Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community of Mulberry (Morus alba L.) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Intercropping System in Northwest Liaoning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Varieties and Planting Patterns
2.2. Collection and Chemical Property Analysis of Soil Samples
2.3. DNA Extraction and Sequencing of Soil Microorganisms
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Mulberry-Alfalfa Intercropping on Soil CNP Stoichiometry
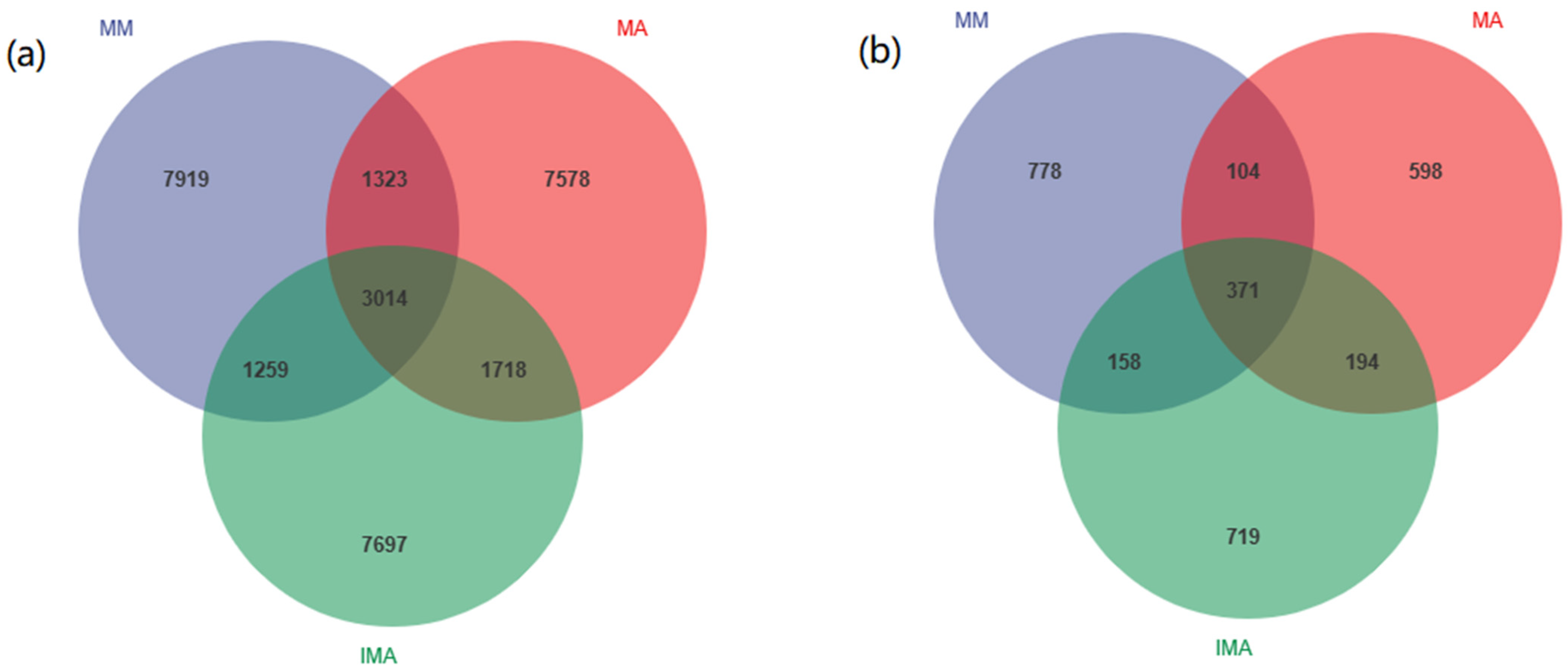
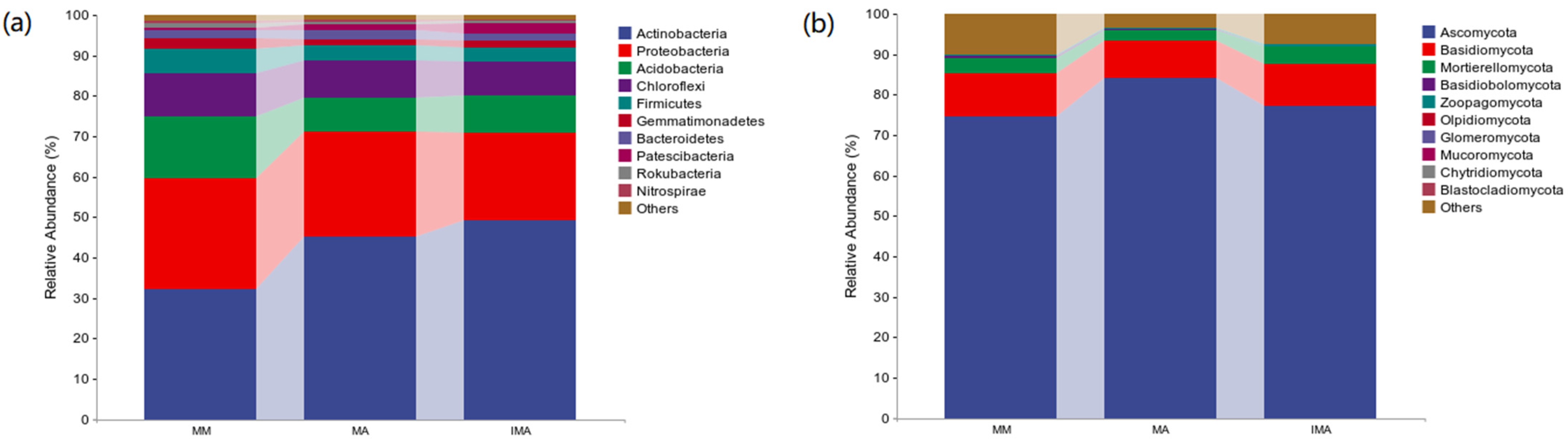
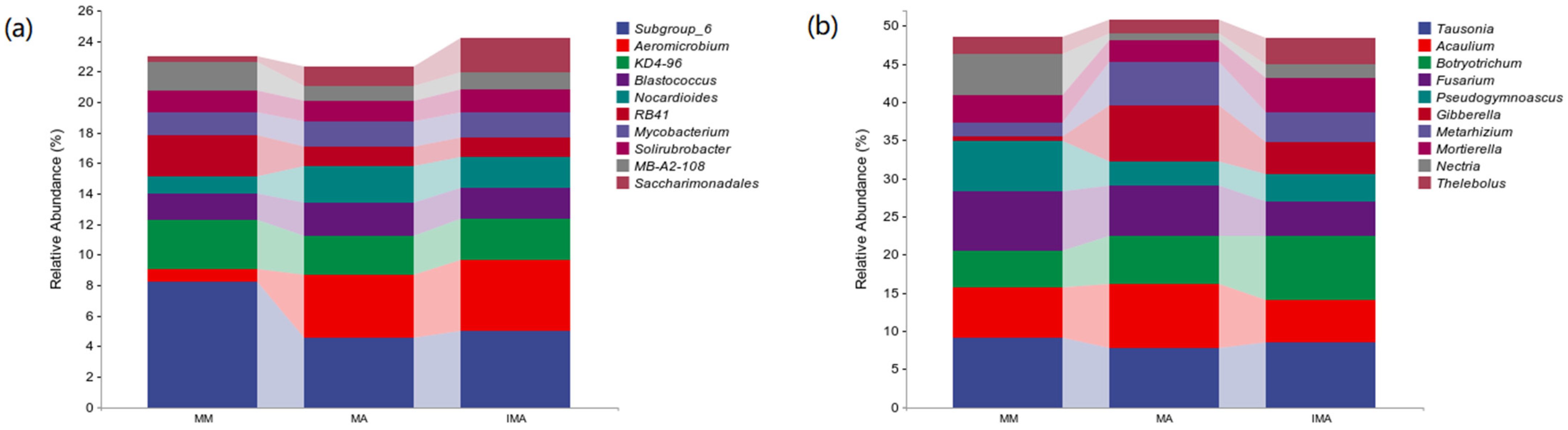
3.2. Effects of Mulberry-Alfalfa Intercropping on Soil Microflora Composition and Structure
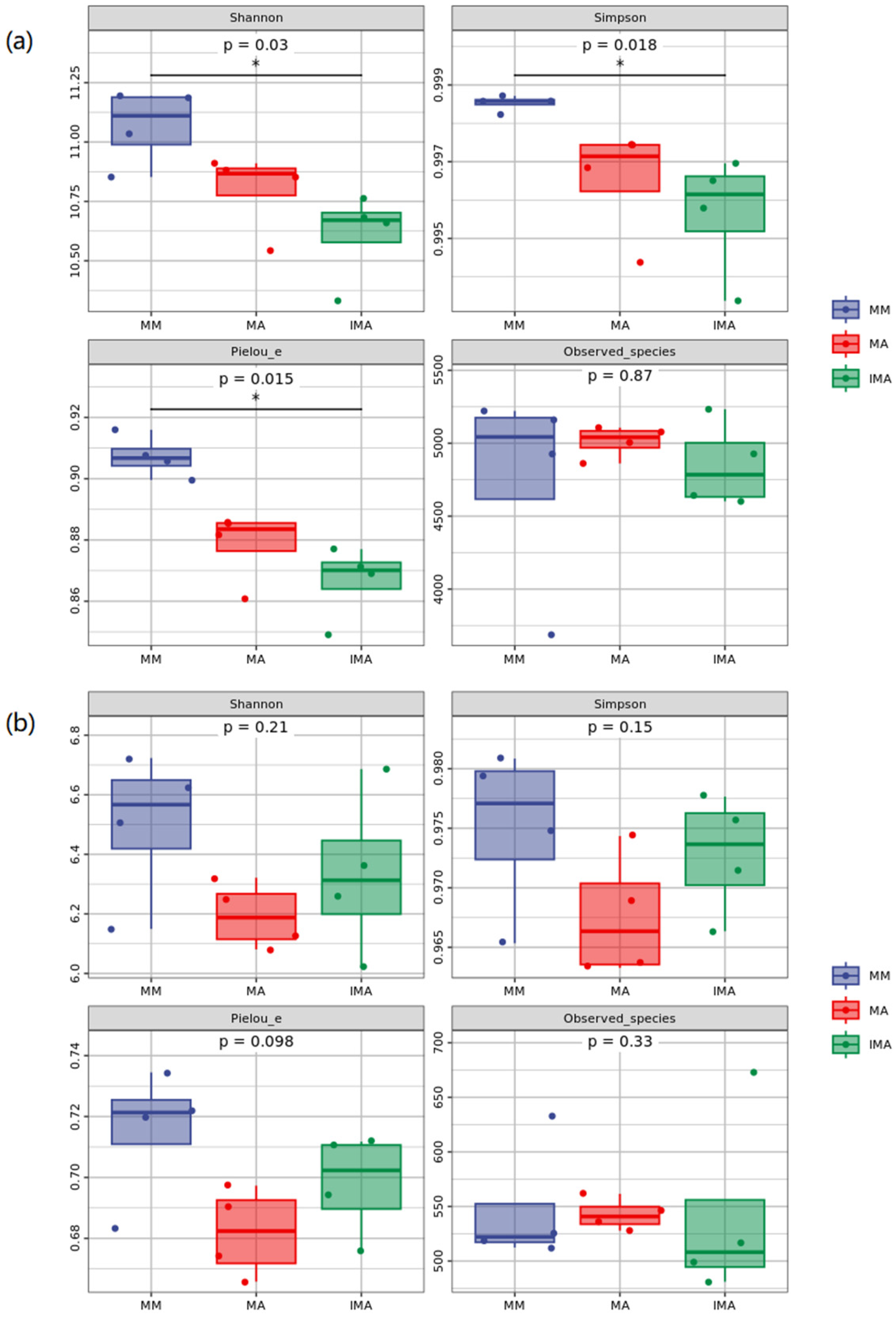
3.3. The Impact of Mulberry-Alfalfa Intercropping on Diversity of Soil Microbial Populations
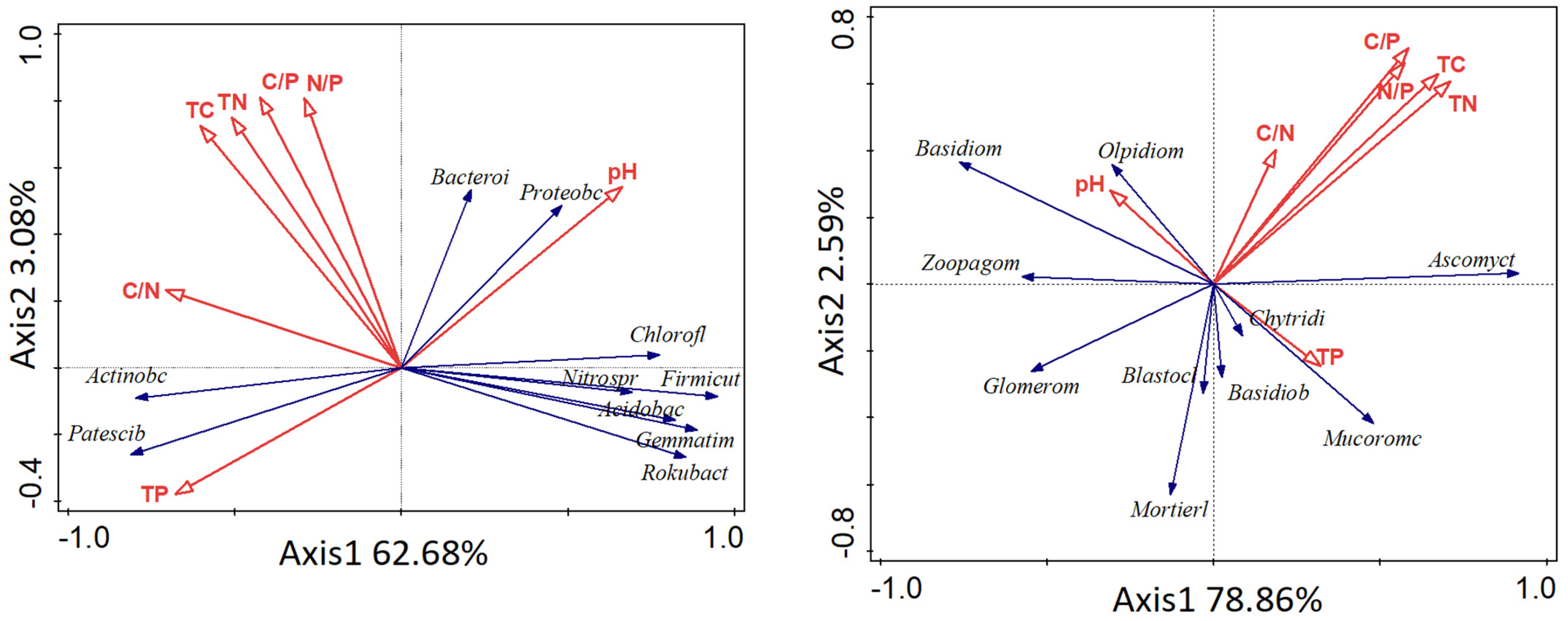
3.4. Correlation Analysis between Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Soil Microorganisms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, L.; Bai, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Luo, Y.; Song, S.; Zhang, W.-H. A new model of two-sown regime for oat forage production in an alpine region of northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 70520–70531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Hou, L.; Yang, J.; Song, S.; Mao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, W.; Pan, Q.; Zhou, Q. Establishment and management of alfalfa pasture in cold regions of China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 1651–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüstholz, J.; Carrasco, S.; Berger, U.; Sundrum, A.; Bellof, G. Silage of young harvested alfalfa (Medicago sativa) as home-grown protein feed in the organic feeding of laying hens. Org. Agric. 2017, 7, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, K.P.; Thelemann, R.T.; Jung, H.-J.G.; Tschirner, U.W.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Johnson, G.A. Variation due to Growth Environment in Alfalfa Yield, Cellulosic Ethanol Traits, and Paper Pulp Characteristics. BioEnergy Res. 2009, 2, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. An insufficient glucose supply causes reduced lactose synthesis in lactating dairy cows fed rice straw instead of alfalfa hay. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 4771–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Hou, Z.; Gao, S.; Li, Z.; Wei, Z.; Wu, D. Substitution of fresh forage ramie for alfalfa hay in diets affects production performance, milk composition, and serum parameters of dairy cows. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Teng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Cai, D.; Zhang, J.; Meng, F.; Sun, G. Nitrogen application and intercropping change microbial community diversity and physicochemical characteristics in mulberry and alfalfa rhizosphere soil. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 2121–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, N.; Hu, Y.; Sun, G. Changes in soil physicochemical properties and soil bacterial community in mulberry (Morus alba L.)/alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) intercropping system. Microbiol. Open 2018, 7, e00555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyai, C.; Yusakul, G.; Komaikul, J.; Kitisripanya, T.; Likhitwitayawuid, K.; Sritularak, B.; Putalun, W. Improvement of stilbene production by mulberry Morus alba root culture via precursor feeding and co-elicitation. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Liang, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Zou, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, M. Foliar Spraying of 6-Benzylaminopurine Promotes Growth and Flavonoid Accumulation in Mulberry (Morus alba L.). J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 41, 2232–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Kong, W.; Niu, S.; Gao, K.; Yang, H. Community composition and trophic mode diversity of fungi associated with fruiting body of medicinal Sanghuangporus vaninii. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simbaya, J.; Chibinga, O.; Salem, A.Z.M. Nutritional evaluation of selected fodder trees: Mulberry (Molus alba Lam.), Leucaena (Leucaena luecocephala Lam de Wit.) and Moringa (Moringa oleifera Lam.) as dry season protein supplements for grazing animals. Agrofor. Syst. 2020, 94, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Luo, H. Effects of mulberry leaf silage on antioxidant and immunomodulatory activity and rumen bacterial community of lambs. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajnc, A.U.; Ugulin, T.; Paušič, A.; Rabensteiner, J.; Bukovac, V.; Petkovšek, M.M.; Janžekovič, F.; Bakonyi, T.; Berčič, R.L.; Felicijan, M. Morphometric and biochemical screening of old mulberry trees (Morus alba L.) in the former sericulture region of Slovenia. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2019, 88, 3614–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Fang, J.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, Z.; Chang, Y.; Ning, N.; Guo, H.; et al. Structures, bioactivities and future prospective of polysaccharides from Morus alba (white mulberry): A review. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.-C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.-X.; Li, P.-D. Effects of intercropping of peanut with the medicinal plant Atractylodes lancea on soil microecology and peanut yield in subtropical China. Agrofor. Syst. 2013, 87, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, L.; Tang, B.; Guo, H.; Cao, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, S.; Chen, Z. Dynamic changes of rhizosphere soil bacterial community and nutrients in cadmium polluted soils with soybean-corn intercropping. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N. Embracing the unknown: Disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Long, Y.; Sarkar, B.; Li, Y.; Lü, G.; Ali, A.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.-E. Influence of soil microorganisms and physicochemical properties on plant diversity in an arid desert of Western China. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 2645–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, M.K.; Wang, F.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.-N.; Lan, T.-J.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, P.; Yang, L.-T.; Li, Y.-R. Rhizospheric and endospheric diazotrophs mediated soil fertility intensification in sugarcane-legume intercropping systems. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1911–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Wagg, C. Soil microbial diversity and agro-ecosystem functioning. Plant Soil 2013, 363, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollini, D.; Rigsby, C.M.; Barto, E.K. Microbes as Targets and Mediators of Allelopathy in Plants. J. Chem. Ecol. 2012, 38, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julia, K.; Karina, E.C.; Erik, K.; Björn, L.D. Below-ground organic matter accumulation along a boreal forest fertility gradient relates to guild interaction within fungal communities. Ecol. Let. 2017, 20, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Bonkowski, M.; Shen, Y.; Griffiths, B.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, B. Root ethylene mediates rhizosphere microbial community reconstruction when chemically detecting cyanide produced by neighbouring plants. Microbiome 2020, 8, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanová, M.; Šnajdr, J.; Baldrian, P. Composition of fungal and bacterial communities in forest litter and soil is largely determined by dominant trees. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 84, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaeem, M.; Nadeem, M.; Pham, T.H.; Ashiq, W.; Ali, W.; Gilani, S.S.M.; Elavarthi, S.; Kavanagh, V.; Cheema, M.; Galagedara, L.; et al. The potential of corn-soybean intercropping to improve the soil health status and biomass production in cool climate boreal ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13148–13165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, N.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Cai, D.; Guo, J.; Wu, D.; Sun, G. Soil Physicochemical Properties and the Rhizosphere Soil Fungal Community in a Mulberry (Morus alba L.)/Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Intercropping System. Forests 2019, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. QIIME 2: Reproducible, interactive, scalable, and extensible microbiome data science. PeerJ Prepr. 2018, 6, e27295v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kõljalg, U.; Nilsson, R.H.; Abarenkov, K.; Tedersoo, L.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bahram, M.; Bates, S.T.; Bruns, T.D.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Callaghan, T.M.; et al. Towards a unified paradigm for sequence-based identification of fungi. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5271–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverria, A.; Gonzalez, E.M. Root system of Medicago sativa and Medicago truncatula: Drought effects on carbon metabolism. Plant Soil 2021, 463, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautges, N.E.; Jungers, J.M.; DeHaan, L.R.; Wyse, D.L.; Sheaffer, C.C. Maintaining grain yields of the perennial cereal intermediate wheatgrass in monoculture v. bi-culture with alfalfa in the Upper Midwestern USA. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 156, 758–773. [Google Scholar]
- Crews, T.E.; Blesh, J.; Culman, S.W.; Hayes, R.C.; Jensen, E.S.; Mack, M.C.; Peoples, M.B.; Schipanski, M.E. Going where no grains have gone before: From early to mid-succession. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 223, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilakarathna, M.S.; McElroy, M.S.; Chapagain, T.; Papadopoulos, Y.A.; Raizada, M.N. Belowground nitrogen transfer from legumes to non-legumes under managed herbaceous cropping systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, M.L.M.; Ana, B.; Li, S.; Jensen, E.S. Agronomic performance, nitrogen acquisition and water-use efficiency of the perennial grain crop Thinopyrum intermedium in a monoculture and intercropped with alfalfa in Scandinavia. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, E.S.; Carlsson, G.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H. Intercropping of grain legumes and cereals improves the use of soil N resources and reduces the requirement for synthetic fertilizer N: A global-scale analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 40, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carof, M.; Godinot, O.; Ridier, A. Diversity of protein-crop management in western France. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 39, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.S.; Peoples, M.B.; Boddey, R.; Gresshoff, P.M.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Alves, B.J.; Morrison, M.J. Legumes for mitigation of climate change and the provision of feedstock for biofuels and biorefineries. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 329–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anke, H.; Franziska, N.; Thorsten, H.; Christian, B.; Jürgen, H.; Jens, D.; Georg, J.R.; Florian, W. Evidence of considerable C and N transfer from peas to cereals via direct root contact but not via mycorrhiza. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11424. [Google Scholar]
- Latati, M.; Aouiche, A.; Rebou, Y.N.; Laouar, M. Modeling the functional role of the microorganisms in the daily exchanges of carbon and nitrogen in intercropping system under Mediterranean conditions. Agron. Res. 2019, 17, 559–573. [Google Scholar]
- Yvonne, O.; Markus, L.; Sophia, L.; Christiane, R.; Felipe, A.; Fabian, A.; Nina, B.; Doreen, B.; Steffen, B.; Runa, B.S.; et al. Above and belowground biodiversity jointly tighten the P cycle in agricultural grasslands. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4431. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.; Bhatia, A.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, B. The effects of elevated CO2 and elevated O3 exposure on plant growth, yield and quality of grains of two wheat cultivars grown in north India. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F.; Han, J.; Wen, X.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Vinay, N.; Jia, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Liao, Y. Quantifying regional effects of plastic mulch on soil nitrogen pools, cycles, and fluxes in rain-fed agroecosystems of the Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Tian, H.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. Shoot-soil ecological stoichiometry of alfalfa under nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization in the Loess Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C.A.S. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohain, A.; Manpoong, C.; Saikia, R.; De Mandal, S. Actinobacteria: Diversity and biotechnological applications. In Recent Advancements in Microbial Diversity, 2nd ed.; Mandal, D.S., Bhatt, P., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020; pp. 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Auwal, M.; Singh, B.P.; Van Zwieten, L.; Xu, J. Biochar accelerates soil organic carbon mineralization via rhizodeposit-activated Actinobacteria. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2022, 58, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, S.; Hafsa, C.S.; Ali, C.B.; Allaoua, S.; Manal, E.; Lenka, L.; Faizah, N.A.; Lassaad, B. Improvement of Medicago sativa crops productivity by the co-inoculation of Sinorhizobium meliloti—Actinobacteria under salt stress. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 1344–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.-D.; Johnson, R.L.; Lehmann, J.; Olk, D.C.; Neves, E.G.; Thompson, M.L.; Schmidt-Rohr, K. Abundant and Stable Char Residues in Soils: Implications for Soil Fertility and Carbon Sequestration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9571–9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, O.H.B.; Costa, F.S.; Rodrigues, G.R.; da Costa, R.A.; Fernandes, G.D.R.; Júnior, O.R.P.; Barreto, C.C. Soil Acidobacteria Strain AB23 Resistance to Oxidative Stress Through Production of Carotenoids. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 81, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challacombe, J.F.; Hesse, C.N.; Bramer, L.M.; Ann, M.L.; Mary, L.; Samuel, P.; Carrie, N.; Verne, G.G.L.; Andrea, P.A.; Kuske, C.R. Genomes and secretomes of Ascomycota fungi reveal diverse functions in plant biomass decomposition and pathogenesis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wei, Y.; Yin, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, Y. The effect of intercropping mulberry (Morus alba L.) with peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.), on the soil rhizosphere microbial community. Forests 2022, 13, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, W. Soil acidification amendments change the rhizosphere bacterial community of tobacco in a bacterial wilt affected field. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 9781–9791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Ghosh, S.K. Diversity of soil fungi in North 24 Parganas and their antagonistic potential against Leucinodes orbonalis Guen. (Shoot and fruit borer of brinjal). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 8707–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Duan, T. Green Manure Crops Affected Soil Chemical Properties and Fungal Diversity and Community of Apple Orchard in the Loess Plateau of China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 1089–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Cheng, X.; Shu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Linking soil bacterial and fungal communities to vegetation succession following agricultural abandonment. Plant Soil 2018, 431, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banakar, S.P.; Thippeswamy, B.; Thirumalesh, B.V.; Naveenkumar, K.J. Diversity of soil fungi in dry deciduous forest of Bhadra Wildlife sanctuary, western Ghats of southern India. J. For. Res. 2012, 23, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, A.; Sayer, E.J.; Yuan, Z.; Lin, F.; Fang, S.; Ye, J.; Liu, S.; Hao, Z.; Wang, X. Soil Stoichiometry Mediates Links Between Tree Functional Diversity and Soil Microbial Diversity in a Temperate Forest. Ecosystems 2022, 25, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Weng, B.-S.; Huang, F.-Y.; Su, J.-Q.; Yang, X.-R. pH regulates ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in paddy soils in Southern China. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6113–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyika, T.W.; Stafford, W.; Cowan, D.A. The soil and plant determinants of community structures of the dominant actinobacteria in Marion Island terrestrial habitats, Sub-Antarctica. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Chemistry | MM | MA | IMA |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH Value | 7.91 ± 0.03 a | 7.86 ± 0.01 a | 7.74 ± 0.05 b |
| TC (g kg−1) | 4.54 ± 0.18 c | 8.97 ± 0.39 a | 5.60 ± 0.26 b |
| TN (g kg−1) | 0.47 ± 0.01 b | 0.82 ± 0.06 a | 0.52 ± 0.01 b |
| TP (g kg−1) | 0.44 ± 0.01 b | 0.47 ± 0.03 ab | 0.51 ± 0.01 a |
| C: N | 9.70 ± 0.19 b | 11.08 ± 0.45 a | 10.75 ± 0.27 a |
| C: P | 10.42 ± 0.62 b | 19.12 ± 1.40 a | 11.11 ± 0.76 b |
| N: P | 1.07 ± 0.05 b | 1.75 ± 0.19 a | 1.03 ± 0.05 b |
| Phylum | MM | MA | IMA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Actinobacteria | 0.32 ± 0.03 b | 0.45 ± 0.01 a | 0.49 ± 0.01 a |
| Proteobacteria | 0.27 ± 0.02 a | 0.26 ± 0.01 a | 0.22 ± 0.01 b | |
| Acidobacteria | 0.15 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 b | 0.09 ± 0.01 b | |
| Chloroflexi | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 b | 0.08 ± 0.01 b | |
| Fungi | Ascomycota | 0.75 ± 0.02 b | 0.84 ± 0.019 a | 0.77 ± 0.03 ab |
| Genus | MM | MA | IMA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Subgroup_6 | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | 0.05 ± 0.01 b |
| Aeromicrobium | 0.01 ± 0.01 b | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | |
| Fungi | Tausonia | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 a |
| Acaulium | 0.07 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | |
| Botryotrichum | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | 0.06 ± 0.01 ab | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | |
| Fusarium | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | 0.07 ± 0.02 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | |
| Pseudogymnoascus | 0.07 ± 0.01 a | 0.03 ± 0.01 ab | 0.04 ± 0.01 b | |
| Gibberella | 0.01 ± 0.01 b | 0.07 ± 0.02 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 ab | |
| Alpha Diversity | pH | TC | TN | TP | C/N | C/P | N/P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Shannon | 0.113 | 0.210 | 0.207 | 0.119 | 0.103 | 0.178 | 0.159 |
| Simpson | 0.604 * | −0.416 | −0.332 | −0.641 * | −0.555 | −0.234 | −0.120 | |
| Pielou_e | 0.625 * | −0.304 | −0.224 | −0.54 8 | −0.490 | −0.147 | −0.046 | |
| Observed_species | 0.528 | −0.374 | −0.301 | −0.563 | −0.480 | −0.203 | −0.104 | |
| Fungi | Shannon | −0.124 | −0.105 | −0.024 | −0.042 | −0.400 | −0.100 | −0.021 |
| Simpson | −0.018 | −0.754 ** | −0.693 * | −0.089 | −0.611 * | −0.710 ** | −0.613 * | |
| Pielou_e | −0.058 | −0.649 * | −0.567 | −0.095 | −0.660 * | −0.610 * | −0.499 | |
| Observed_species | −0.177 | −0.674 * | −0.611 * | −0.001 | −0.574 | −0.655 * | −0.563 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Wei, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, W.; Bai, X.; Zhou, Y. Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community of Mulberry (Morus alba L.) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Intercropping System in Northwest Liaoning. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010114
Li M, Wei Y, Yin Y, Zhu W, Bai X, Zhou Y. Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community of Mulberry (Morus alba L.) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Intercropping System in Northwest Liaoning. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(1):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010114
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Muzi, Yawei Wei, You Yin, Wenxu Zhu, Xuejiao Bai, and Yongbin Zhou. 2023. "Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community of Mulberry (Morus alba L.) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Intercropping System in Northwest Liaoning" Microorganisms 11, no. 1: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010114
APA StyleLi, M., Wei, Y., Yin, Y., Zhu, W., Bai, X., & Zhou, Y. (2023). Characteristics of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microbial Community of Mulberry (Morus alba L.) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Intercropping System in Northwest Liaoning. Microorganisms, 11(1), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010114






