCloskey, A.; Zarate, S.; Hernández, X.; Almandoz, G. Influence of manufacturing tolerances and eccentricities on the unbalanced magnetic pull in permanent magnet synchronous motors. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–26 August 2020; pp. 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, G.; Guo, Y.; Lin, J.; Han, W.; Zheng, M.; Chen, X. Principles of an In-Process Monitoring System for Precision Grinding Machine. In Proceedings of the 2011 Second International Conference on Mechanic Automation and Control Engineering, Hohhot, China, 15–17 July 2011; pp. 7546–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, S.S.; Vázquez, C.O.; García, J.G.; Ortega, J.G. Quality Inspection of Machined Metal Parts Using an Image Fusion Technique. Measurement 2017, 111, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, A.; Meyer, A.; Seefried, J.; Weigelt, M.; Lutz, B.; Sultani, D.; Hampl, M.; Franke, J. Potentials of Machine Learning in Electric Drives Production Using the Example of Contacting Processes and Selective Magnet Assembly. In Proceedings of the 2017 7th International Electric Drives Production Conference (EDPC), Würzburg, Germany, 5–6 December 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-S.; Cha, K.-S.; Park, J.-C.; Lim, M.-S. Tolerance-Insensitive Design of the Magnet Shape for a Surface Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Energies 2020, 13, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narahari, Y.; Sudarsan, R.; Lyons, K.W.; Duffey, M.R.; Sriram, R.D. Design for tolerance of electro-mechanical assemblies: An integrated approach. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1999, 15, 1062–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mayr, A.; Weigelt, M.; von Lindenfels, J.; Seefried, J.; Ziegler, M.; Mahr, A.; Urban, N.; Kühl, A.; Hüttel, F.; Franke, J. Electric Motor Production 4.0—Application Potentials of Industry 4.0 Technologies in the Manufacturing of Electric Motors. In Proceedings of the 2018 8th International Electric Drives Production Conference (EDPC), Schweinfurt, Germany, 4–5 December 2018; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, A.; Weigelt, M.; Masuch, M.; Meiners, M.; Hüttel, F.; Franke, J. Application Scenarios of Artificial Intelligence in Electric Drives Production. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 24, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zuo, B. Detection of surface cutting defect on magnet using Fourier image reconstruction. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercan, H.; Khawli, T.A.; Eppelt, U.; Büscher, C.; Meisen, T.; Jeschke, S. Improving the Laser Cutting Process Design by Machine Learning Techniques. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 2017, 11, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, D. Using manufacturing tolerances and practices to minimize unbalance [in electric motors]. In Proceedings of the Electrical Insulation Conference and Electrical Manufacturing and Coil Winding Conference, Rosemont, IL, USA, 22–25 September 1997; pp. 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotlih, J.; Brezocnik, M.; Pal, S.; Drstvensek, I.; Karner, T.; Brajlih, T. A Holistic Approach to Cooling System Selection and Injection Molding Process Optimization Based on Non-Dominated Sorting. Polymers 2022, 14, 4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Manufacturing Process | Noise and Vibration Test | Cogging Torque Test | Running Temperature Test | DC Hipot Test | Surge Test | Rotor Eccentricity Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lamination | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Insulation | √ | √ | ||||
| Winding | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Contacting | √ | |||||
| Impregnation | √ | √ | √ | |||
| Bearing | √ | √ | ||||
| Shaft | √ | √ | ||||
| Assembly | √ | √ |
| Parameters | Nominal Value (mm) | Range of Deviation (%) | Change in Back EMF (%) | Change in Torque Ripple (%) | Change in Shaft Torque (%) | Change in Cogging Torque (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stator outer diameter | 200 | 0.5 | 0 | 5.21 | 1.85 | 0.002 |
| Stator inner diameter | 142.6 | 0.42 | 4.61 | 11.84 | 1.51 | 30.505 |
| Slot opening | 2.4 | 16.67 | 0.26 | 1.02 | 0.39 | 3.02 |
| Air gap | 0.55 | 18.18 | 0.064 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 19.65 |
| Rotor magnet thickness | 5.8 | 6.9 | 0.58 | 1.65 | 1.4 | 1.04 |
| Rotor magnet bar width | 14.7 | 3.4 | 2.81 | 1.58 | 2.9 | 10.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popsi, N.R.S.; Anik, A.; Verma, R.; Viana, C.; Iyer, K.L.V.; Kar, N.C. Influence of Electric Motor Manufacturing Tolerances on End-of-Line Testing: A Review. Energies 2024, 17, 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081913
Popsi NRS, Anik A, Verma R, Viana C, Iyer KLV, Kar NC. Influence of Electric Motor Manufacturing Tolerances on End-of-Line Testing: A Review. Energies. 2024; 17(8):1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081913
Chicago/Turabian StylePopsi, Nusrat Rezwana Shahreen, Animesh Anik, Rajeev Verma, Caniggia Viana, K. Lakshmi Varaha Iyer, and Narayan C. Kar. 2024. "Influence of Electric Motor Manufacturing Tolerances on End-of-Line Testing: A Review" Energies 17, no. 8: 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081913
APA StylePopsi, N. R. S., Anik, A., Verma, R., Viana, C., Iyer, K. L. V., & Kar, N. C. (2024). Influence of Electric Motor Manufacturing Tolerances on End-of-Line Testing: A Review. Energies, 17(8), 1913. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081913






