Improved Mechanical Properties of Polyurethane-Driven 4D Printing of Aluminum Oxide Ceramics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
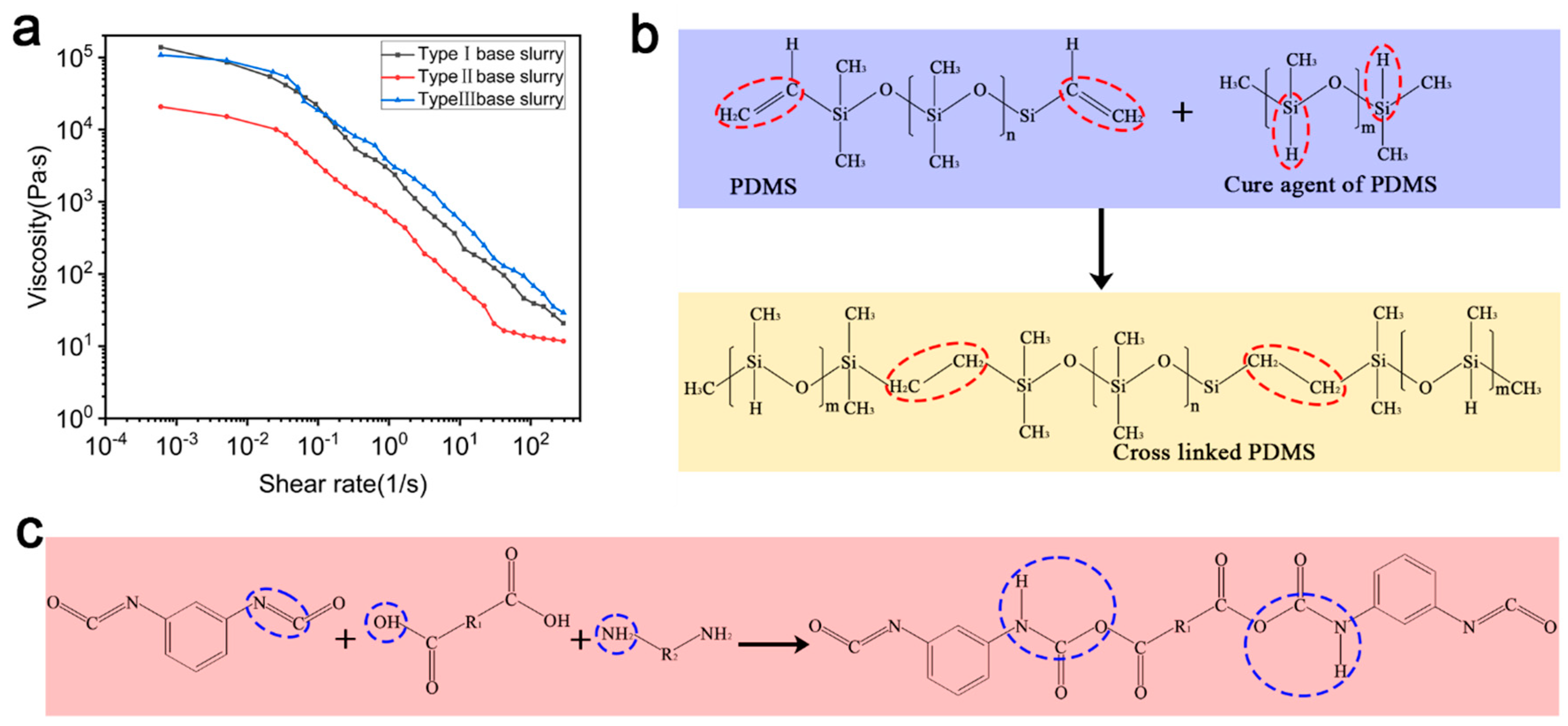
2.2. Preparation of Precursor Slurry
2.3. Rheology Analysis of Slurry
2.4. Three-Dimensional Printing
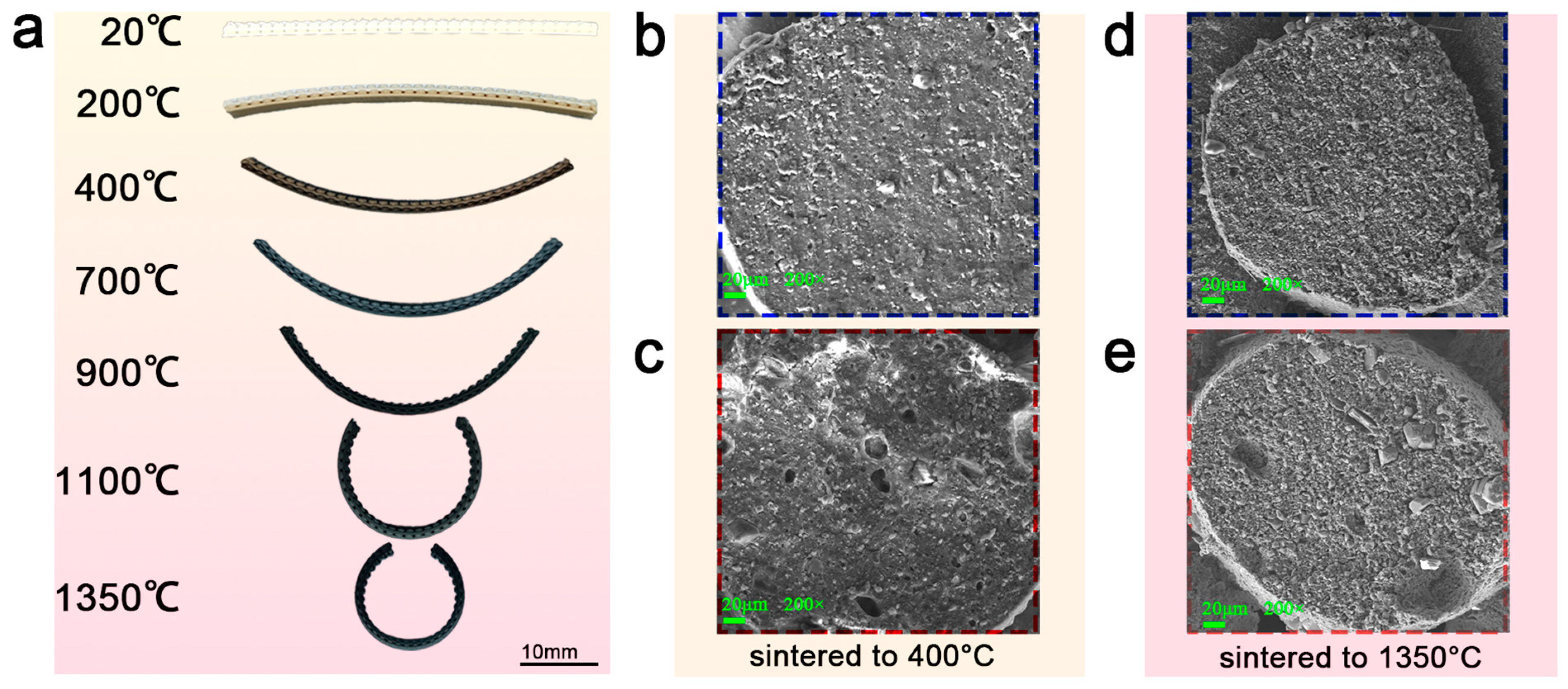
2.5. Sintering
2.6. Characterization
2.7. Mechanical Performance Test
3. Results
3.1. Basic Deformation Principles
3.2. Basic Deformation Laws and 4D Printing of Deformed Ceramics with Complex Shapes
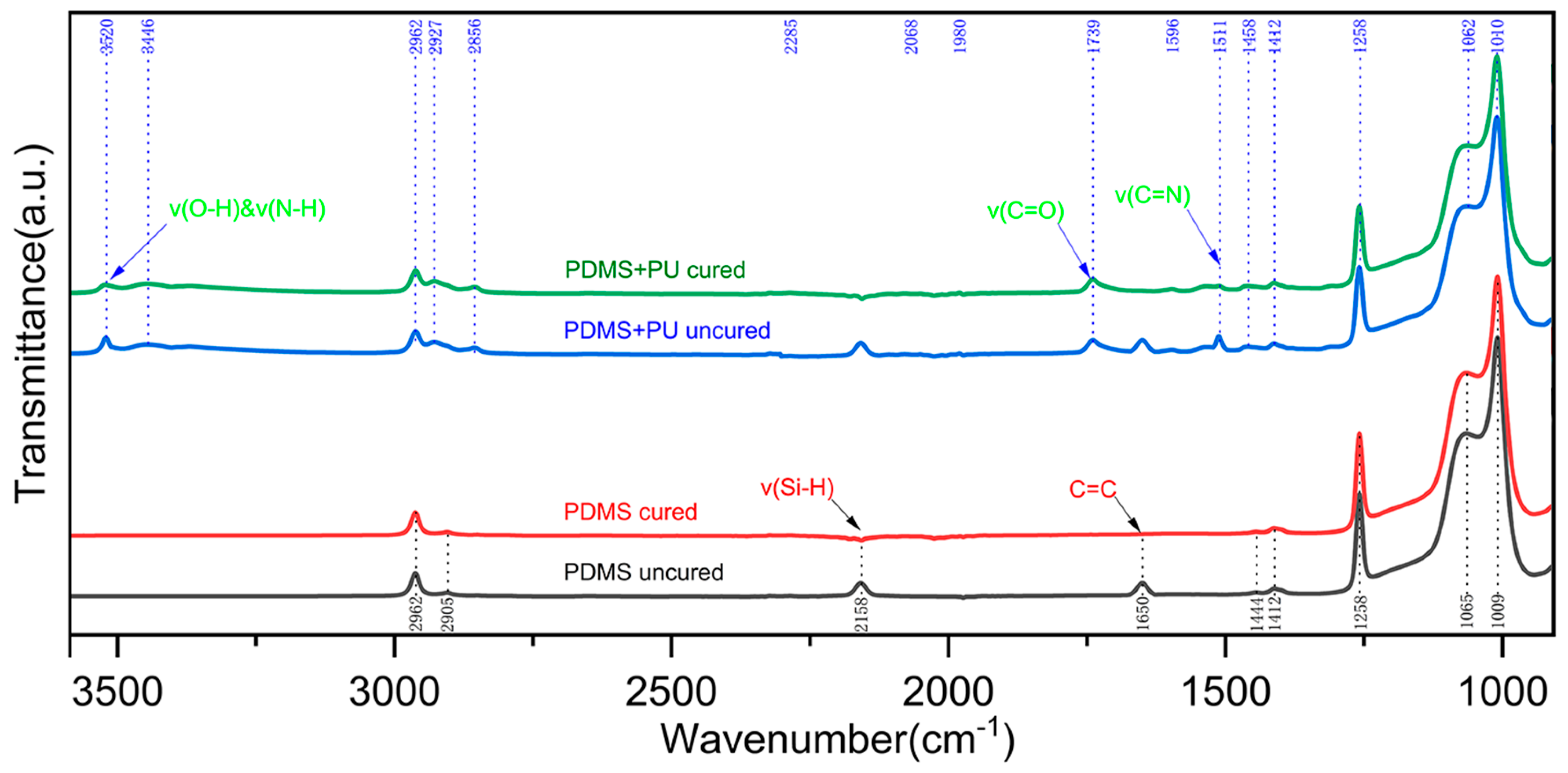
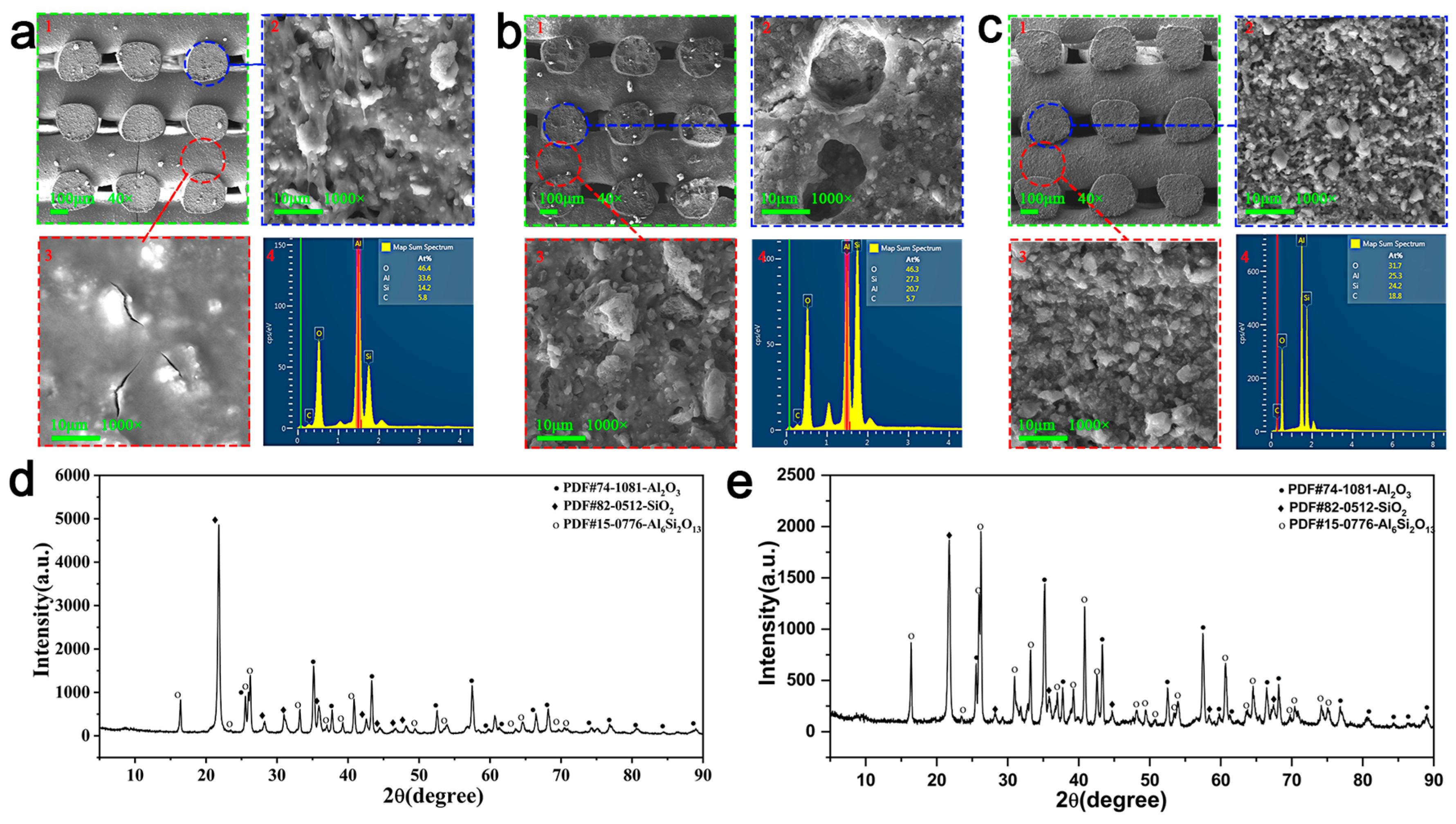
3.3. Optimization of Curing Reaction Process of Slurry and Ceramic Precursor for 3D Printing
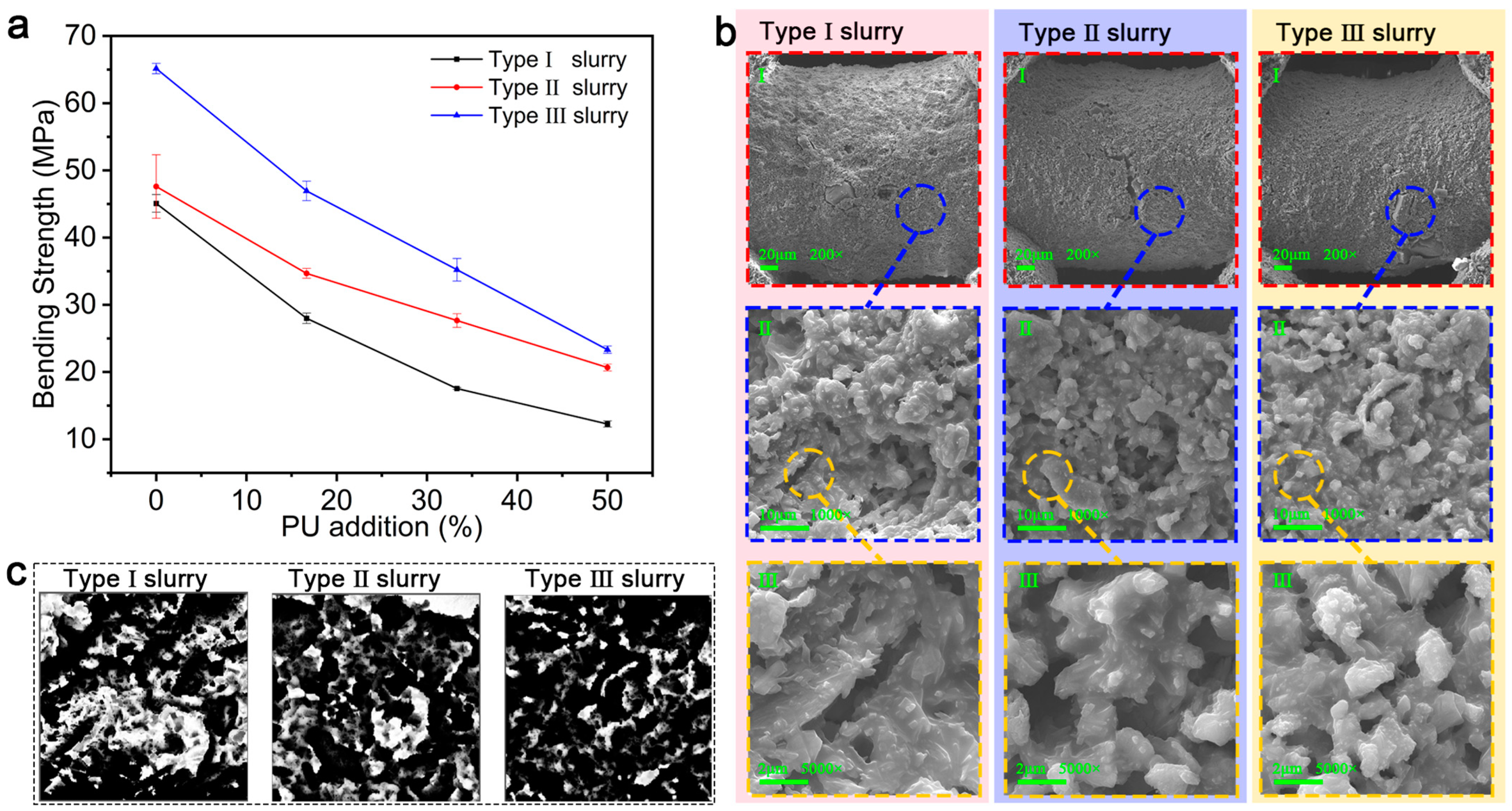
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Optimized Ceramics
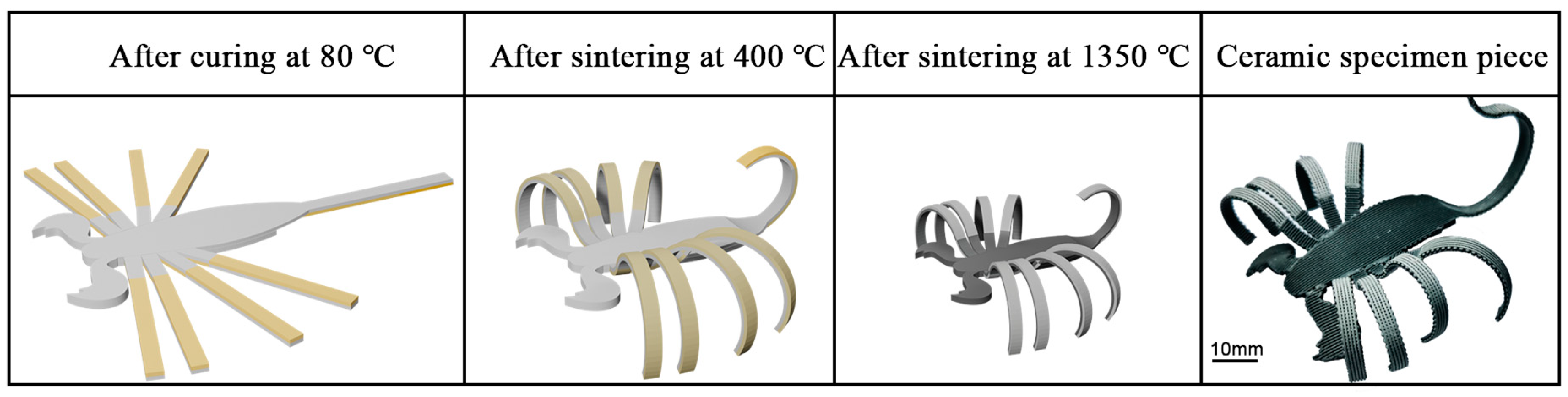
3.5. Deformability of Optimized Ceramics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DIW | Direct Ink Writing |
| SLA | Stereo Lithography Apparatus |
| EPS | Expanded Polystyrene |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| SE 1700 | Dow Corning SE 1700 polydimethylsiloxane silicone rubber |
| DC 184 | Dow Corning DC 184 polydimethylsiloxane silicone rubber |
| Al2O3 | Alumina Nanoparticles |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| EDS | Energy Dispersive Spectrometry |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer |
Appendix A
| Group I | Type I Slurry | Type II Slurry | Type III Slurry | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PU Addition | b (mm) | h (mm) | P(N) | b (mm) | h (mm) | P(N) | b (mm) | h (mm) | P(N) |
| 0 | 3.58 | 3.15 | 45.19 | 3.59 | 3.16 | 42.04 | 4.04 | 3.55 | 92.92 |
| 1/6 | 3.84 | 3.38 | 34.56 | 3.76 | 3.31 | 40.64 | 4.18 | 3.68 | 75.99 |
| 1/3 | 4.01 | 3.53 | 24.17 | 3.87 | 3.41 | 35.25 | 4.26 | 3.75 | 55.61 |
| 1/2 | 4.08 | 3.59 | 18.46 | 3.92 | 3.45 | 27.27 | 4.28 | 3.76 | 39.23 |
| Group II | Type I Slurry | Type II Slurry | Type III Slurry | ||||||
| PU Addition | b (mm) | h (mm) | P(N) | b (mm) | h (mm) | P(N) | b (mm) | h (mm) | P(N) |
| 0 | 3.52 | 3.12 | 41.46 | 3.58 | 3.15 | 50.36 | 4.01 | 3.53 | 89.20 |
| 1/6 | 3.81 | 3.36 | 32.38 | 3.75 | 3.29 | 38.69 | 4.16 | 3.65 | 69.94 |
| 1/3 | 3.98 | 3.50 | 23.90 | 3.85 | 3.39 | 32.54 | 4.25 | 3.73 | 60.37 |
| 1/2 | 4.04 | 3.56 | 16.71 | 3.91 | 3.43 | 25.65 | 4.25 | 3.73 | 37.42 |
| Group III | Type I Slurry | Type II Slurry | Type III Slurry | ||||||
| PU Addition | b (mm) | h (mm) | P(N) | b (mm) | h (mm) | P(N) | b (mm) | h (mm) | P(N) |
| 0 | 3.57 | 3.13 | 44.58 | 3.57 | 3.16 | 49.08 | 4.03 | 3.53 | 91.33 |
| 1/6 | 3.82 | 3.37 | 34.37 | 3.76 | 3.32 | 39.37 | 4.16 | 3.67 | 73.26 |
| 1/3 | 4 | 3.51 | 24.06 | 3.86 | 3.4 | 35.06 | 4.26 | 3.74 | 58.71 |
| 1/2 | 4.07 | 3.56 | 17.79 | 3.91 | 3.43 | 26.68 | 4.25 | 3.75 | 39.57 |
References
- Kantaros, A.; Ganetsos, T.; Piromalis, D. 4D Printing: Technology Overview and Smart Materials Utilized. J. Mechatron. Robot. 2023, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patadiya, J.; Naebe, M.; Wang, X.; Joshi, G.; Kandasubramanian, B. Emerging 4D Printing Strategies for On-Demand Local Actuation & Micro Printing of Soft Materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 184, 111778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Sato, T.; Taguchi, Y. Additive Manufacturing Method of Electrothermal 4D Bimorph Microactuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 356, 114348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Mao, Z.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; Lyu, F.; Cao, Z.; He, Y.; Yin, J.; Han, X.; Chan, W.Y.K.; et al. Direct 4D Printing of Gradient Structure of Ceramics. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Park, S. 4D Printed Untethered Milli-Gripper Fabricated Using a Biodegradable and Biocompatible Electro- and Magneto-Active Hydrogel. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 384, 133654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. 4D Printing of Multiple Shape Memory Polymer and Nanocomposites with Biocompatible, Programmable and Selectively Actuated Properties. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 53, 102689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbits, S. 4D Printing: Multi-material Shape Change. Archit. Des. 2014, 84, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantaros, A.; Ganetsos, T. From Static to Dynamic: Smart Materials Pioneering Additive Manufacturing in Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, W.; Zheng, P.; Xiong, Y. Reusability and Energy Absorption Behavior of 4D Printed Continuous Fiber-Reinforced Auxetic Composite Structures. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2023, 169, 107529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnakorn, A.; Nuansing, W.; Bodaghi, M.; Rolfe, B.; Zolfagharian, A. Recent Progress of 4D Printing in Cancer Therapeutics Studies. SLAS Technol. 2023, 28, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yue, C.; Liu, L.; Leng, J.; Liu, Y. Mechanical Behavior Analyses of 4D Printed Metamaterials Structures with Excellent Energy Absorption Ability. Compos. Struct. 2023, 304, 116360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zou, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Mass-Producible near-Body Temperature-Triggered 4D Printed Shape Memory Biocomposites and Their Application in Biomimetic Intestinal Stents. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 256, 110623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, G.; Wu, X.; et al. 4D-Printed Bilayer Hydrogel with Adjustable Bending Degree for Enteroatmospheric Fistula Closure. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 16, 100363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Mei, H.; Chang, P.; Lu, M.; Cheng, L. Molecule Editable 3D Printed Polymer-Derived Ceramics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 422, 213486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belluomo, R.; Khodaei, A.; Amin Yavari, S. Additively Manufactured Bi-Functionalized Bioceramics for Reconstruction of Bone Tumor Defects. Acta Biomater. 2023, 156, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, R.; Zhou, D.; Guo, T.; He, W.; Cui, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; et al. 4D Printing of Shape Memory Inferior Vena Cava Filters Based on Copolymer of Poly(Glycerol Sebacate) Acrylate-Co-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate (PGSA-HEMA). Mater. Des. 2023, 225, 111556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namvar, N.; Zolfagharian, A.; Vakili-Tahami, F.; Bodaghi, M. Reversible Energy Absorption of Elasto-Plastic Auxetic, Hexagonal, and AuxHex Structures Fabricated by FDM 4D Printing. Smart Mater. Struct. 2022, 31, 055021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Ghoreishi, M.; Narooei, K. 4D Printing of Shape Memory Polylactic Acid Beams: An Experimental Investigation into FDM Additive Manufacturing Process Parameters, Mathematical Modeling, and Optimization. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 85, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhao, W.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. A 4D-Printed Programmable Soft Network with Fractal Design and Adjustable Hydrophobic Performance. Matter 2023, 6, 940–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholkhoev, B.C.; Bardakova, K.N.; Epifanov, E.O.; Matveev, Z.A.; Shalygina, T.A.; Atutov, E.B.; Voronina, S.Y.; Timashev, P.S.; Burdukovskii, V.F. A Photosensitive Composition Based on an Aromatic Polyamide for LCD 4D Printing of Shape Memory Mechanically Robust Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Hao, P.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Wang, K.; Ren, L.; Zhou, X.; et al. Stiffness-Tunable and Self-Sensing Integrated Soft Machines Based on 4D Printed Conductive Shape Memory Composites. Mater. Des. 2023, 228, 111851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Kesharwani, P. The Clinical Significance of 4D Printing. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaniga, A.; Foppoli, A.; Cerea, M.; Palugan, L.; Cirilli, M.; Moutaharrik, S.; Melocchi, A.; Maroni, A. Towards 4D Printing in Pharmaceutics. Int. J. Pharm. X 2023, 5, 100171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Raza, A.; Xue, Y.-Q.; Yang, G.; Hayat, U.; Yu, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.-J.; Wang, J.-Y. Water-Responsive 4D Printing Based on Self-Assembly of Hydrophobic Protein “Zein” for the Control of Degradation Rate and Drug Release. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 23, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruque, M.O.; Lee, Y.; Wyckoff, G.J.; Lee, C.H. Application of 4D Printing and AI to Cardiovascular Devices. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 80, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parimita, S.; Kumar, A.; Krishnaswamy, H.; Ghosh, P. Solvent Triggered Shape Morphism of 4D Printed Hydrogels. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 85, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Hu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Li, X.; Sang, S.; McClements, D.J.; Chen, L.; Long, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Peanut Protein-Polysaccharide Hydrogels Based on Semi-Interpenetrating Networks Used for 3D/4D Printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, W.T.; Dong, Y.; Pramanik, A.; Leng, J.; Ramakrishna, S. Smart Polyurethane Composites for 3D or 4D Printing: General-Purpose Use, Sustainability and Shape Memory Effect. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 223, 109104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.; Devaramani, R.; Adinarayanappa, S.M. Modelling, Simulation, and Experiments of 4D Printed Twisting Actuator. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 101, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, H.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Hsia, K.J.; Liu, M. Morphing Matter: From Mechanical Principles to Robotic Applications. Soft Sci. 2023, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Guo, Y.; Bae, J.; Choi, S.; Song, H.Y.; Park, S.; Hyun, K.; Ahn, S. 4D Printing of Hygroscopic Liquid Crystal Elastomer Actuators. Small 2021, 17, 2100910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winhard, B.F.; Haida, P.; Plunkett, A.; Katz, J.; Domènech, B.; Abetz, V.; Furlan, K.P.; Schneider, G.A. 4D-Printing of Smart, Nacre-Inspired, Organic-Ceramic Composites. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 77, 103776. [Google Scholar]
- Ayode Otitoju, T.; Ugochukwu Okoye, P.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Onyeka Okoye, M.; Li, S. Advanced Ceramic Components: Materials, Fabrication, and Applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 85, 34–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Dutta, S.P. Application Trend in Advanced Ceramic Technologies. Technovation 2001, 21, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Cheng, L.; Huo, M.; Yin, J.; Hao, F.; Chen, S.; Wang, P.; et al. Additive Manufacturing of Structural Materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 145, 100596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, G.; Lu, J. Origami and 4D Printing of Elastomer-Derived Ceramic Structures. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat0641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Lv, W.; Zhu, P.; et al. 4D Printing of Ceramic Structures. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 63, 103411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, J.; Shi, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Meng, S.; Lu, J. Lightweight and Geometrically Complex Ceramics Derived from 4D Printed Shape Memory Precursor with Reconfigurability and Programmability for Sensing and Actuation Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yuan, C.; Cheng, J.; He, X.; Ye, H.; Jian, B.; Li, H.; Bai, J.; Ge, Q. Direct 4D Printing of Ceramics Driven by Hydrogel Dehydration. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; He, Y.; Ren, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, K.; Li, B.; Liu, Q. Multi-Parameter-Encoded 4D Printing of Liquid Crystal Elastomers for Programmable Shape Morphing Behaviors. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 61, 103376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwa, L.C.; Rajoo, S.; Noor, A.M.; Ahmad, N.; Uday, M.B. Recent Advances in 3D Printing of Porous Ceramics: A Review. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 21, 323–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pztrov, Z.S. Polyurethane Elastomers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1991, 16, 695–836. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharyan, E.M.; Maksimov, A.L. Pyrolysis of Polyurethanes. Process Features and Composition of Reaction Products. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2022, 95, 191–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Xin, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Wu, C.; Bai, X. Improved Mechanical Properties of Polyurethane-Driven 4D Printing of Aluminum Oxide Ceramics. Materials 2025, 18, 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081750
Wang Z, Xin Z, Jiao Z, Wu C, Bai X. Improved Mechanical Properties of Polyurethane-Driven 4D Printing of Aluminum Oxide Ceramics. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081750
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhaozhi, Zhiheng Xin, Zhibin Jiao, Chenliang Wu, and Xu Bai. 2025. "Improved Mechanical Properties of Polyurethane-Driven 4D Printing of Aluminum Oxide Ceramics" Materials 18, no. 8: 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081750
APA StyleWang, Z., Xin, Z., Jiao, Z., Wu, C., & Bai, X. (2025). Improved Mechanical Properties of Polyurethane-Driven 4D Printing of Aluminum Oxide Ceramics. Materials, 18(8), 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081750





