Abstract
In case of emergency, evacuation signs play an important role in guiding people to evacuate safety exits in large space buildings. Large space buildings are characterized by high ceilings and large areas. In the existing legislation and standards, the height setting of evacuation signs is fixed, but the influence of height changes on the visibility of evacuation signs is very important. This study fully considers the relationship between the height setting change of evacuation signs and the visual range and puts forward a smart safety design strategy for evacuation signs. The smart safety design consists of two parts, one is the mathematical relationship between the height change of evacuation signs and the visual range of personnel, and the other is the integration of the application process of smart devices. Firstly, the visual range of two different sizes of evacuation signs placed at the height of 1.7 to 6 m was measured experimentally in China. The results showed that: (1) with an increase in the height of the evacuation signs, their viewing distance gradually decreased and the visual range was reduced; (2) the mathematical model of the change between the height and the visual range of evacuation signs was established; (3) the height of evacuation signs between 3 to 5 m agreed more with the visual habits of the people. Then, on this basis, the smart safety design method can use related mathematical models to set the evacuation signs at the optimal height based on the actual distance between people and evacuation signs, ensuring that people can see the signs the first time, thus providing evacuation guidance for evacuees and improving the safety of large space buildings.
1. Introduction
With continuous urbanization and rapid economic development, the public demand for quality of life and the use of space is increasing. To meet people’s needs for complex building functions, an increasing number of large space buildings, such as exhibition halls, stadiums, airport terminals, and railway stations, have been constructed [1]. Large space buildings are characterized by high ceilings, large areas, large space capacity, and large numbers of people. When a large number of people gather in a building space, evacuation signs play a key role in the safety of people in case of emergencies such as fires and earthquakes [2]. The reasonable setting of evacuation signs can guide evacuation to safety exits (areas) quickly, reduce the wayfinding time in a complex space, and thus improve the evacuation efficiency of people [3].
During an emergency, one of the main ways that people use to make evacuation decisions is information received from signs [4]. The primary condition for people to obtain information through evacuation signs is that the signs must be visible and legible [5]. Previous studies mainly focused on the legibility of the evacuation signs, including the text [6], graphics [7,8], color [9,10], size [11], brightness characteristics [12], light source type, and flash rate [13,14]. However, there are many entrances and exits in a large space building, which leads to the possibility of multiple combinations of passages and intersections in the building space. The improper setting of evacuation signs has greatly affected people’s wayfinding in the buildings [15]. At the same time, obstacles, cubicles, and structures in large space buildings can block people’s sight and make the signs invisible [16,17]. People cannot evacuate quickly and safely, which leads to a high risk of casualties.
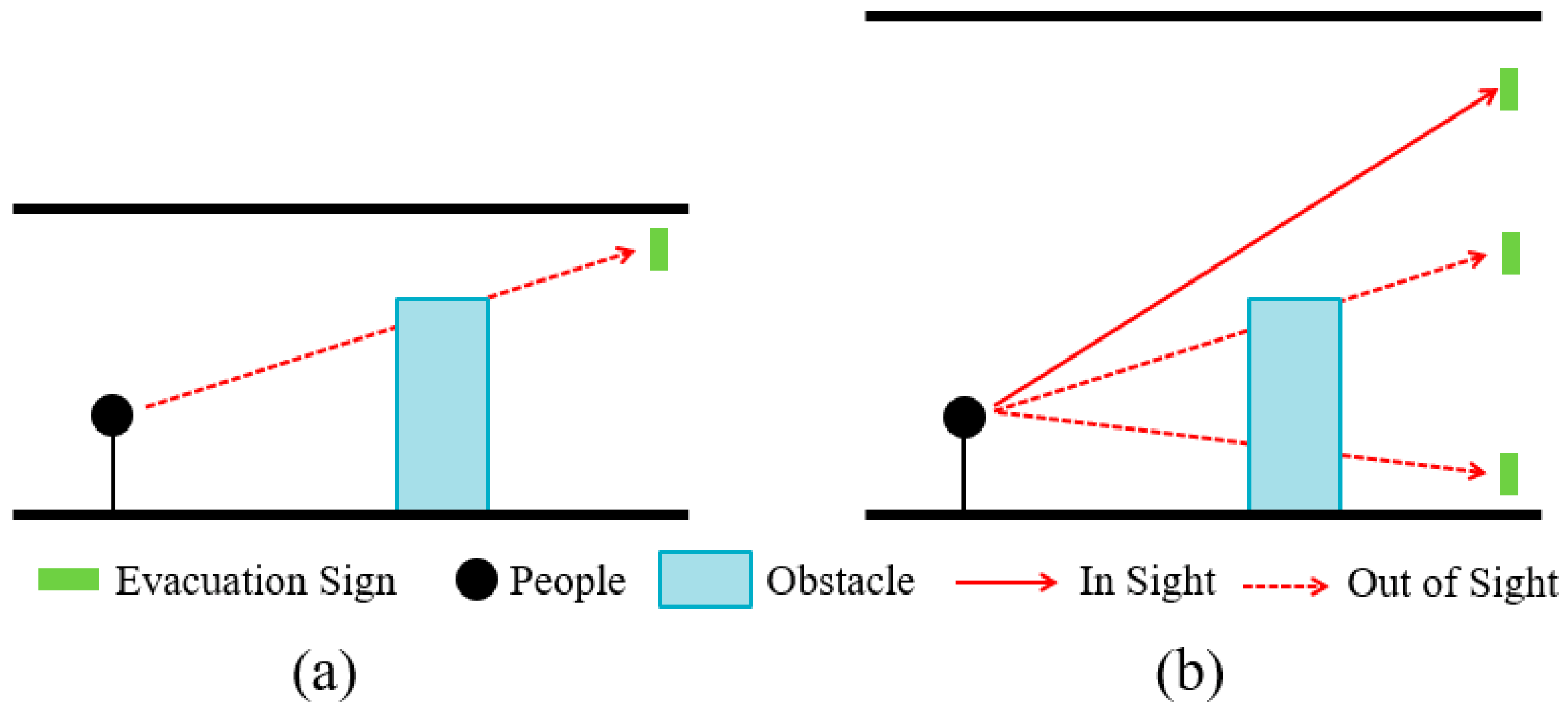
ISO 16069:2017 (Graphical symbols—Safety signs—Safety way guidance systems) classifies evacuation signs into high-, intermediate-, and low-location placement according to their different heights of placement, with low-placed signs generally on or slightly above the ground and high-placed ones at a distance of more than 1.8 m from the ground. Kobes et al. [3,18] found that smoke during a fire reduces the ambient visibility, and therefore low-placed evacuation signs are better for people to recognize during evacuation than high-placed signs. Unlike residences and offices, large space buildings typically have ceiling heights of greater than 10 m [19], allowing enough space for smoke storage at the top of the building [20] to quickly exhaust smoke [21,22] through natural and mechanical ventilation [23], thus effectively controlling the impact of smoke-induced changes in ambient visibility on the visibility of high-placed evacuation signs. In addition, the impact of smoke can be ignored [24] in emergency events other than fires (e.g., terrorist attacks and earthquakes). Ding [25], Fu et al. [26], and Zhu et al. [27] research experimentally showed that high-location signs have a positive impact on the choice of evacuation routes and have a greater guiding effect than that of low-location signs. The setting of high-placed evacuation signs in large space buildings avoids the situation where low-location signs would be blocked by front people and obstacles and is thus more conducive to evacuation (Figure 1).
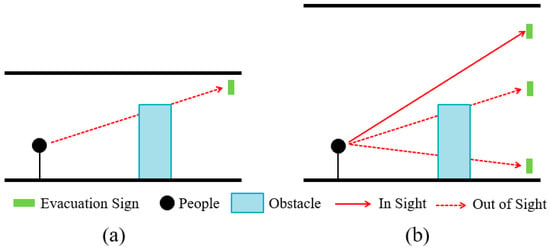
Figure 1.
Visual relation between an evacuation sign, an obstacle, and a person. (a) In a building space with low ceilings, the evacuation sign is obstructed by the obstacle; (b) In a large space building, the evacuation sign at high-location can avoid being obstructed by the obstacle.
Various countries have issued corresponding standards for the location of evacuation signs, such as GB 50016-2014 and GB 51309-2018 in China, NFPA 101-2018 in the United States, and BS 5499-4:2013 in the United Kingdom. Evacuation signs are installed on the walls, columns, corridors, and the top of safety exits in buildings. The height of evacuation signs is generally 0.1–0.3 m higher than the door (the height of the door is 2.2–3.5 m), that is, the height of evacuation signs is 2.3–3.8 m. These standards and guidelines are formulated based on design experience or public suggestions but lack full consideration of the particularity of the high ceilings and the height setting of evacuation signs in large space buildings.
Kubota et al. [28] used a virtual reality (VR) experiment and found that the installation position of evacuation signs (i.e., distance, angle of interaction) affects people’s choice of evacuation direction and routes. Ding [25] and Jiang et al. [29] conducted reality and MR (Mixed-Reality) evacuation experiments with eye-tracking devices, and found that setting an effective position for evacuation signs can help people follow building safety guidelines. Filippidis et al. [30] referred to the spatial area where people can visually receive evacuation sign guidance information as the Visibility Catchment Area (VCA), i.e., the set of maximum viewing distances at which the human eye can distinguish the content of evacuation signs. The recognition of evacuation signs depends on the size of the signs, the distance between observers and signs, and the observation angle. Yang et al. [31] set the height of evacuation signs according to the human viewing distance in combination with the viewing angle. Xie et al. [32] established a theoretical model to explain the relationship between VCA and observation angle. Seo et al. [33] found that the obstruction of the human visual field affected the recognition of evacuation signs in terms of height. Kim et al. [34] proposed an Effective Cognition Area (ECA), which considered the cognitive changes of people on evacuation signs under smoke conditions and obtained the actual visible range of evacuation signs. Shi et al. [35] selected two sign heights (1.5 m and 2 m), and Bae et al. [36] set the height range from 0.3 m to 2.7 m to study the influence of evacuation sign height on sign recognition. However, these still paid attention to the height of ordinary buildings (e.g., office buildings, teaching buildings, metro stations), which are generally not higher than 4.5 m, without considering the characteristics of high ceilings of large space buildings. The height setting of evacuation signs has not been fully considered, let alone the impact of changes in the height of evacuation signs on their visual range.
In summary, the high ceilings of large space buildings are conducive to the optimal height setting of evacuation signs, but the studies on the influence of the height changes of evacuation signs on the visibility of signs are few. The existing standards, studies, and practical applications have not considered the correlation between the height and visual range of evacuation signs. Thus, the purpose of this study is to determine the relationship between the visual range of evacuation signs and the change of setting height and put forward the smart safety design strategy of evacuation signs, to provide a choice for the optimal setting height of the evacuation sign system.
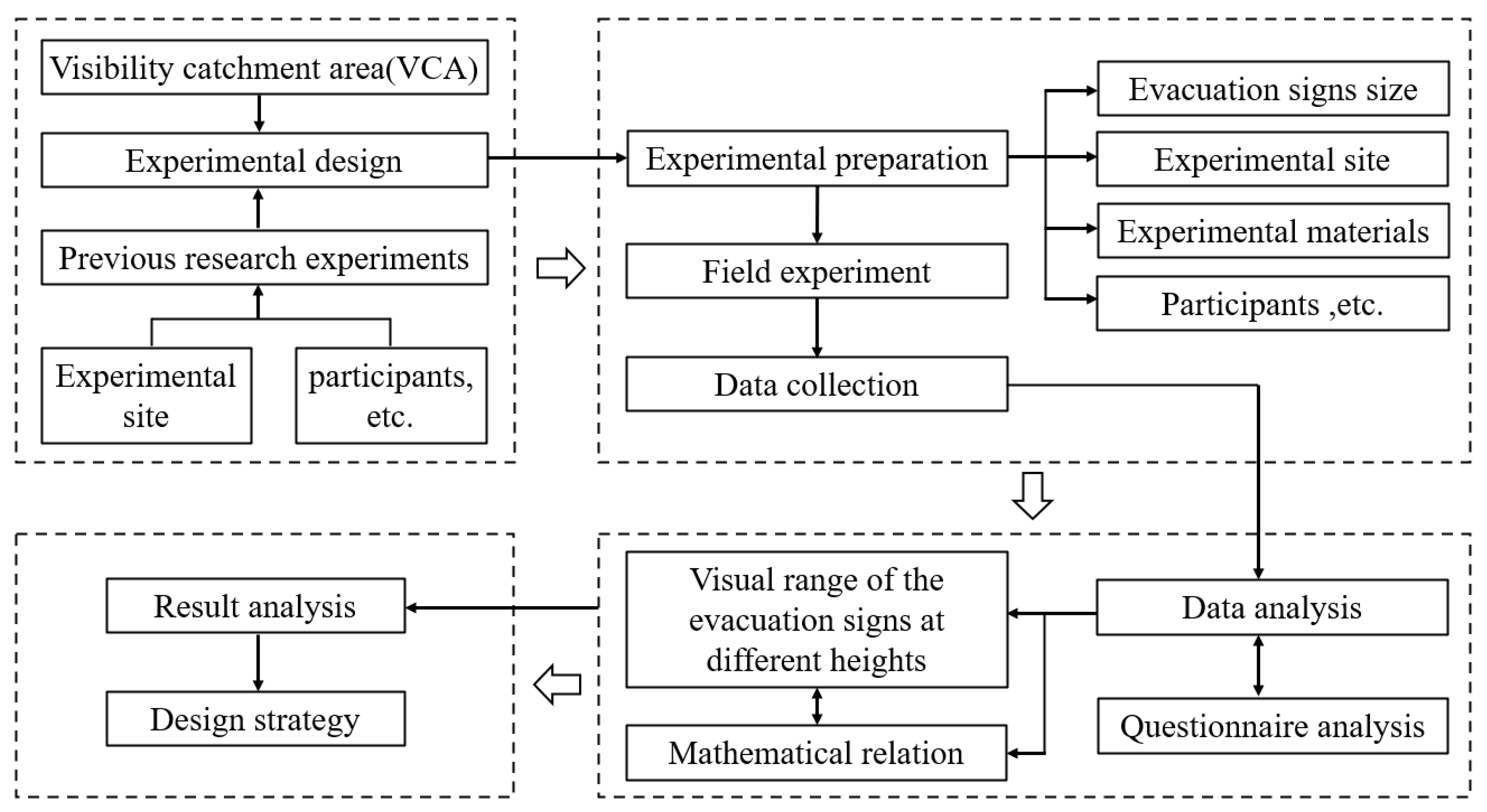
In this paper, firstly, the VCA concept is introduced, and participants are recruited to conduct experiments to observe and measure the viewing distance of evacuation signs recognized by a single person under different height and angle settings. Then, this study utilizes statistical methods to obtain a mathematical model for the relation between the height and visual range of evacuation signs, so as to quantify the viewing distance of people to the signs under different heights setting of evacuation signs. Finally, in view of the impact of changes in the height of evacuation signs on their visibility, it is proposed to create a smart safety design for evacuation signs based on height changes without changing their architectural features, in order to improve fire safety and evacuation efficiency of large space buildings. The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes the experimental setup and process in detail. The experimental results are analyzed in Section 3. Finally, Section 4, Section 5 and Section 6 are devoted to the discussion of experimental results, application of design strategies, conclusion, limitation, and future work, respectively (Figure 2).
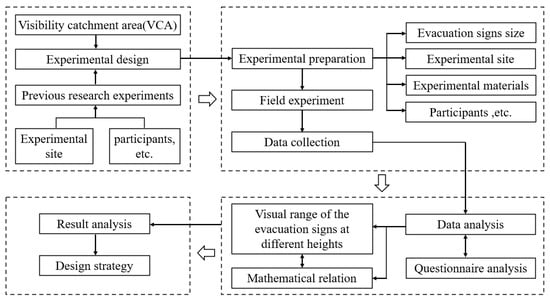
Figure 2.
Research process.
2. Methodology
The purpose of this experiment was to investigate the relationship between the height change and the visual range of evacuation signs without considering the obstacles. The height setting and viewing distance of evacuation signs determine the VCA of signage. Therefore, this research conducted an experiment to get the visual range of the sign. The visual range of an evacuation sign in a building space is a three-dimensional (3D) volume that is jointly represented by the horizontal plane and the vertical height. In the present study, the observation experiment method was adopted to determine the maximum viewing distance of evacuation signs corresponding to different combinations of offset angles and heights. According to related research [32] and Technical Standard for Fire Emergency Lighting and Evacuation Indexing System (GB 51309-2018), six offset angles θ (0°, 15°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 75°) were selected based on the horizontal plane, and six vertical heights (1.7 m, 2 m, 3 m, 4 m, 5 m, and 6 m) were considered. The experimental site, personnel characteristics (age, gender, eye height, etc.), and number of participants in this experiment were inspired by previous studies, and the details are described as follows.
2.1. Participants
Despite the differences in the visual characteristics among individuals, this experiment was conducted to emphasize their physiologically objective perception of the visibility of evacuation signs as a requirement. Generally speaking, people’s visual ability will deteriorate with age. Hence, only individuals with ages ranging from 20 to 35 years were recruited as participants, to reduce the probability of outliers with respect to vision. In order to determine the appropriate number of experimenters, this study referred to existing related research [37,38]. Based on the actual situation of the experimental site and personnel, 40 students from a university in Chongqing were chosen as the subjects. However, due to physical reasons, the two participants did not complete all the experiments, so the analysis of the experimental results was based on 38 participants who completed the experiment, 19 males and 19 females, aged between 22 and 30 years (mean = 26.03, SD = 1.82). The participants had visual acuity or corrected visual acuity of 4.9 or higher and did not suffer from visual impairments such as color blindness and color weakness.
Walking is the primary evacuation behavior [39,40], the eye height of the participants while standing was used as the benchmark. At the same time, in order to control the variables and avoid the influence of height differences between males and females on the experiment, this research chose to set the eye height of people to a fixed value. Based on the adult height standard in Human Dimensions of Chinese Adults (GB 10000-1988) and the data on people’s eye height in previous studies (1.6–1.75 m) [30,34,37,41], the eye height of the participants was set to 1.70 m, and the eye height was adjusted by increasing or decreasing the thickness of the shoe sole.
2.2. Experimental Materials and Preparation
2.2.1. Selection of Evacuation Signs
The content of evacuation signs includes information such as fonts (Chinese and English) and patterns (arrows, icons) and so on. If the size of the signs remains the same, the more content the signs contain, the smaller the size of individual information, and the less convenient it is for personnel to judge cognitive abilities [33]. Therefore, in order to consider the comprehensiveness of the experiment, evacuation signs with smaller information content sizes were selected as experimental objects to obtain the visual range of the signs.
In this experiment, evacuation signs that meet the requirements of the Chinese building code standards (Technical standard for fire emergency lighting and evacuate indicating system, GB 51309-2018) and are used in large space buildings are selected, namely, evacuation sign A and evacuation sign B (Figure 3). Evacuation signs were produced by Zhejiang Taiyi Fire Holdings Co., Ltd., Zhejiang, China and the material and brightness of the signs met the code requirements (Table 1).

Figure 3.
Evacuation signs were used in the experiment. (a) Evacuation sign A (607 mm in length × 205 mm in height); (b) evacuation sign B (807 mm in length × 255 mm in height).

Table 1.
Basic parameters of evacuation signs.
2.2.2. Experimental Site
In previous studies, office or school corridors were chosen as experimental sites. However, because this study focuses on the influence of the height setting of evacuation signs on the visual range, it is impossible to carry out experiments in corridors with a height of 3–4.5 m.
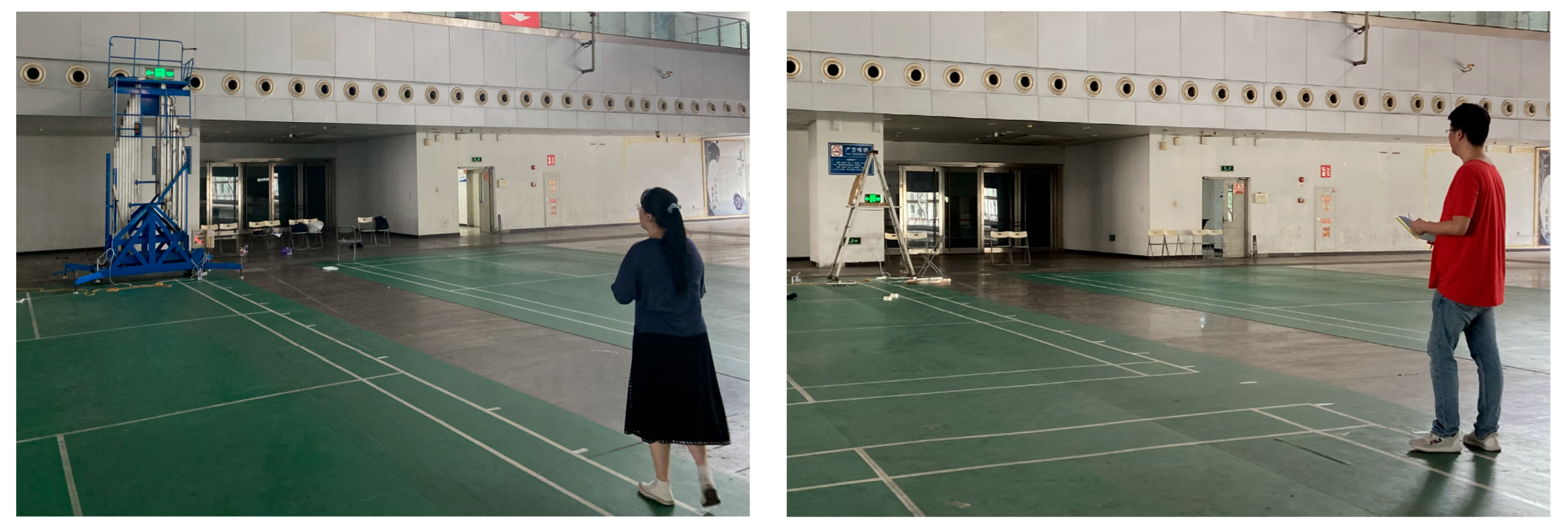
Therefore, this experimental site needs to choose a site with a high ceiling. The third floor of the Chongqing International Convention & Exhibition Center in China was ultimately selected as the experimental site. The ceiling height of this large space building was 14 m, and the lighting could be adjusted manually (ceiling lights and wall lights are installed). A straight passageway, with a length of 80 m and a width of 0.5 m, was separated on the floor ground with an evacuation sign set at one end of the channel and the starting point for the participants in the experiment at the other end.
2.2.3. Setting of the Ambient Lighting Conditions
The lighting conditions of the entire site met the requirements of the Chinese building code GB 51309-2018. The horizontal illuminance of the experimental site under normal lighting conditions was measured along the long side of the straight passageway at eight measurement points spaced at intervals of 10 m by using a luxmeter (TES, TES-1330A). Before the illuminance measurement, the overhead lights were turned on in advance to ensure the uniformity and stability of the illuminance. The measurement results showed that the illuminance had a mean value of 70 lux (SD = 4.5).
2.2.4. Preparation of Other Experimental Materials
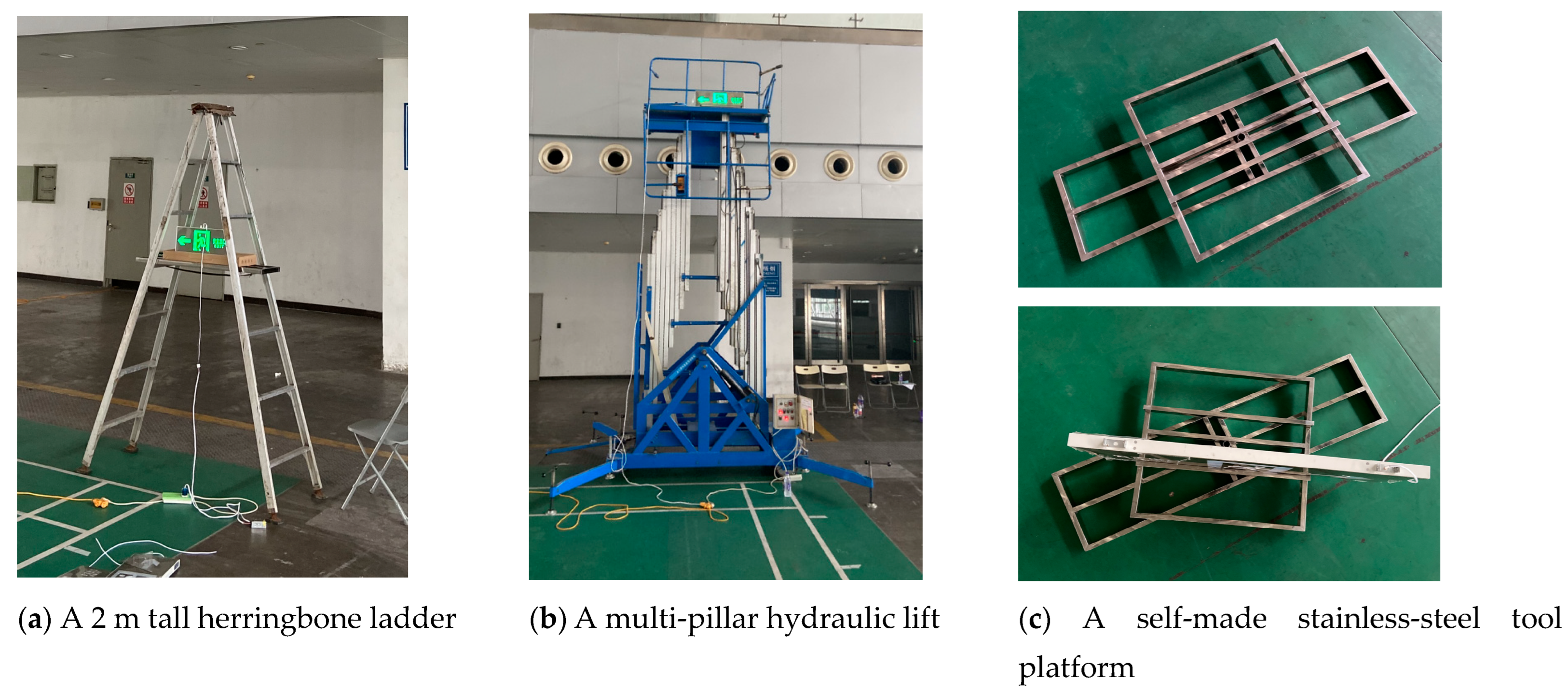
A 2 m tall herringbone ladder and a multi-pillar hydraulic lift (with a lifting height of 2 to 18 m) manufactured by the Chongqing Minghua Machinery Co., Ltd., Chongqing, China, were used for the height adjustments in the experiment. The evacuation signs were placed on a self-made stainless-steel tool platform that could perform a 360° free rotation to meet the requirement of the different horizontal offset angles in the experiment (Figure 4).
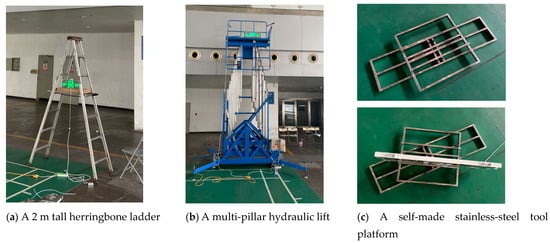
Figure 4.
Experimental materials.
2.3. Experimental Process
There was no indoor direct sunlight incident on the experimental site. Prior to the start of the experiment, the lighting conditions of the experimental site were established, and the experimental equipment was commissioned according to the experimental preparation requirements in Section 2.2. The overall experimental procedure is described as follows.
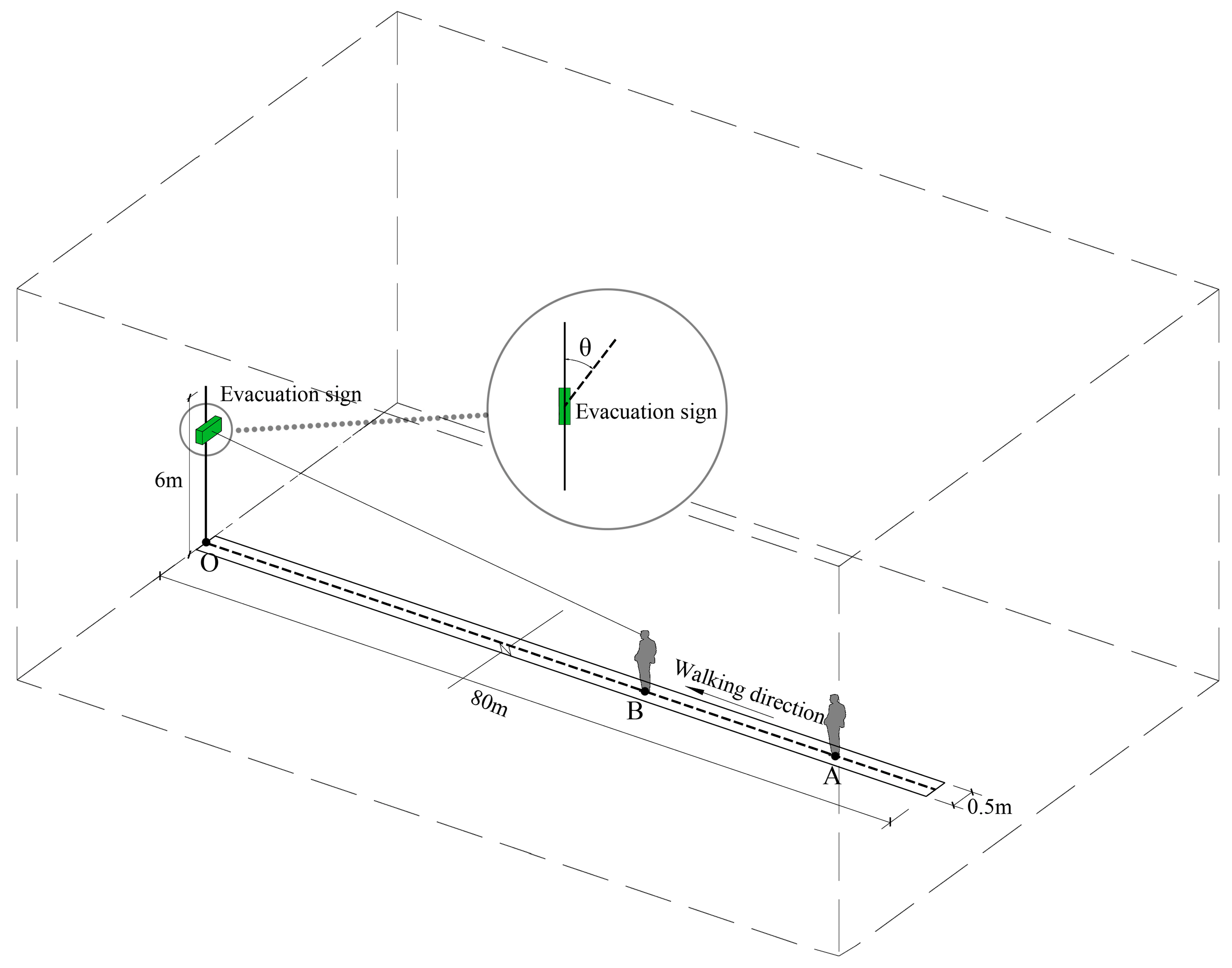
(1) Prior to the start of the experiment, the evacuation sign was rotated to adjust the offset angle, θ, between the evacuation sign and the participant. It was then raised to a height required by the experiment.
(2) The participants were required to perform in a natural and comfortable state, i.e., without extreme rotation of the eyes or the body. After the experiment began, the participants were asked to walk along the centerline of the delineated passageway from point A at a normal walking speed, keeping their heads level to march along a straight line to the other side of the passageway where the sign was located and continuously approaching the sign. Since graphic signs are easier to recognize and understand than textual signs [42], participants stopped when they could clearly and unambiguously recognize the direction indicated by the arrow in the evacuation sign, and their stopping point was marked as point B. The horizontal linear distance between point B and evacuation sign O was measured and recorded as the maximum viewing distance of the sign (Figure 5). The experiment was repeated multiple times. In each experiment, the direction of the arrow was randomly adjusted to avoid the inertia of the participants in recognizing the direction graphically indicated by the evacuation sign.
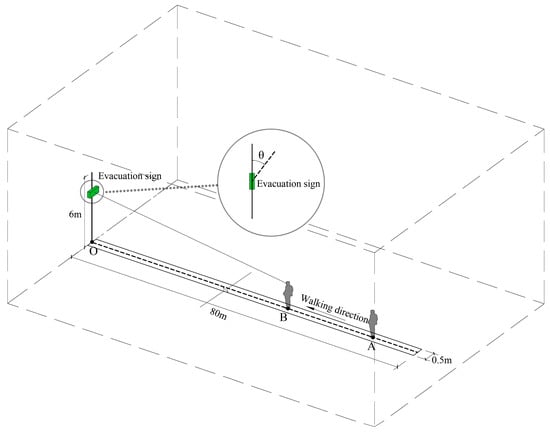
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the experimental method.
(3) After all the experimenters completed the operation in steps (1) and (2). Then, the experiment was changed to a new scene, and the participants repeated the previous operation (Figure 6). During this process, each participant was required to relax for at least 3 min to reduce the effect of visual fatigue. Each participant needs to participate in all of the 72 experimental scenes (2 evacuation signs × 6 offside angles × 6 heights).

Figure 6.
Experimental process.
(4) After the entire experiment was completed, the participants were asked to fill out a post-test questionnaire to obtain their feelings of the authenticity and effectiveness of the heights and angles of the evacuation signs.
3. Results
3.1. Visual Range of the Evacuation Signs at Different Heights
The maximum viewing distance of evacuation signs A and B under the different heights and horizontal offset angles was obtained from 38 participants in the experiment. Based on experimental data on evacuation signs A and B, this research compares the differences in the viewing distance of evacuation signs between males and females and conducts statistical tests (independent sample t-test) on each group of data. The results showed that there was no significant difference (p > 0.05) between males and females in the visual distance of identifying evacuation signs.
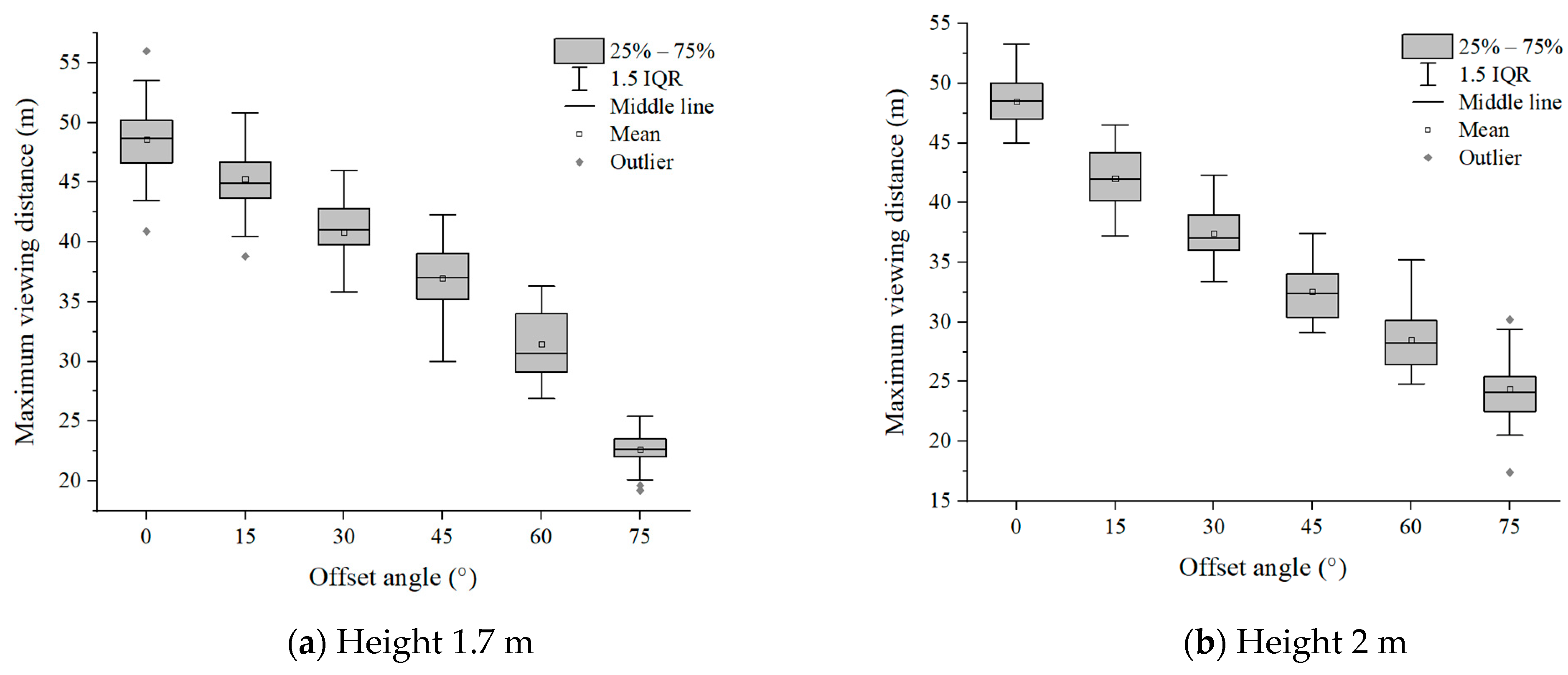
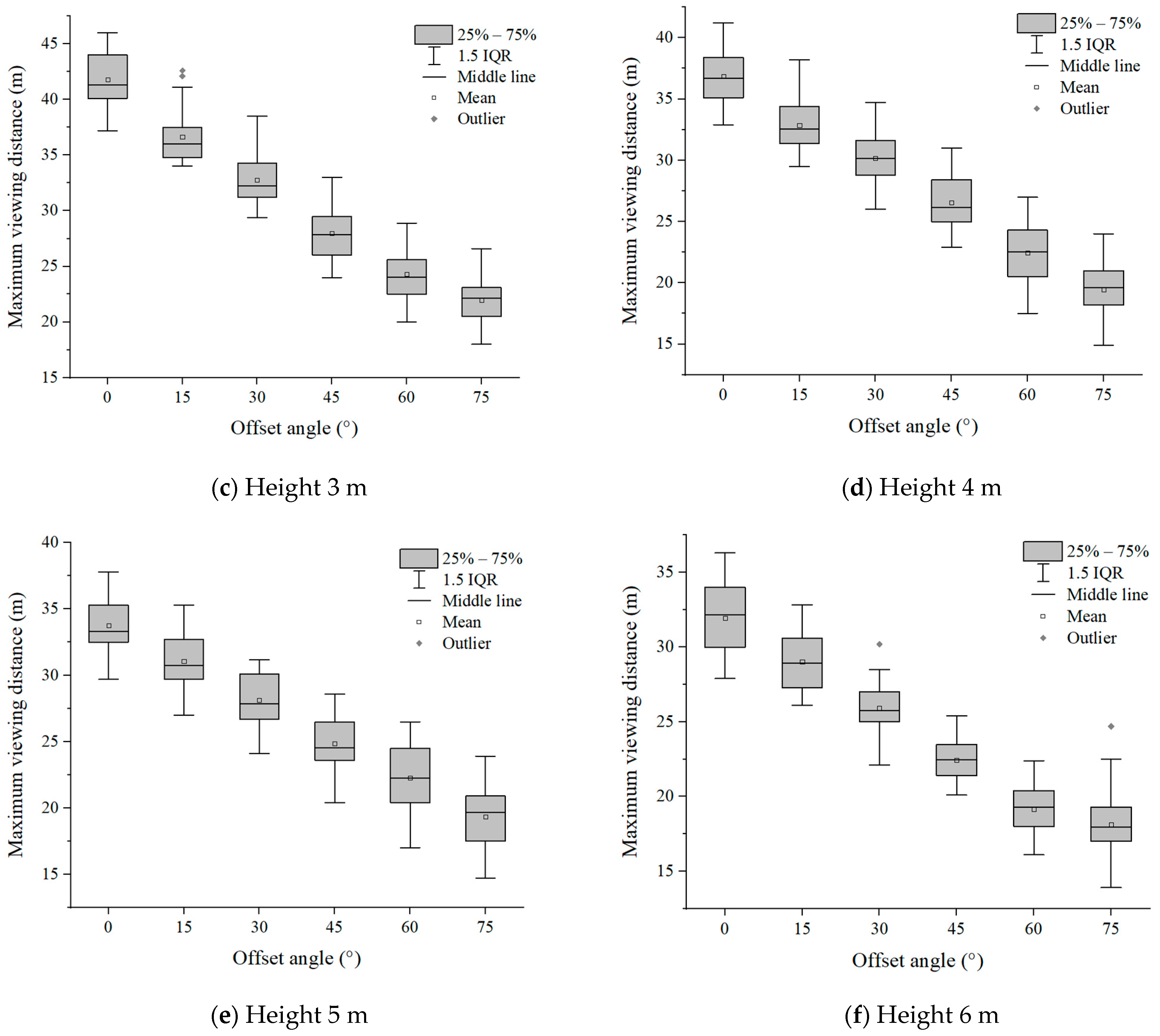
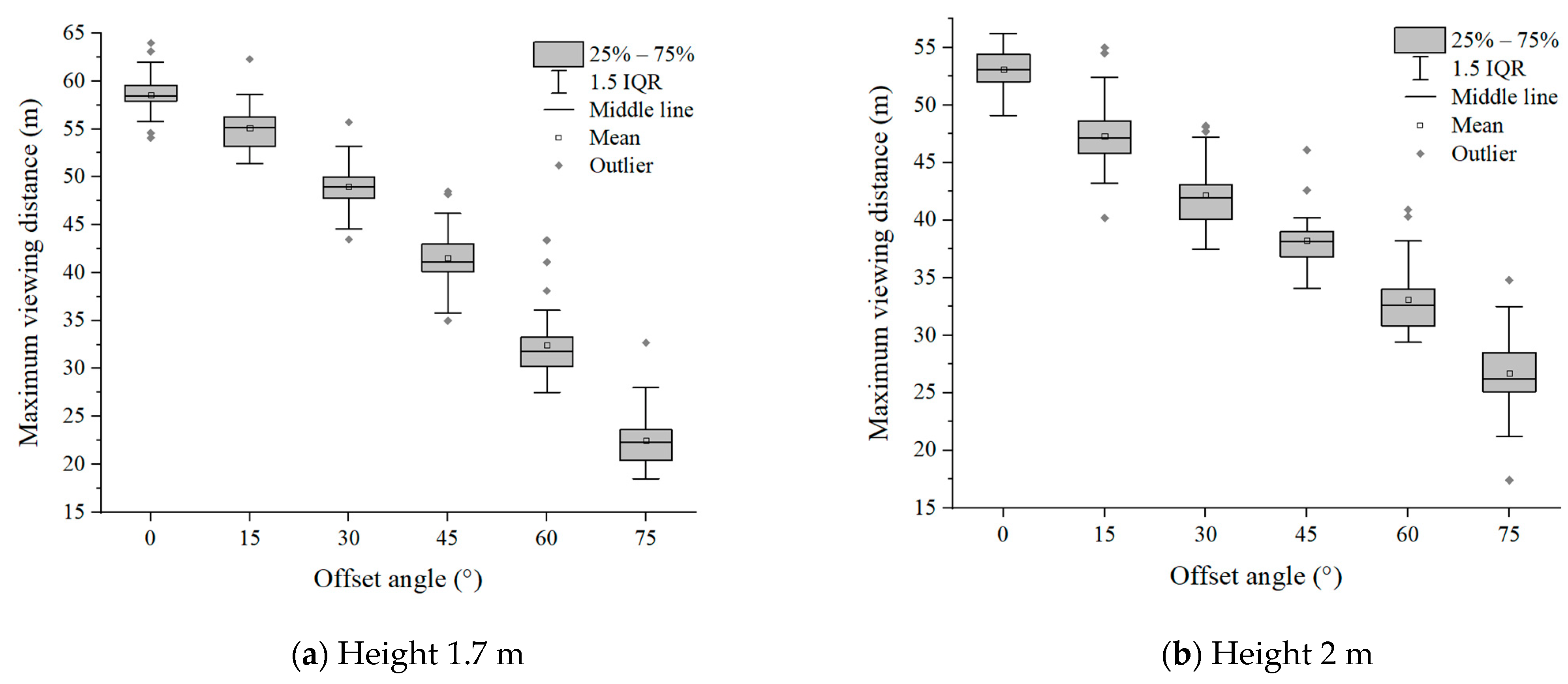
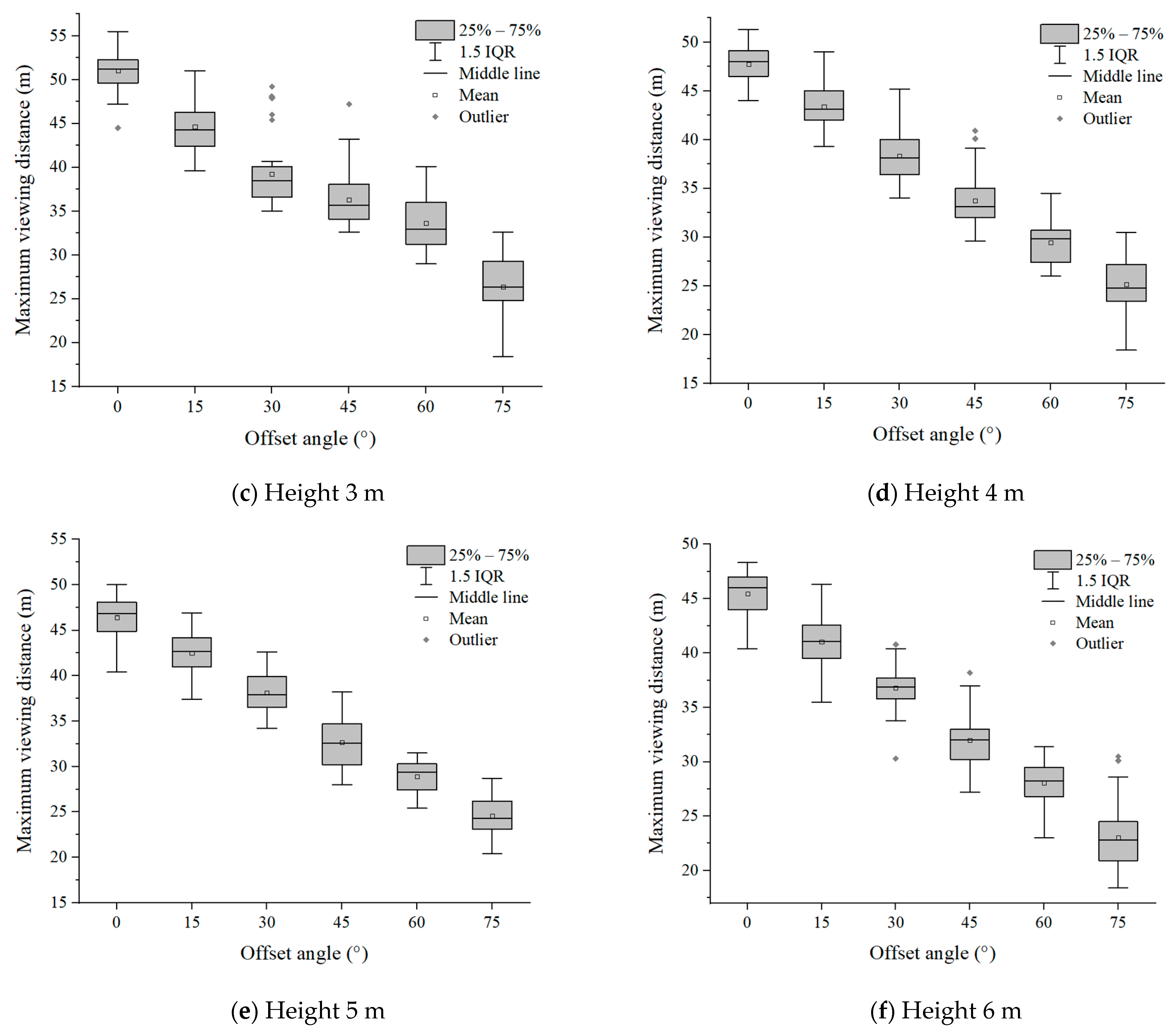
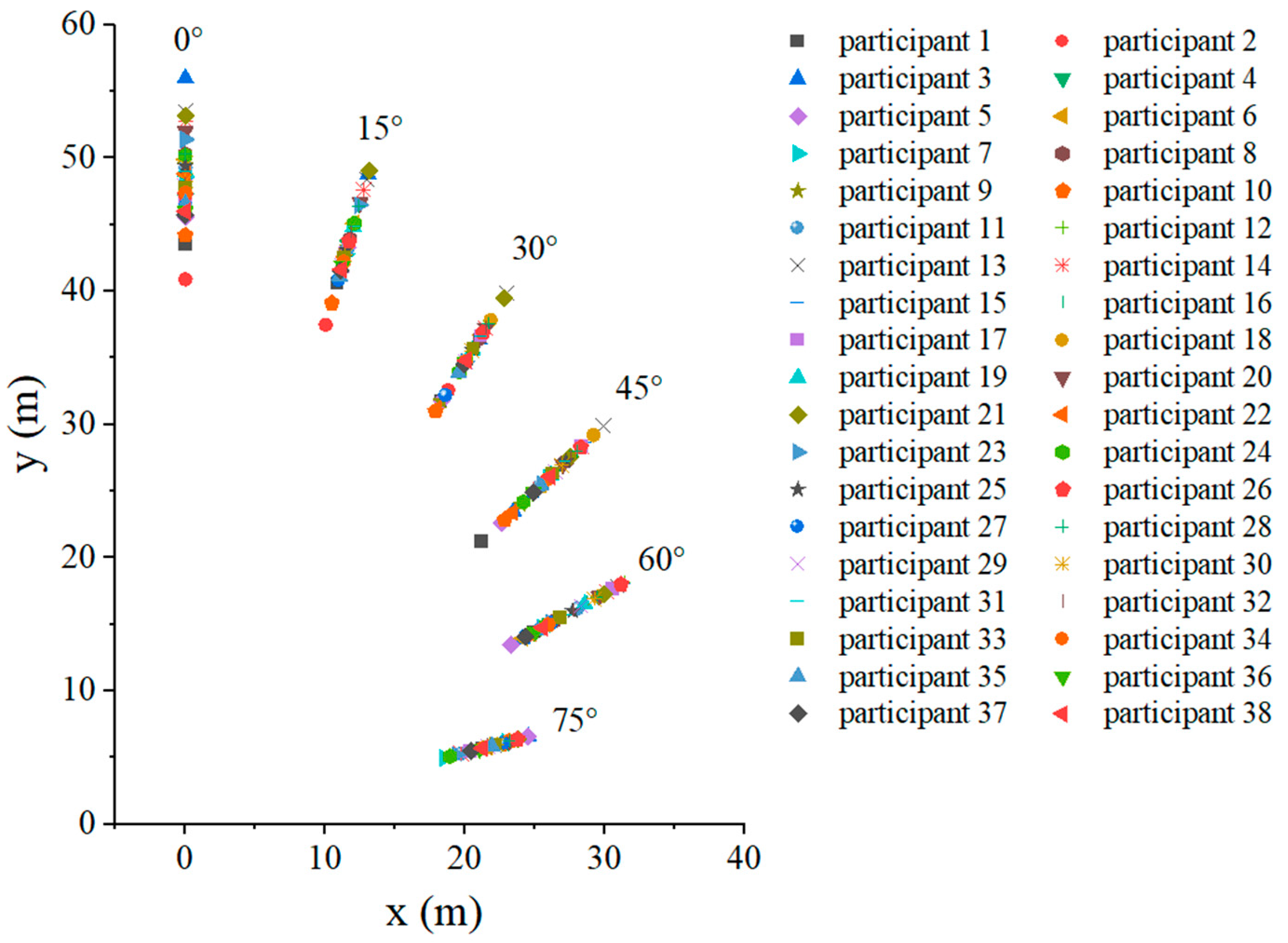
Six groups of experimental data with evacuation signs A and B between 1.7 m–6 m were analyzed, respectively. It can be seen from Figure 7 and Figure 8 that in the range of the offset angle from 0–75°, as the offset angle became larger, the viewing distance became shorter. This is because the offset angle of evacuation signs gradually becomes larger, and finally it is parallel to the line of sight of participants, which makes it difficult for participants to recognize the evacuation signs. This result was consistent with the findings of Xie et al. [32]. In addition, the same sign was at the same offset angle, and its maximum viewing distance was different when the setting height was different (Table 2 and Table 3). This is a new discovery, and the relationship between the setting height of evacuation signs and the viewing distance had not been paid attention to in the previous research.
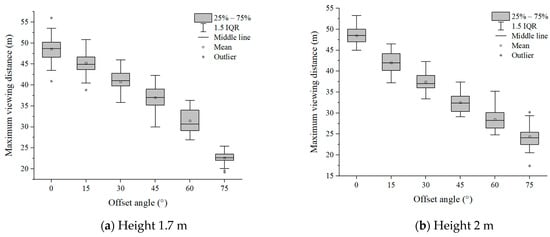
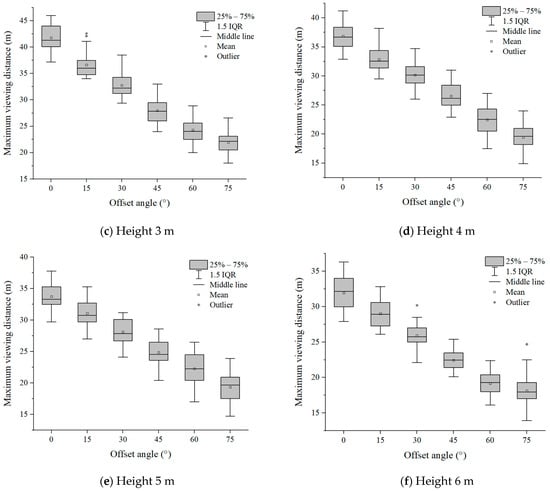
Figure 7.
The experimental results of evacuation sign A.
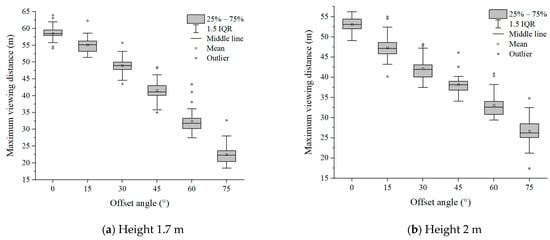
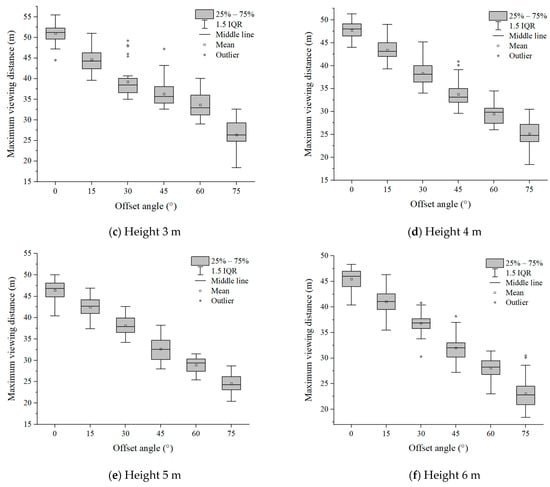
Figure 8.
The experimental results of evacuation sign B.

Table 2.
Mean value of participant data of viewing distance of evacuation sign A.

Table 3.
Mean value of participant data of viewing distance of evacuation sign B.
On this basis, the experimental test results are transformed into rectangular coordinate system and expressed according to the equation:
where the θ is the offset angle; the ρ is the maximum viewing distance; x and y represent data in rectangular coordinate system, respectively.
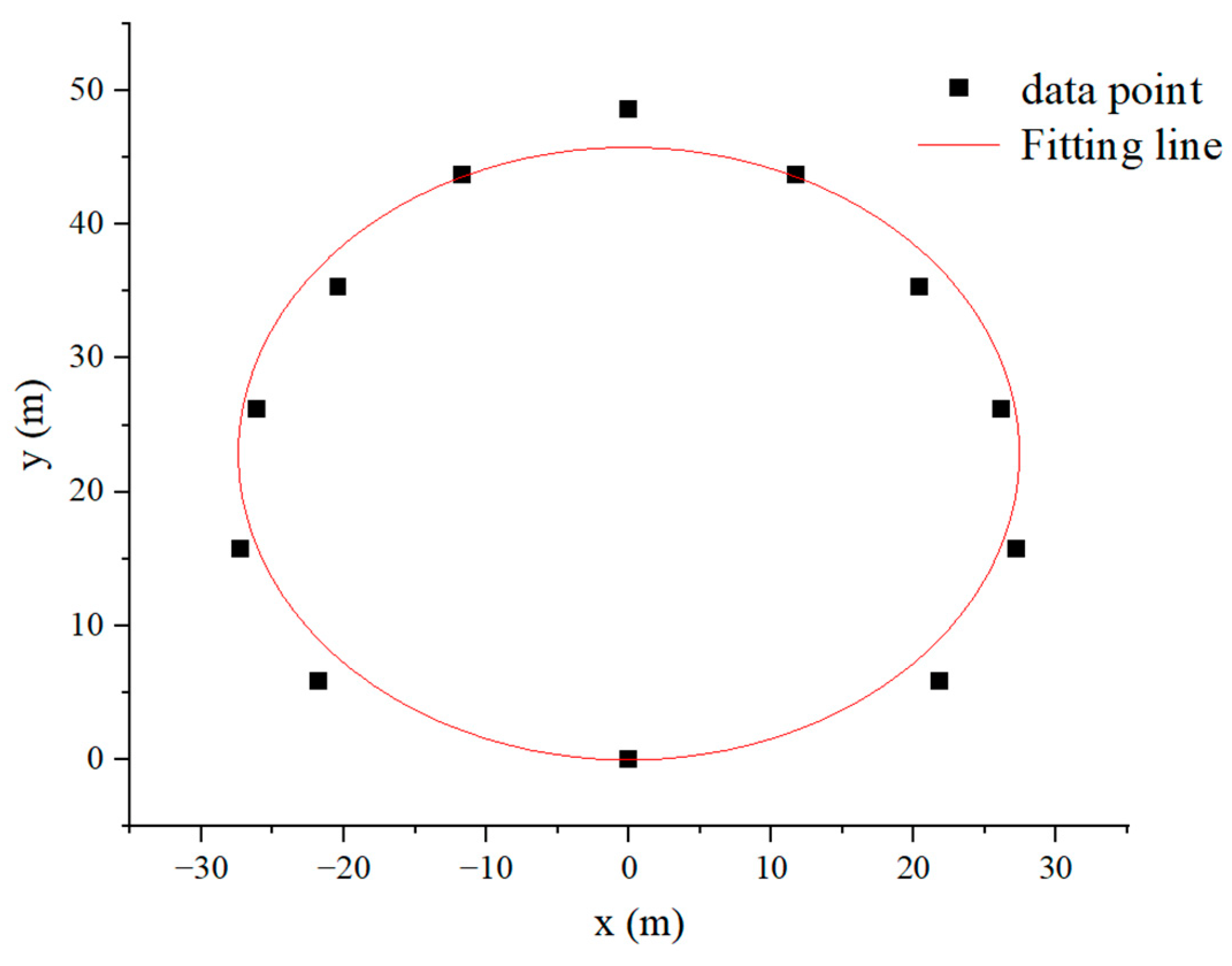
By using the data processing of the evacuation sign A at a height of 1.7 m as an example, obtain the visual range of the evacuation signs (Figure 9). When the offset angle was in the range of 0–90°, and the visual range of the evacuation signs was approximately half an ellipse. Furthermore, the average and standard deviation of the maximum viewing distances of the evacuation sign A at a height of 1.7 m under six offset angles was obtained (Table 4).
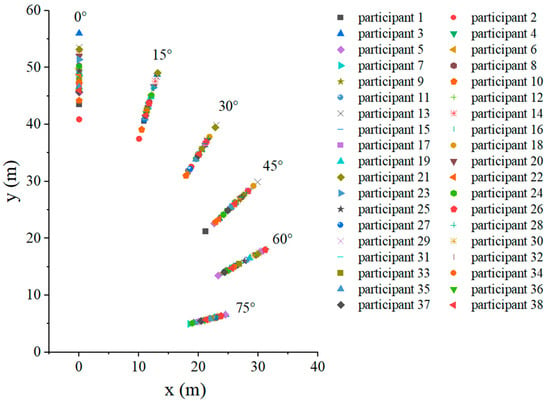
Figure 9.
Visual range data of 38 participants of evacuation sign A at a height of 1.7 m.

Table 4.
The average of viewing distances of evacuation sign A at a height of 1.7 m.
Considering that the viewing distance of the participants in the experiment was independent of the direction in which they observed the evacuation sign, the viewing distance at an offset angle of 90–180° was the same as that at an offset angle of 0–90°. In addition, the coordinates of the evacuation sign were set to (0, 0) due to the fixed location of the evacuation sign in the experiment (Figure 10). On this basis, a nonlinear implicit function fitting regression was performed using Origin pro 2018C SR1 based on the ellipse equation:
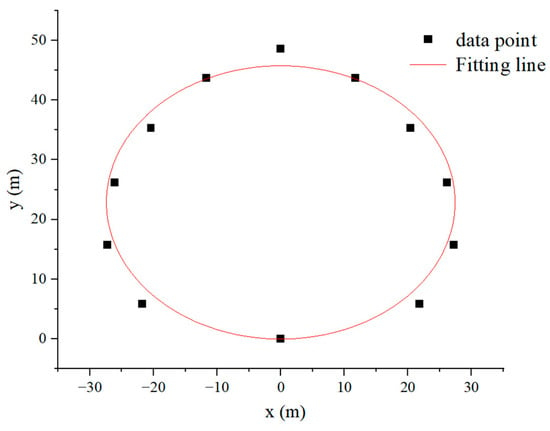
Figure 10.
Fitted curve of the visual range of evacuation sign A at a height of 1.7 m.
The fitting function equation is given as follows:
Thus, the visual range of evacuation sign A at a height of 1.7 m was obtained (Figure 8):
where the goodness-of-fit test index of the curve fitting was R2 = 0.99719; and the semi-major and minor axes a and b were 27.42 and 22.86, respectively.
Using the same method, the visual ranges of evacuation signs A (Table 5) and B (Table 6) at different heights (1.7–6 m) were obtained.

Table 5.
Data of fitting curve of visual range of evacuation sign A at different heights.

Table 6.
Data of fitting curve of visual range of evacuation sign B at different heights.
3.2. Mathematical Relation between the Height and Visual Range of the Evacuation Signs
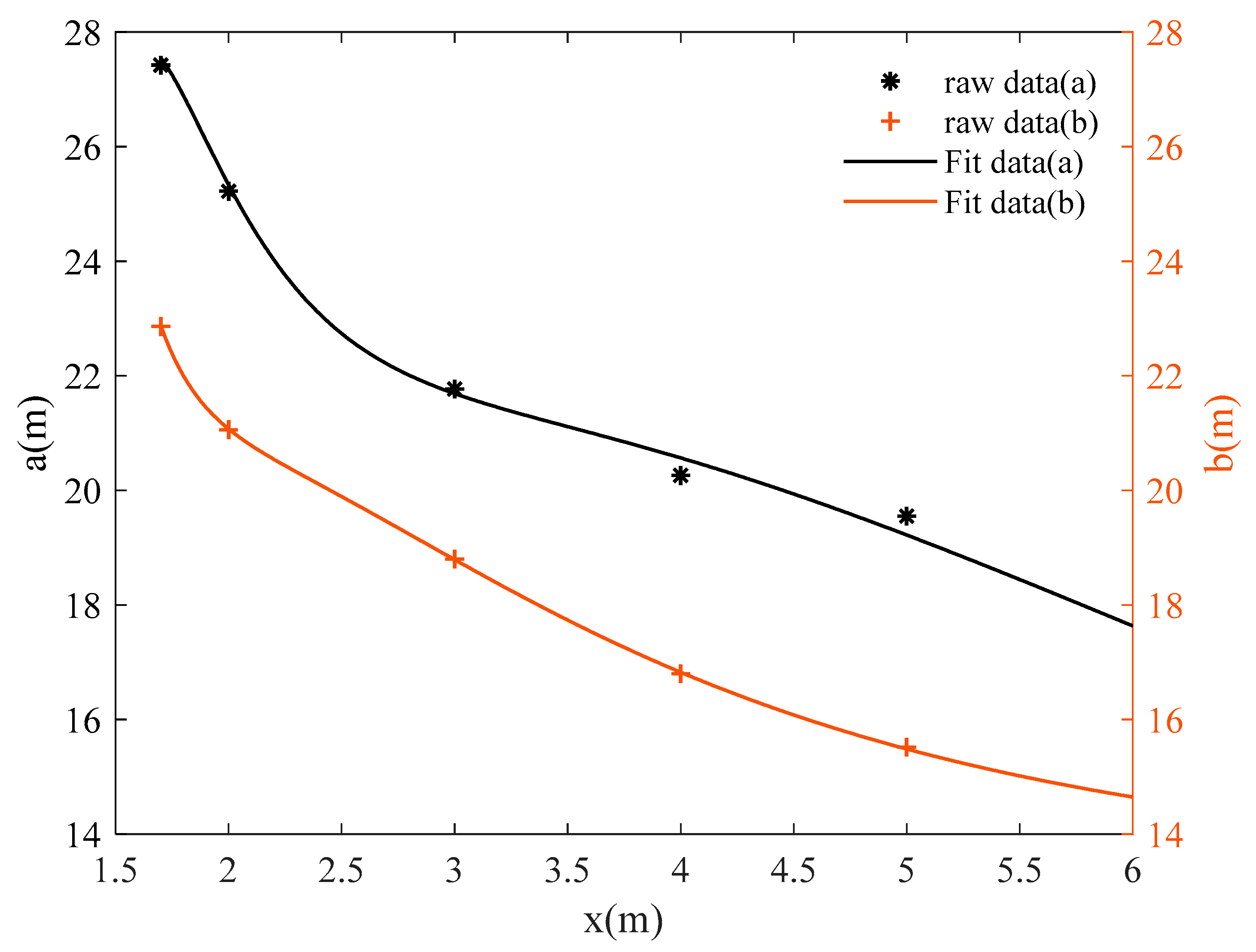
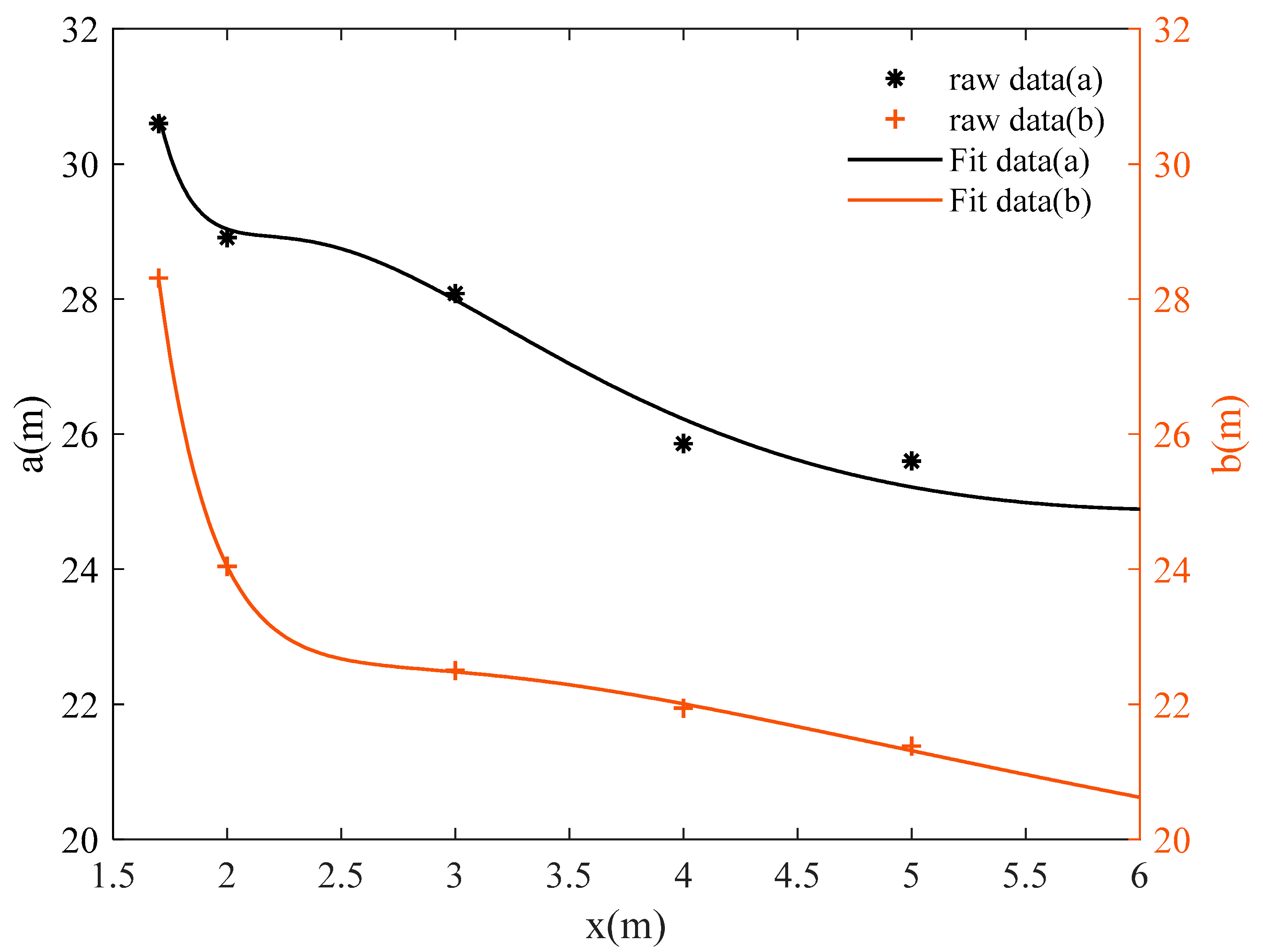
According to Equation (1), the factors affecting the visual range of the evacuation signs are the semi-major and minor axes, a and b, of the ellipse. Figure 11 and Figure 12 describe the relation between the visual range axes a and b and the height z of evacuation signs A and B, respectively. Through multiple linear regression analysis, considering the monotonic decrease of a and b with respect to z and the steep degree of change. According to Occam’s Razor, Ockham’s Razor, the model should be simplified as much as possible. Therefore, this research set the fitting model as a polynomial model of about 1/z, which is essentially a simple linear model.
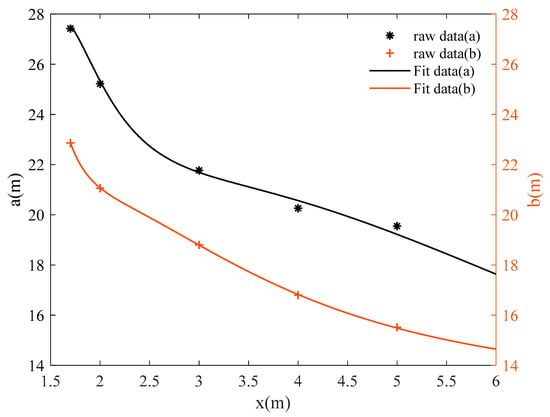
Figure 11.
Curve fitting of the semi-major and minor axes, a and b, of the visual range of evacuation sign A with height z.
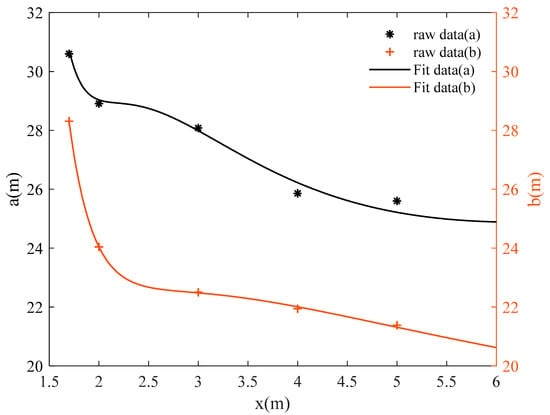
Figure 12.
Curve fitting of the semi-major and minor axes, a and b, of the visual range of evacuation sign B with height z.
The relation between the height and visual range of evacuation sign A is expressed by Equation (5).
where the R2 = 0.9834 for a(z) and R2 = 0.9998 for b(z).
The relation between the height and visual range of evacuation sign B is expressed by Equation (6)
where the R2 = 0.9386 for a(z) and R2 = 0.9987 for b(z).
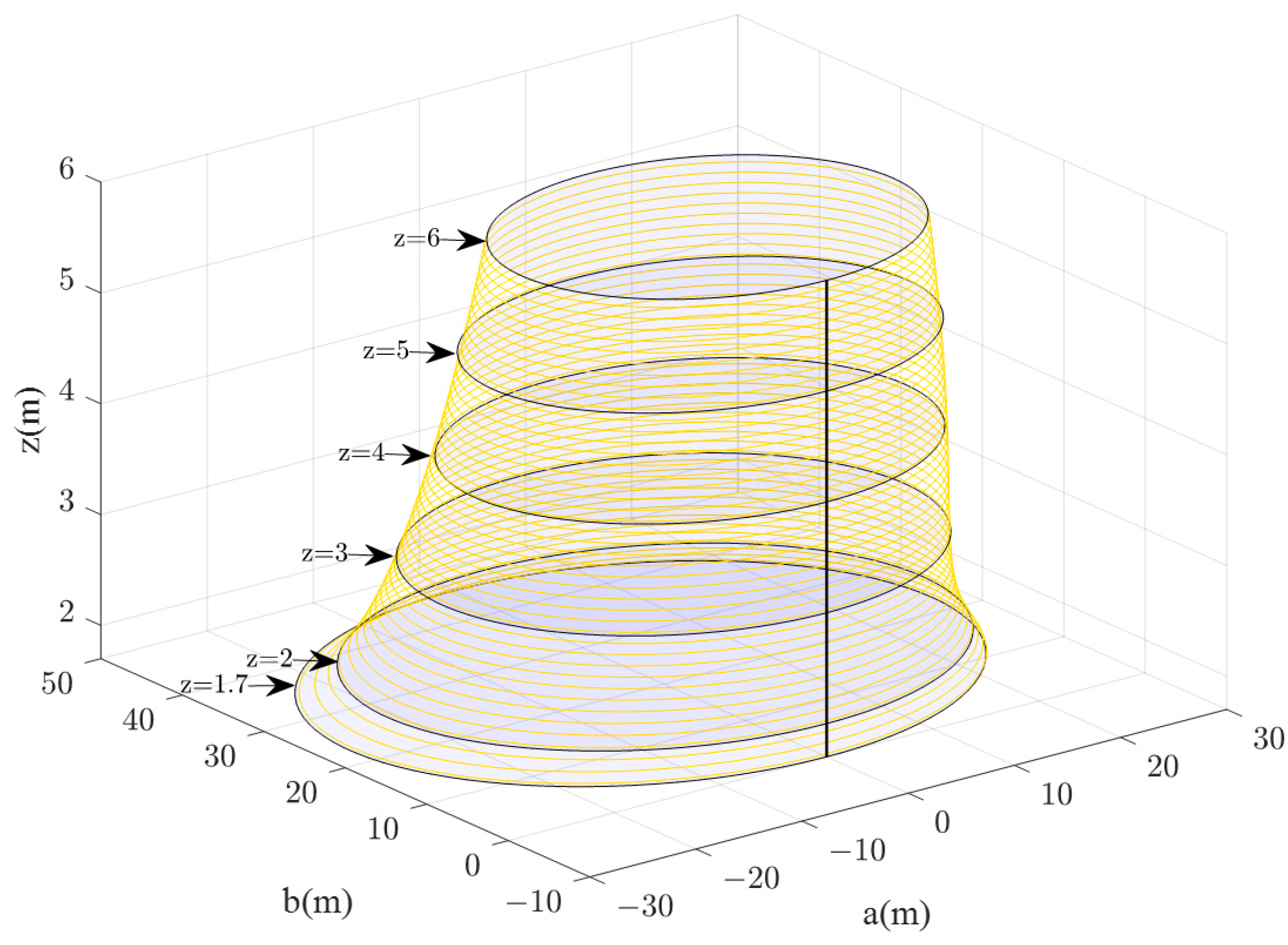
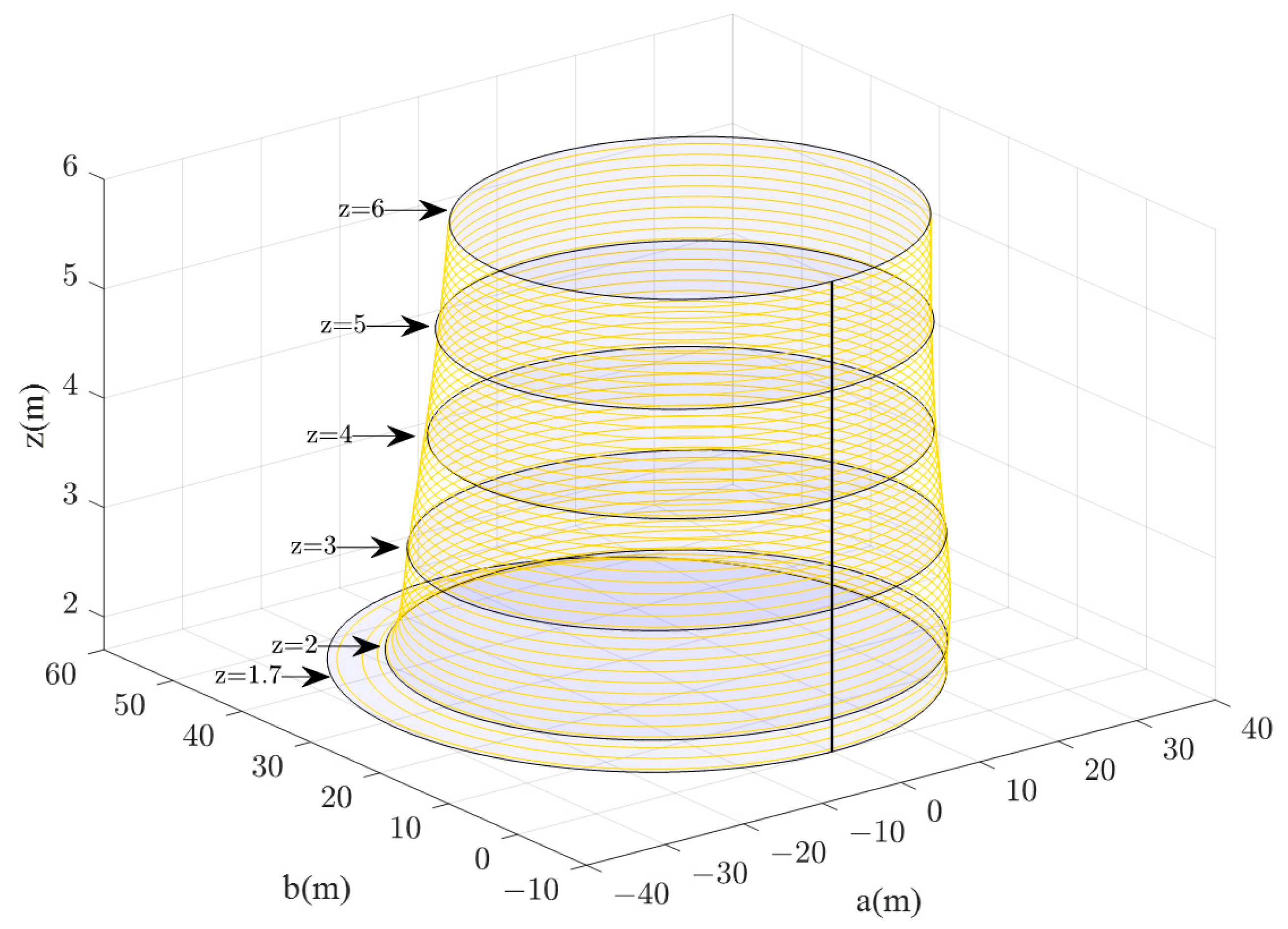
On this basis, according to Equations (5) and (6), the 3D diagrams of the visual range of evacuation signs A and B with heights of 1.7–6 m were obtained (Figure 13 and Figure 14). The researcher can clearly get the area of the visual range of evacuation signs A and B with different heights of 1.7–6 m and can also understand the changes between the visual range areas of evacuation signs and the height setting.
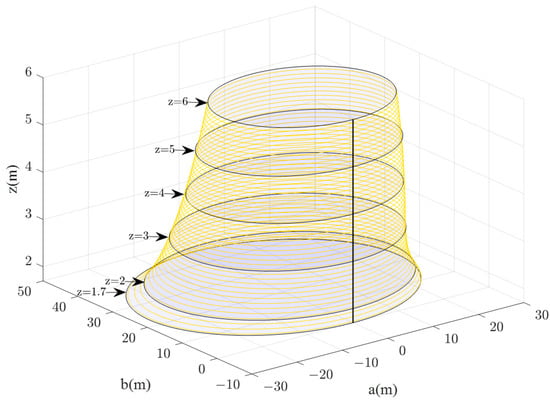
Figure 13.
3D diagram of the visual range of evacuation sign A with a height of 1.7–6 m.
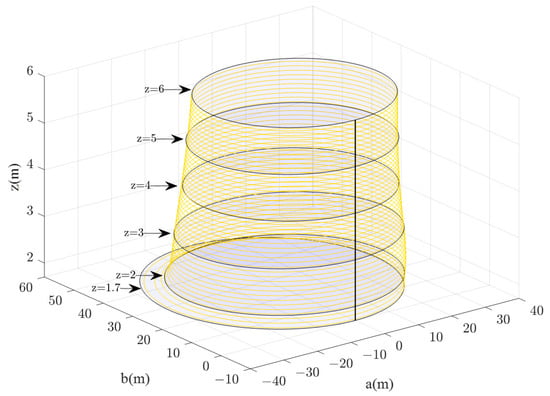
Figure 14.
3D diagram of the visual range of evacuation sign B with a height of 1.7–6 m.
3.3. Questionnaire Analysis
In order to better understand the situation of people’s recognition of evacuation signs, a questionnaire survey was conducted among 38 participants. The questionnaire mainly included: the influence of the vertical height change of evacuation signs on the distance of personnel identification signs and the appropriate height of evacuation signs.
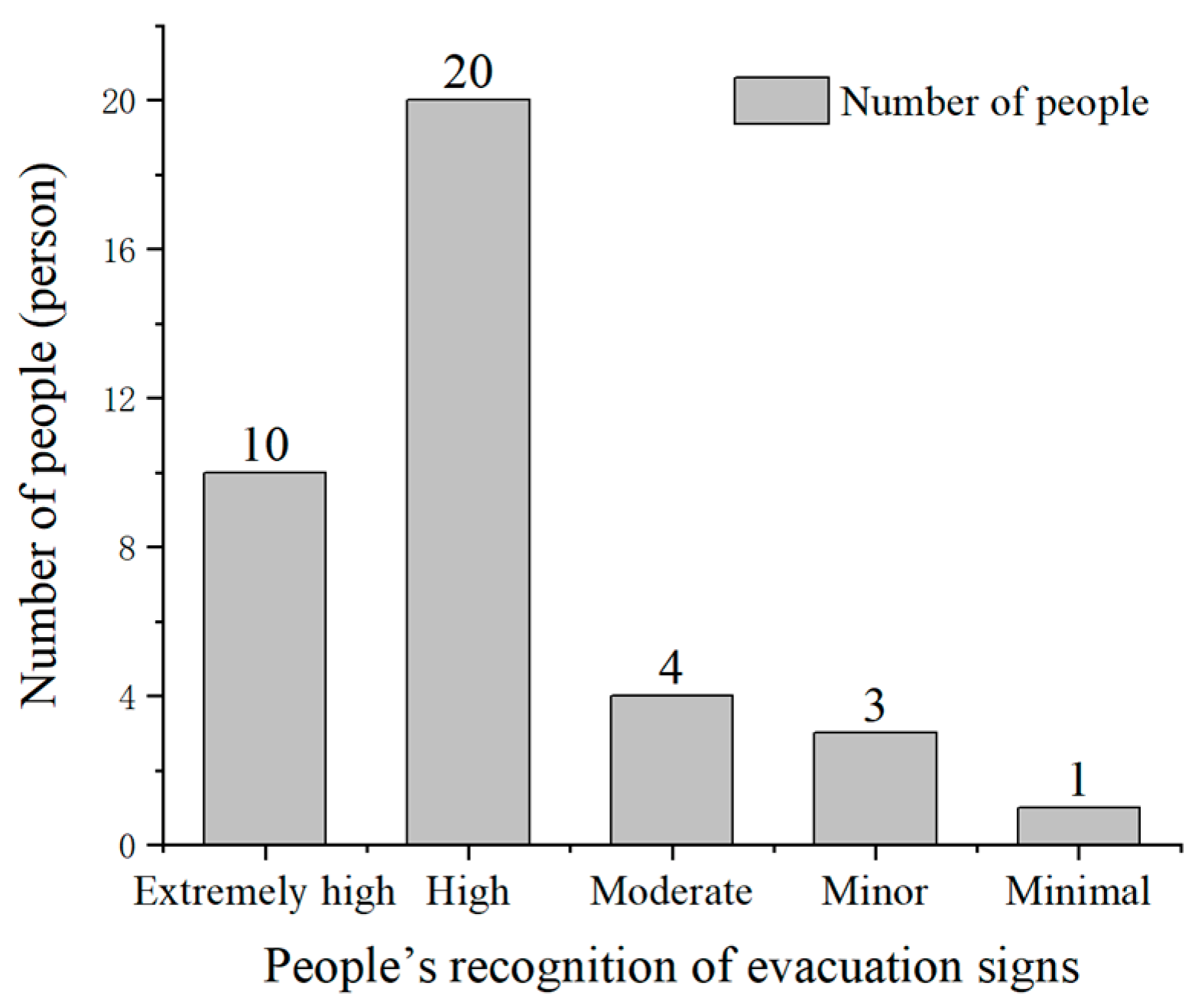
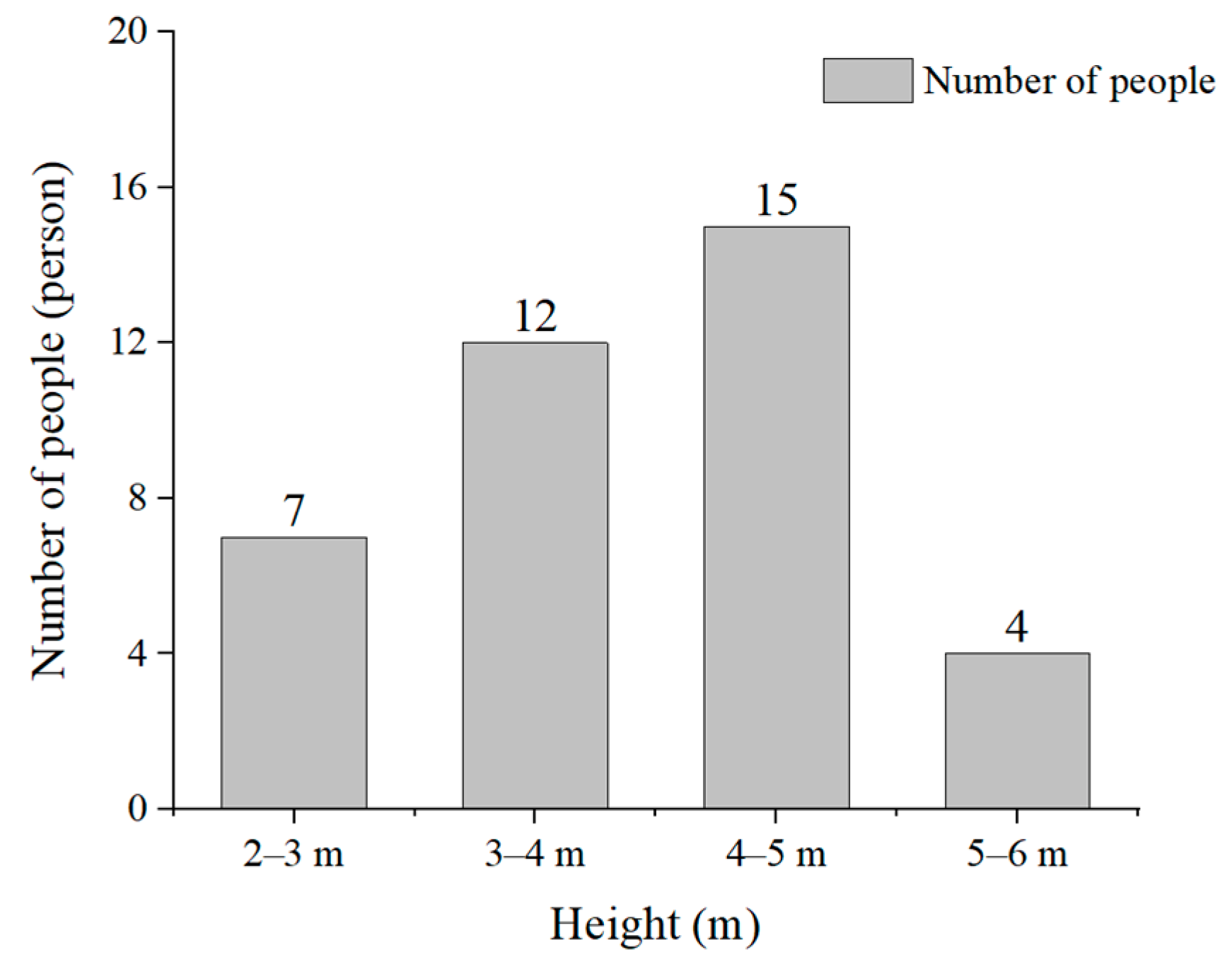
Regarding the factors that did affect sign recognition, the influence of the height of the evacuation signs on sign recognition distance was considered extremely high, high, moderate, minor, and minimal by 10 (26.32%), 20 (52.63%), 4 (10.53%), 3 (7.89%), and 1 (2.63%) participants, respectively (Figure 15). Therefore, greater than 75% of the participants noted that the height of evacuation signs had an impact on the visual range of the participants’ recognition. In addition, the participants’ selection of evacuation sign height tended to be between 3 and 5 m, accounting for 70% of the total number of participants, which agreed more with the visual habits of the participants (Figure 16).
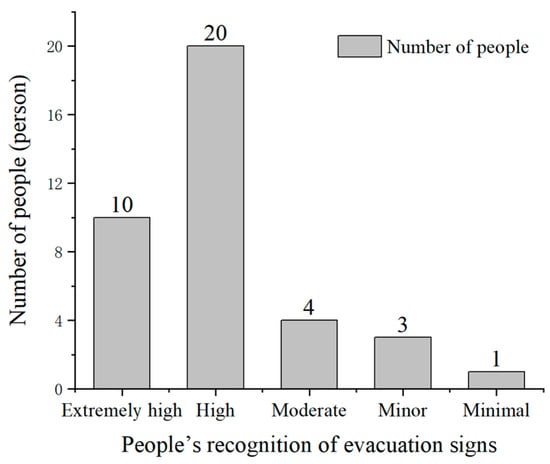
Figure 15.
Impact of the evacuation sign height on people’s recognition distance of evacuation signs.
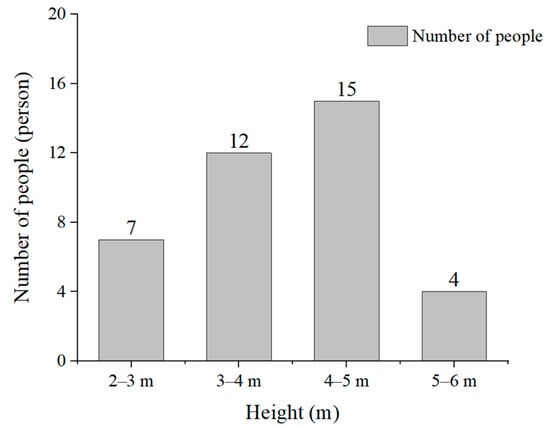
Figure 16.
Selection of the appropriate height of evacuation signs.
Overall, setting the height of signs too high or too low was not conducive to personnel identification. Therefore, it was necessary to design the layout of evacuation signs based on fully considering the relevant data of the visual range of evacuation signs. At the same time, if there were no special requirements, it was suggested that the height of the sign should be set within the range of 3–5 m.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of the Change in Evacuation Sign Height on the Visual Range
The visual range of evacuation signs was elliptical in the two-dimensional plane at different heights, but the visual ranges of evacuation signs A and B were different. The visual range of evacuation sign A was less than that of evacuation sign B under the same height and offset angle of the evacuation signs. This indicated that the size of the evacuation sign itself influenced the visual range of the sign. However, there was a consistent overall variation trend of the visual range with the height of evacuation signs.
As the height of evacuation signs increased, the visual ranges of evacuation signs A and B decreased nonlinearly, and the shorter the viewing distances, the smaller the visual range. For example, the visual range of evacuation sign A was 1058.76 m2 at a height of 4 m and 794.57 m2 at a height of 6 m, showing a significant reduction of 25.9% in the area of the visual range as the height increased from 4 m to 6 m. As can be seen from Figure 11 and Figure 12, there is a significant change in the slope of the curve between the sign height of 1.7 m and 3 m, while the change in slope slows down and tends to level off as the sign height increased from 3 m to 6 m. Based on the analysis of the results, the viewing distance was significantly reduced as the line of sight changed from horizontal to upward.
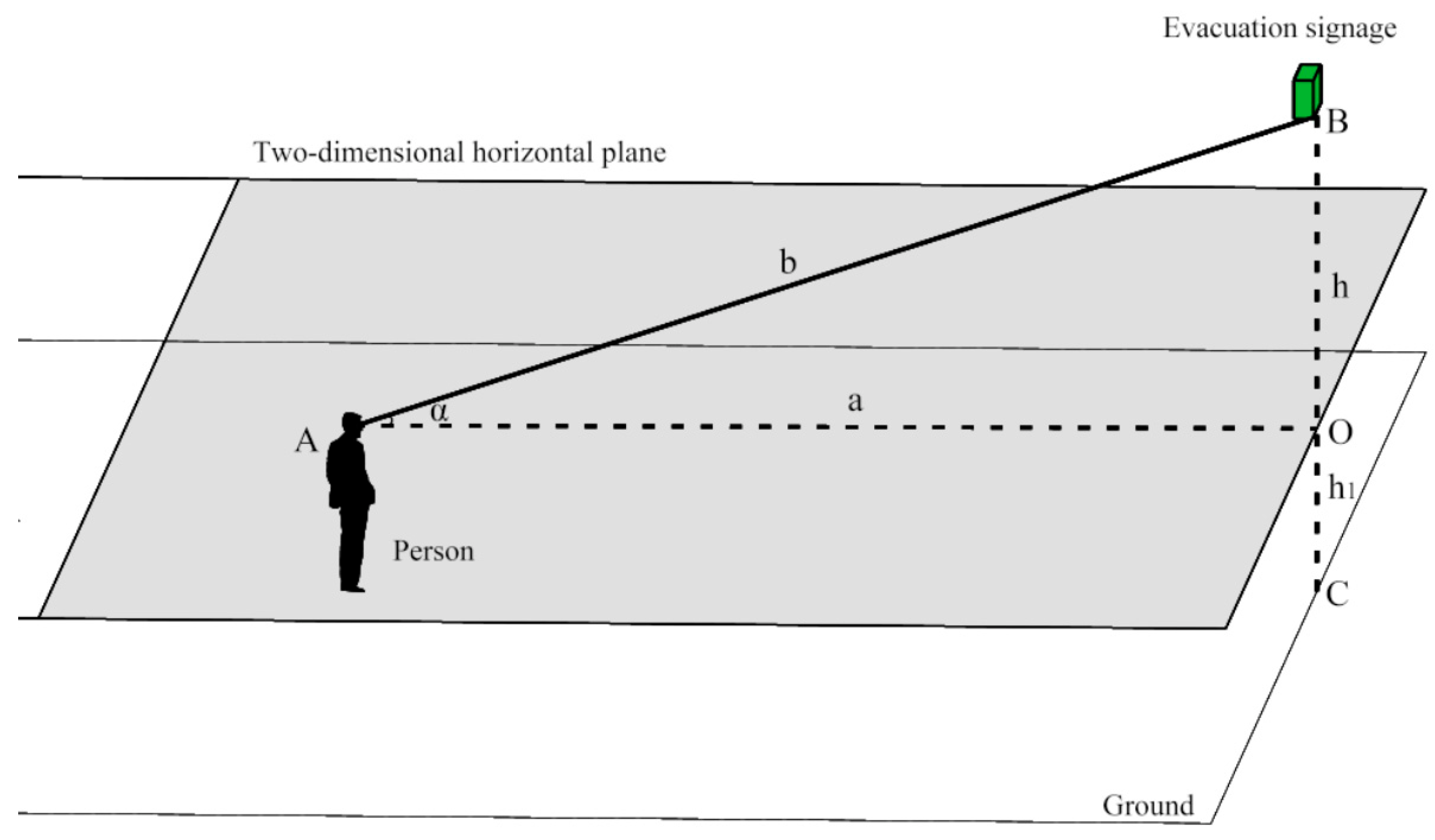
The visual ranges of the evacuation signs were related in the 3D space. The relation between the height change and visual range of the evacuation sign is discussed. The 3D space was simplified and converted to a two-dimensional horizontal plane at the height of the human eye viewpoint, regardless of the actual size of the evacuation sign. In Figure 17, the coordinate points, A and B, correspond to the human eye and the evacuation sign,
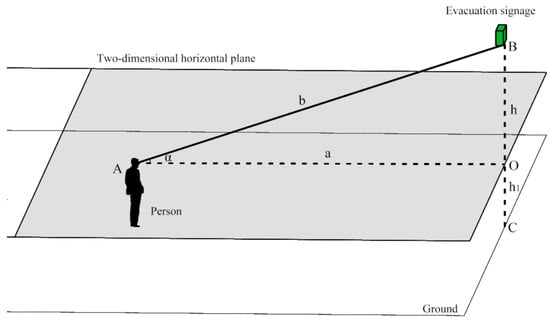
Figure 17.
Schematic diagram of the relation between a person and an evacuation sign.
It can be determined that the maximum viewing distance, a, of the evacuation sign is related to the height, h, and the linear distance, b, between the human eye and the sign. Note that b between human eyes and evacuation signs is a fixed value.
When the eye height of a person is the same as the height of the evacuation sign (i.e., h = 0), b = a. The angle, α, between the human eye and the sign increases with an increase in h, that is, when the height, h, of the sign increases, the viewing distance, a, between a person, and the sign gradually decreases, thereby reducing its visual range. However, in actual application and research, the maximum viewing distance, a, between a person and an evacuation sign is set to a fixed value, which is not in agreement with the actual situation.
In the existing Code for Fire Protection Design of Buildings (GB 50016-2014) of China, the spacing of evacuation signs at any height is uniformly set to 30 m, regardless of the influence of the height and size of the evacuation signs. Previous studies have ignored the variation in viewing distance caused by different heights of evacuation signs [15,24]. The setting distance of evacuation signs is fixed, such as 30 m. By using evacuation sign A as an example, a comparison of Equation (5) with the current code demonstrated that the visual range of the evacuation sign will be reduced if its height is set higher. When the sign A height is set to 6 m, the spacing between signs would be less than 30 m, which would cause a blind area of the visual range to appear that would affect the evacuation of people. Therefore, more detailed consideration should be added into the current code standard regarding the specific height of evacuation signs to ensure that the spacing between signs meets the requirement. In large space buildings, it is difficult for an evacuation sign to play a guiding role if the size is too small. The size of evacuation signs is closely related to their individual prices. The larger the size of the sign, the higher its cost. If the economic situation is not considered, the larger the better. But, in the case of limited economic conditions, the choice of evacuation sign size must be considered in combination with the length and width of the building space of the specific actual design project. The reasonable selection of sign size would help evacuees see the sign and read the information clearly within an appropriate viewing distance.
According to the questionnaire analysis in Section 3.3, the optimal setting height of evacuation signs is 3–5 m. This conclusion will change the requirements of the Chinese Code (GB 50016-2014). The height of evacuation signs is closely related to the height of doors, which is 2.2–3.5 m, so the corresponding standards and regulations need to be revised in the future. When considering the setting height of evacuation signs in large space buildings, this research can make full use of the characteristics of high ceilings of buildings and do not have to stick to the specified value of setting height in the Code (GB 50016-2014). According to the experimental results and people’s visual habits, the optimal height of evacuation signs is determined for large space buildings with different scene types.
For large space buildings such as airport terminals, and railway stations, when there are no obstacles or low obstacles (rest seats, service desks, etc., <1.7 m) in the building space, people’s sight should not be blocked by obstacles. According to the mathematical model of evacuation sign setting height and visual range are set, and it is suggested that the optimal height of evacuation signs should be set at 3–4 m so that the visual range area of a single evacuation sign can be increased and more people can recognize evacuation signs. However, for large space buildings such as exhibition halls, there are high obstacles (such as booths, display cabinets, etc., >1.7 m). Based on the experimental data and mathematical model obtained in this study, this research needs to use the existing research [3,43] to carry out specific intelligent calculations to get the specific optimal height value. When there is no corresponding intelligent calculation, and the obstacle is high (>1.7 m), it is recommended that the setting height of the evacuation sign is 5 m, which can minimize the possibility of the evacuation sign being blocked by obstacles.
In general, these findings provide a new understanding of the relation between the height and the visual range of an evacuation sign. The height of the sign will become a new indicator to measure its visual range, and the relation between the two can be applied to the safety design of the evacuation sign layout.
4.2. Smart Design of a Height Adjustment Device for Evacuation Signs
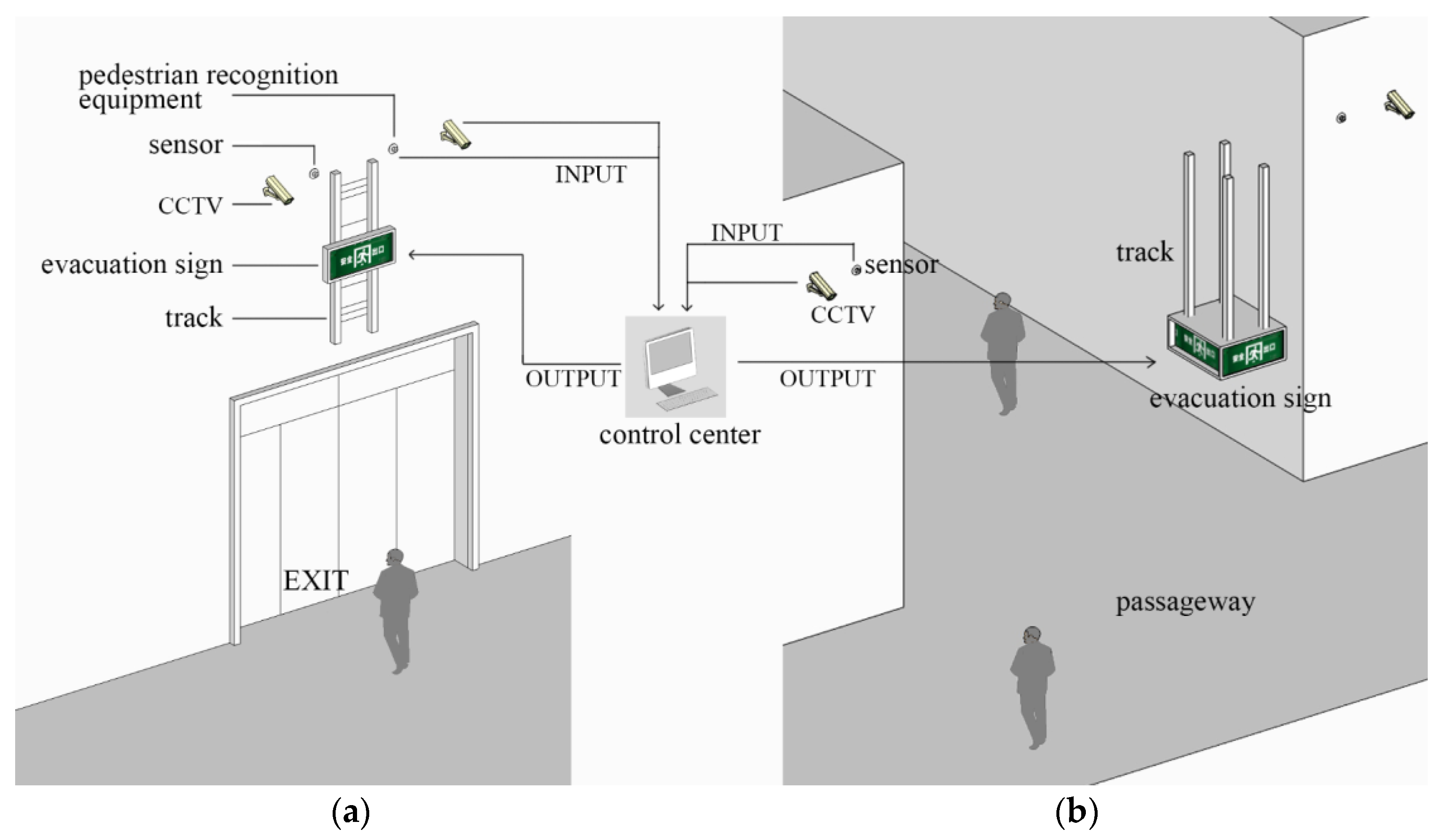
According to the above discussion and especially based on the mathematical quantitative relation between the height and visual range of an evacuation sign, the visual range of evacuation signs with different sizes and at different heights can be calculated. This research now proposes a smart design of an evacuation sign height adjustment device applicable to different scenarios of large space buildings. The height adjustment device for evacuation signs as a display terminal for evacuation information has two salient advantages. First, the dynamic adjustment of the height of evacuation signs changes the situation, whereas the height of the traditional signage system is fixed. This effectively increases the probability of people recognizing evacuation signs and is a supplement to an existing evacuation signage system. Second, the device is simple and can be applied to different large-space building scenarios without changing the interior layout of the building and can be added to the required location at any time.
The application scenarios of the height adjustment device for evacuation signs are mainly divided into two types. For large space buildings that are newly built or under construction, smart evacuation sign devices should be used in architectural design and construction instead of the most common fixed evacuation signs at present, which can better adapt to the unreasonable space layout that may occur during the use of building space. For large space buildings that have been built, smart evacuation sign device is added in some important space nodes, such as major safety exits, intersections, and long passages, which can reduce the impact on the building structure and layout during the space transformation of large space buildings, increase the attention of personnel to evacuation signs, and then improve evacuation efficiency. The height adjustment device for evacuation signs makes smart changes based on the distance between a person and an evacuation sign. During an evacuation process, when a person is within the visual range of a sign, the height of the evacuation sign is adjusted according to the distance from the person to ensure that the person can recognize the sign in the most suitable manner.
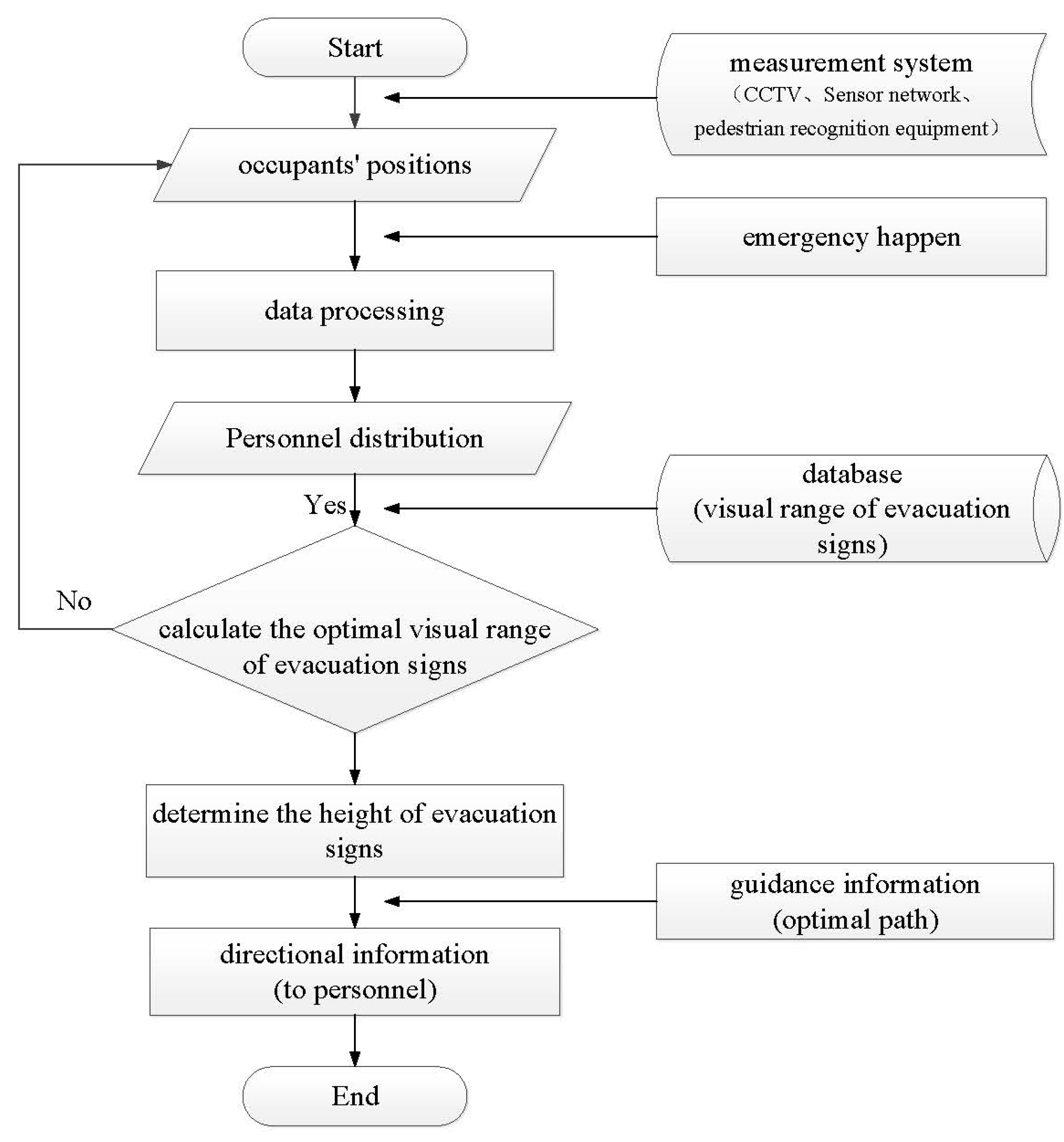
The entire device system includes two stages. In the first stage, evacuation signs and measurement facilities (CCTV cameras, pedestrian recognition equipment, and sensor networks) will be installed in the same spatial area to grasp the characteristics of people [44]. And, the data are transmitted to the control center for processing to obtain the distribution of people in the building (the visual distance between a single person or the main guide of a group of people and the evacuation sign). Only the situation of people who are about to reach the boundary of the visible range of evacuation signs is analyzed to attract their attention to the signs, and they will continue to observe the evacuation signs in other locations and finally evacuate to the safety exit. In the second stage, after the emergency evacuation information is received, people are provided with the optimal evacuation route obtained by using intelligent algorithms [45,46]. By combining the distribution of people and the database of visual ranges of evacuation signs at different heights (e.g., Equations (5) and (6)), the evacuation signs are adjusted to the optimal heights in time through the control center.
The smart evacuation signs devices are not in a real-time changing state, but it is necessary to find the evacuation behavior of people in a stage (such as within 30 s, 50 s, or 60 s) according to data processing and observation, so as to dynamically set the height of evacuation signs. For example, when people gather inside a building, it is necessary to raise the height of evacuation signs around the building to reduce the possibility of being blocked and ensure that they can see the location of the safety exit. When people reach the safety exit near the wall, it is necessary to lower the height of evacuation signs to ensure that people can see more comfortably. In addition, the evacuation guidance information is transmitted to the evacuation signs to give people prompt and effective evacuation route guidance in a timely manner to improve the efficiency of the evacuation of people, thereby providing a new strategy for managing pedestrian flow in large spaces of densely populated buildings (Figure 18).
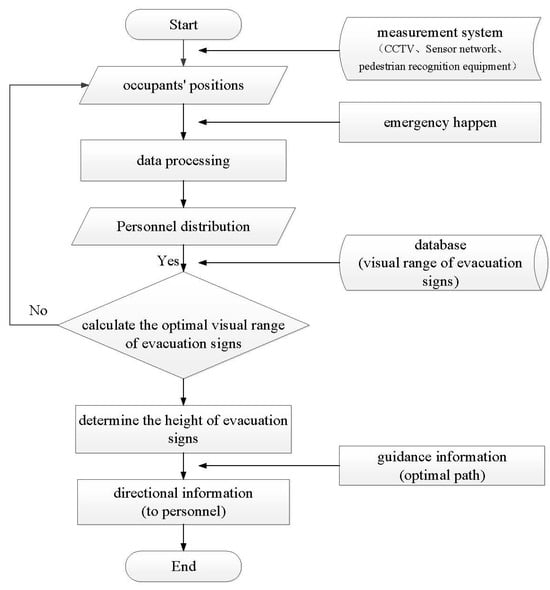
Figure 18.
Flowchart for the smart design of sign height adjustment in large space buildings.
The key to smart safety design for evacuation signs proposed in this article is the ability to predict the location of personnel and the height of evacuation signs, in order to effectively ensure that personnel can recognize evacuation signs and determine evacuation routes as early as possible based on personnel distribution and trends. In addition, the smart safety design compensates for the vertical direction overlooked by other evacuation sign devices. The advantage of this smart design can be set to an appropriate size and height according to the need of different scenarios. The overall device adopts a combination of modular evacuation signs and movable slide rails that are equipped with slots for fixing evacuation signs of different sizes. For buildings (e.g., the exhibition hall) where there are obstructions such as booths, the height of evacuation signs can be increased to 5 m. Although the visual range will be reduced, it can effectively reduce the impact of the sign being blocked by obstacles. For buildings (e.g., airport terminals or railway stations) where no obstruction exists inside them, the height of evacuation signs can be appropriately reduced to increase the visual range, and the height can be set to 3–4 m. Traditional evacuation signs are generally single-sided or double-sided, but it is advisable to adopt multi-faceted evacuation signs at the interior intersections of large space buildings to avoid blind spots and improve the visibility of evacuation signs (Figure 19).
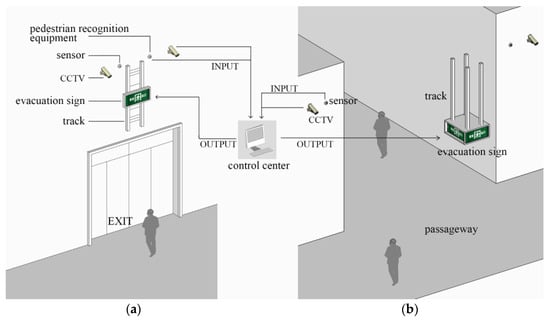
Figure 19.
Schematic diagram of the application scenario for the smart device for the evacuation sign height adjustment. (a) safety exit; (b) interior intersection of a large space building.
5. Conclusions
Evacuation signs play a very important role in guiding the evacuation of people in large space buildings. A mathematical model for the visual range of evacuation signs at a height of 1.7 to 6 m was obtained using experiments. It was found that the visual range of evacuation signs increases with the increase in size and decreases with the increase in height. At the same time, if there were no special requirements, it was suggested to set the height of the sign within the range of 3–5 m, which agreed more with the visual habits of the participants.
This study provides a new contribution to the height setting of evacuation signs. The height of evacuation signs is introduced, and the breakthrough point of sign visibility research is extended from a two-dimensional plane to three-dimensional space. One needs to pay attention to the impact of height change on the visual range of evacuation signs. The height of evacuation signs should not be set according to the code specifications only; it should be determined through a comprehensive consideration of the environment inside the building. When setting evacuation signs in a large space building, the relevant experimental data can be referenced to determine the optimal height.
The data and key findings of the present study provided valuable suggestions for setting the location of evacuation signs in large space buildings and analyze the relationship between the setting position of evacuation signs and the visual range in three-dimensional space. It can quantitatively guide the setting of evacuation signs at the most appropriate height and offer the corresponding support for the improvement and supplementation of existing codes. In addition, the present study also proposed a preliminary design concept of a smart height adjustment device for evacuation signs to improve the applicability of evacuation signs in different types of large space building scenarios.
6. Limitation and Future Work
In terms of research limitations, the selection of participants in the present study was not comprehensive, and the experimental analysis was conducted only for the same eye height of a specific young population. In addition, due to the small number of experimental people, the data may be biased. But even so, for the possible deviation relationship between the height change of evacuation signs and the visual range does not affect the objective law.
In future research, it is necessary to carry out more experiments, recruit more people with different types of people, different age groups, and different eye heights, and increase the number of experimental samples, so as to further study the influence of the setting height of evacuation signs on the visual range of signs. By supplementing actual parameter data, a more accurate quantitative relation and mathematical model between the height and visual range of evacuation signs can be determined to form a complete database for such relation and apply it in practice. In future research will be combined with communication engineering and electronic information to further improve the smart design of a height adjustment device for evacuation signs and make this design a reality. This will allow for the safer design of setting the height of evacuation signs that can be widely promoted and applied in large space buildings, thereby reducing casualties and improving public safety.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.W.; methodology, Z.W. and T.Z.; validation, Z.W., T.Z. and J.X.; writing-original draft, Z.W.; writing-review and editing, T.Z.; supervision, T.Z.; experiments, J.X.; data curation, J.X.; formal analysis, G.P.; software, G.P.; project administration, Z.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers: 52278005 and 52108032).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All subjects gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Chongqing University.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all participants involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for their comments and nice suggestions, which greatly improved the manuscript..
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tu, D.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, H. Thermal environment optimization in a large space building for energy-saving. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 51, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Wu, W.; Lin, C. Using virtual reality to determine how emergency signs facilitate way-finding. Appl. Ergon. 2009, 40, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobes, M.; Helsloot, I.; de Vries, B.; Post, J.G. Building safety and human behaviour in fire: A literature review. Fire Saf. J. 2010, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kyriakidis, M.; Dang, V.N. Incorporating human factors in emergency evacuation—An overview of behavioral factors and models. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 60, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Filippidis, L.; Galea, E.R.; Blackshields, D.; Lawrence, P.J. Experimental analysis of the effectiveness of emergency signage and its implementation in evacuation simulation. Fire Mater. 2012, 36, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, B.L. Visibility of Exit Signs and Directional Indicators. J. Illum. Eng. Soc. 2013, 20, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.; Lo, K. Experimental study on visibility of exit signs in buildings. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Hur, M.; Oh, Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Jeong, J.-J. The Effect of the Running-Man Emergency Exit Sign and Its Installed Location on Human Directional Choice. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2016, 30, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinateder, M.; Warren, W.H.; Schloss, K.B. What color are emergency exit signs? Egress behavior differs from verbal report. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 75, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olander, J.; Ronchi, E.; Lovreglio, R.; Nilsson, D. Dissuasive exit signage for building fire evacuation. Appl. Ergon. 2017, 59, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Yamada, T.; Kawai, S.; Takahashi, S. Evaluation of the Conspicuousness of Emergency Exit Signs. Fire Saf. Sci. 1991, 3, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Sano, T.; Ohmiya, Y. Influence of lit emergency signs and illuminated settings on walking speeds in smoky corridors. Fire Saf. J. 2021, 120, 103026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronchi, E.; Nilsson, D.; Kojić, S.; Eriksson, J.; Lovreglio, R.; Modig, H.; Walter, A.L. A Virtual Reality Experiment on Flashing Lights at Emergency Exit Portals for Road Tunnel Evacuation. Fire Technol. 2016, 52, 623–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, E.R.; Xie, H.; Deere, S.; Cooney, D.; Filippidis, L. Evaluating the effectiveness of an improved active dynamic signage system using full scale evacuation trials. Fire Saf. J. 2017, 91, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.K.; Khoo, W.P.; Morad, M.G.; Hölscher, C.; Kapadia, M. AUTOSIGN: A multi-criteria optimization approach to computer aided design of signage layouts in complex buildings. Comput. Graph. 2020, 88, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jia, L.; Qin, Y. Optimal number and location planning of evacuation signage in public space. Saf. Sci. 2017, 91, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horasan, M. Occupant evacuation and orientation problems in large halls—An exhibition building case study. Fire Mater. 1999, 23, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobes, M.; Helsloot, I.; de Vries, B.; Post, J.G.; Oberijé, N.; Groenewegen, K. Way finding during fire evacuation; an analysis of unannounced fire drills in a hotel at night. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, T. Influence of air-conditioning systems on buoyancy driven air infiltration in large space buildings: A case study of a railway station. Energy Build. 2020, 210, 109781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhong, M.; Fu, T.; He, L.; Huo, R. An investigation on spill plume temperature of large space building fires. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2009, 22, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, E.; Bie, Y. Simulation investigation on the smoke spread process in the large-space building with various height. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2020, 18, 100594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-B.; Zhang, H.-Q. Analysis and Countermeasures of Smoke Control Effect for Large Space Buildings. Procedia Eng. 2014, 71, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Huang, W.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lu, P.; Tan, X. Feasibility Analysis on Natural Smoke Extraction for Large Space Warehouse Buildings. Procedia Eng. 2016, 135, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Li, Q.; Kaneko, S.; Chen, J.; Cui, X. Location optimization algorithm for emergency signs in public facilities and its application to a single-floor supermarket. Fire Saf. J. 2009, 44, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N. The effectiveness of evacuation signs in buildings based on eye tracking experiment. Nat. Hazards 2020, 103, 1201–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Cao, S.; Song, W.; Fang, J. The influence of emergency signage on building evacuation behavior: An experimental study. Fire Mater. 2019, 43, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, T.; Ding, N.; Chraibi, M.; Fan, W.-C. Follow the evacuation signs or surrounding people during building evacuation, an experimental study. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 560, 125156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, J.; Sano, T.; Ronchi, E. Assessing the compliance with the direction indicated by emergency evacuation signage. Saf. Sci. 2021, 138, 105210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ding, N.; Shi, J.; Fan, Z. Verify the Validity of Guidance Sign in Buildings: A New Method Based on Mixed Reality with Eye Tracking Device. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippidis, L.; Galea, E.R.; Gwynne, S.; Lawrence, P.J. Representing the Influence of Signage on Evacuation Behavior within an Evacuation Model. J. Fire Prot. Eng. 2006, 16, 37–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Sheng, S. Signaling Design in Crowded Space and Prevention of Prevention of Stampede. J. Catastrophology 2017, 32, 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Filippidis, L.; Gwynne, S.; Galea, E.R.; Blackshields, D.; Lawrence, P.J. Signage Legibility Distances as a Function of Observation Angle. J. Fire Prot. Eng. 2007, 17, 41–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.; Hwang, E.; Kim, W. An Experimental Study on the Cognition of Evacuation Sign in Large Exhibition Space. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2016, 16, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Baek, S.-H.; Bae, Y.-H.; Oh, R.-S.; Choi, J.-H. Evaluation of the Effective Cognition Area (ECA) of Signage Systems with Backlighting under Smoke Conditions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, C.; Yuan, S. The Effects of Ambient Illumination, Color Combination, Sign Height, and Observation Angle on the Legibility of Wayfinding Signs in Metro Stations. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.; Son, J.; Oh, R.; Lee, H.; Lee, Y.; Hong, W.; Choi, J. Optimal Installation Location of Escape Route Signs at T-Type Intersections. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Jia, L. Discrete modeling approach for emergency guidance signage system design in underground spaces: A case study in transportation hubs. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 120, 104275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.; Liao, J.; Chen, W.; Mo, L. The difference in the warning effect of different warning signs. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2022, 28, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Carvel, R.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Z. Experimental investigation on the evacuation performance of pedestrians in a three-lane urban tunnel with natural ventilation in a fire scenario. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 108, 103634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, G.-Y.; Na, W.-J.; Hong, W.-H.; Lee, J.-K. Influence of design and installation of emergency exit signs on evacuation speed. J. Asian Arch. Build. Eng. 2019, 18, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Liu, R. An approach of checking an exit sign system based on navigation graph networks. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 46, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhialini, M.; Bernardini, G.; Ferracuti, F.; Iarlori, S.; D’orazio, M.; Longhi, S. Fire exit signs: The use of neurological activity analysis for quantitative evaluations on their perceptiveness in a virtual environment. Fire Saf. J. 2016, 82, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Zhou, T.; Tang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, L. Smart Design for Evacuation Signage Layout for Exhibition Halls in Exhibition Buildings Based on Visibility. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.P.; Chen, K.; Wong, P.K.-Y.; Chen, W.; Li, C.T. Graph-based network generation and CCTV processing techniques for fire evacuation. Build. Res. Inf. 2021, 49, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Luo, C.; Liu, Y.; Teng, S.; Xin, G. Path intelligent optimization for dense crowd emergency evacuation in heritage buildings. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 47, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirahadi, F.; McCabe, B.Y. EvacuSafe: A real-time model for building evacuation based on Dijkstra’s algorithm. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 34, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).