Abstract
Among orthodontists and scientists, in the last years, upper molar distalization has been a debated topic in the orthodontic aligner field. However, despite that few clinical studies have been published, no insights on aligners’ biomechanics regarding this movement are available. The aim of this study was to assess, through finite element analysis, the force system resulting in the upper arch during second maxillary molar distalization with clear aligners and variable attachments settings. The average tooth distalization was found to be 0.029, with buccal flaring of the upper incisors in all attachment configurations. The mesial deformation of the aligner was registered to be 0.2 mm on average. Different pressure areas on the interface between aligners and upper molars were registered, with the mesial attachment surface to be directly involved when present. Periodontal ligament pressure was reported to range between 67 g/cm2 and 132 g/cm2. Configurations with rectangular attachments from second molar-to-canine and from first molar-to-canine present, in an in silico environment, almost equal efficiency in distalizing the upper second molar. However, attachments from the second molar to the canine are suggested to be adopted in clinical environments due to greater feasibility in everyday practice.
1. Introduction
The demand for minimally invasive solutions led to the development of appliances that combine effectiveness in correcting dental positions with comfort and aesthetics features [1]. Despite the widespread use of orthodontic therapy with clear aligners (CAT), their level of efficiency is still controversial. However, the reliability of CAT has increased due to the implementation of the thermoplastic biomaterials and a better understanding of biomechanics applied in combination with the exponential number of biomedical studies [2,3]. A systematic review by Rossini et al. focused on the predictability of orthodontic movements of teeth with aligners and found only 11 studies that met the inclusion criteria [2]. Among the dental movements analyzed in their study, the most predictable was body distalization. Align Technology’s “best practice protocols” derived from clinical experience with the Invisalign® system, and initially recommended bonded vertical rectangular attachments to control distal bodily movement [4,5,6,7]. One of the reasons why the effectiveness of aligners is still under discussion could be the force transmission mechanism [8,9]. In the traditional system, the orthodontic movement is the result of the interactions of metal wires and brackets to the tooth; conversely, in the aligners system, the forces and moments are generated by the difference between the shape of aligners and the teeth [10]. In addition, the resolution of complex movements such as distalization demands the use of attachments, but just a few studies have been developed to evaluate the biomechanical performance of the aligners and their accessories [8]. The application of engineering knowledge in dentistry with the use of computational techniques has helped to understand oral biomechanics aspects. The finite element method (FEM) is a numerical technique used to perform finite element analysis (FEA) of any given physical phenomenon and is widely accepted for medical purposes. FEM can simplify the physiologic responses of the dento-alveolar complex to orthodontic forces by exhibiting quantitative data and is recently preferred by the researchers of the field [11]. The main advantage of using FEM is that many alternative designs can be tried out for their validity, safety and integrity using the computer in an in silico environment, even before the first prototype is built. Experimental validation studies of FE analyses are encouraged whenever possible [12]. Regarding aligner orthodontics, Barone et al. [8] have introduced a computational design and engineering structure, which allows patient-specific simulations of the mechanical interactions between dental tissues and polymer aligners. This computational approach allows for design based on knowledge of the most suitable aligner characteristics taking into account individual needs.
The aim of this in silico study was to evaluate, through FEM, the orthodontic distalization movement of a second maxillary molar with clear aligners, analyzing different attachment configurations.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was conducted at the Orthodontics Department of the University of Turin—Dental School (Turin, Italy).
CAD Design
The following parts were obtained using SpaceClaim CAD software (SpaceClaim Corporation; Canonsburg, PA, USA):
- Maxillary teeth from second molar to second molar;
- Periodontal ligament (PDL) of each tooth;
- Rectangular attachments from second molar to canine on both sides;
- Dedicated orthodontic aligners.
Teeth were created by one of the authors (GR) starting from a full arch STL file derived from CBCT.
PDL was designed using SpaceClaim offset and Boolean intersection functions, by the same author, based on root shape. The PDL average thickness was 0.25 mm, according to scientific literature [13].
Attachments were built, based on ClinCheck® software (Align Technology, Inc., San Jose, CA, USA) auxiliaries, with the following features:
- Vertical rectangular shape;
- 3 mm height;
- 2 mm width;
- 1 mm thickness.
The shape, size and position of composite attachments were determined by simulating rectangular attachments designed for distalization on a real case with ClinCheck® software.
Aligners were obtained by applying the SpaceClaim software offset function on all tooth crowns and attachments and then manually refined to remove redundant surfaces and increase the accuracy of aligners’ contours. Thus, the shape of the obtained virtual model corresponded to that of a real aligner. After repeated measurements with a Micro-CT Scan (SkyScan 1172: Bruker-microCT; Kontich, Belgium) of Invisalign® aligners (Align Technology, Inc., San Jose, CA, USA), aligner thickness was set at 0.5 mm.
The adopted FE software was ANSYS, in which the model was imported after the CAD process. (ANSYS 18.2, Inc.; Canonsburg, PA, USA).
Material Properties
As reported in the scientific literature, every CAD element except for PDL was considered isotropic and homogeneous [10]. Teeth and attachments were fused together as a unique rigid body. Regarding PDL material properties, a hyperelastic model derived from the literature was adopted [14].
Mesh Discretization
After a convergence study on one single tooth, the mesh was set as follows:
- Mesh size: 0.09 mm;
- Type of element: linear;
- Average nodes: 1,240,850;
- Average elements: 1,435,655.
Contact Settings and Supports Definition
Interface treatment was adopted, according to the paper by Barone et al. [8], as follows:
- PDL/tooth: bonded contact;
- Aligner/tooth: frictionless contact;
- Tooth/tooth: frictionless contact.
A fixed support was applied on each periodontal ligament surface to mimic the role of alveolar bone.
Three experimental models were developed, considering different combinations of attachments:
- No attachments (NO ATT);
- 3 mm vertical rectangular attachment positioned on the buccal crown surface, from the right canine to the right first molar (ATT 3–6);
- 3 mm vertical rectangular attachments on the buccal crown surface, from the right canine to the right second molar (ATT 3–7);
The simulated movement was a distalization of 0.2 mm of the upper second molar, without further movements planned, reproducing real clinical settings [6].
Analyzed Outcomes Included
- Stress developed on aligner;
- Equivalent stress of PDL;
- Teeth displacement pattern;
- Aligner deformation.
3. Results

Table 1.
Tooth displacement.

Table 2.
Aligner deformation.

Table 3.
Aligner/tooth contact pressure.

Table 4.
Periodontal ligament (PDL) stress.
3.1. Subsection
3.1.1. Tooth Displacement
Regarding tooth displacement, the configuration displaying the greater amount of movement on the upper second molar was ATT 3–6 (0.036 mm) in a distal direction, while for NO ATT and ATT 3–7, the movement was by 0.02 mm and 0.021 mm, respectively. Regarding the anterior anchorage unit, the most solicited tooth was the lateral incisor, which displayed 0.025 mm of buccal movement for NO ATT, 0.033 for ATT 3–6, and 0.029 mm for ATT 3–7 (Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3).
3.1.2. Aligner Deformation
Aligner deformation was directed in a mesio-buccal direction, with slightly greater amounts ranging from NO ATT (0.23 mm) to ATT 3–6 (0.2 mm) to ATT 3–7 (0.19 mm) (Figure 4).
3.1.3. Aligner/Tooth Contact Pressure
Furthermore, the max contact pressure between the aligner and the second molar was greater in ATT 3–7 (2099.1 g/cm2) than in NO ATT (1187.7 g/cm2) and ATT 3–6 (964.1 g/cm2). Max pressure areas were distributed differently across the three analyses: the mesial surface of rectangular attachments for ATT 3–7, the mesio-buccal surface of the second molar for ATT 3–6 and the disto-lingual surface of the second molar for NO ATT (Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7).
3.1.4. PDL Stress
3.2. Analysis Shown in Figure
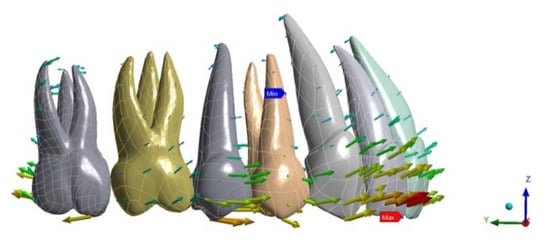
Figure 1.
NO ATT tooth displacement.
Figure 1.
NO ATT tooth displacement.
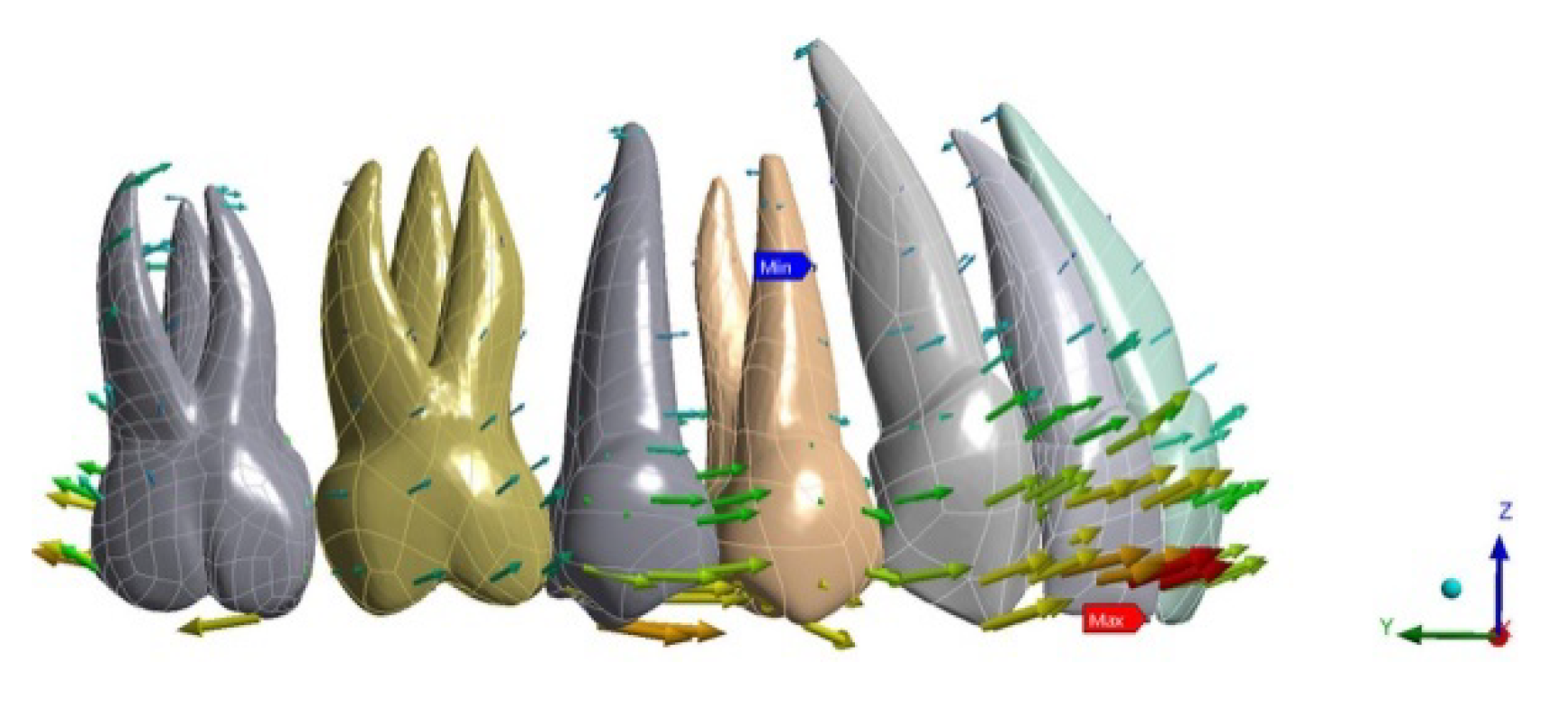
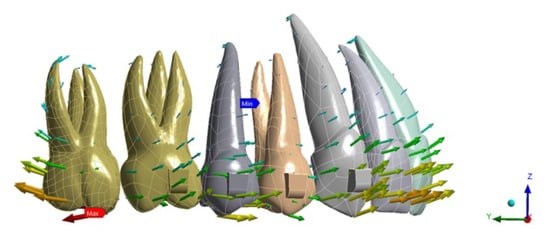
Figure 2.
ATT 3–6 tooth displacement.
Figure 2.
ATT 3–6 tooth displacement.
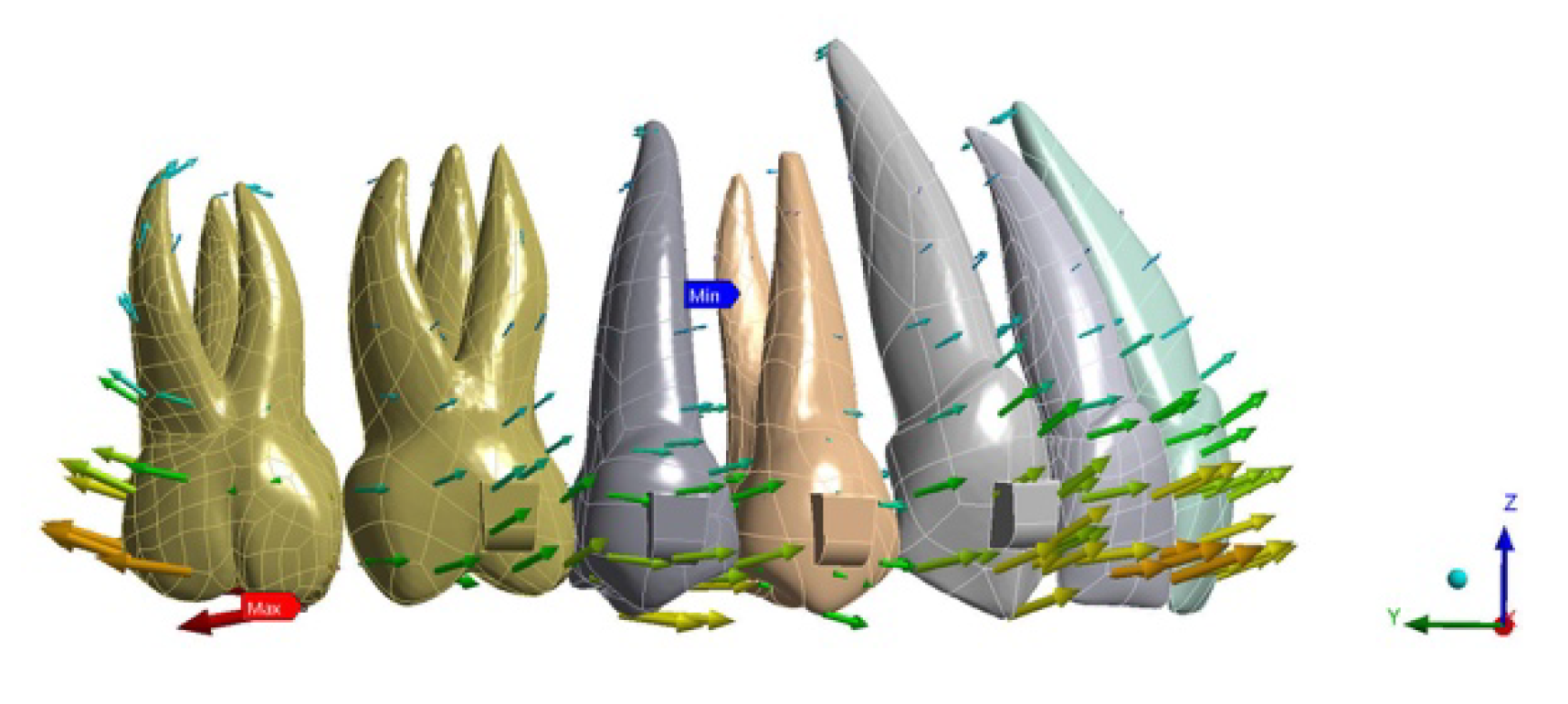
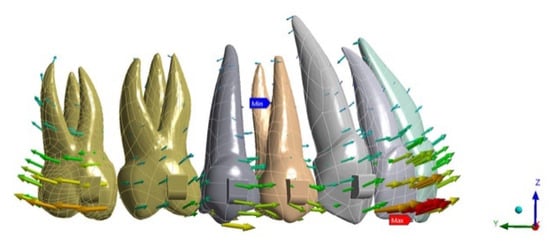
Figure 3.
ATT 3–7 tooth displacement.
Figure 3.
ATT 3–7 tooth displacement.
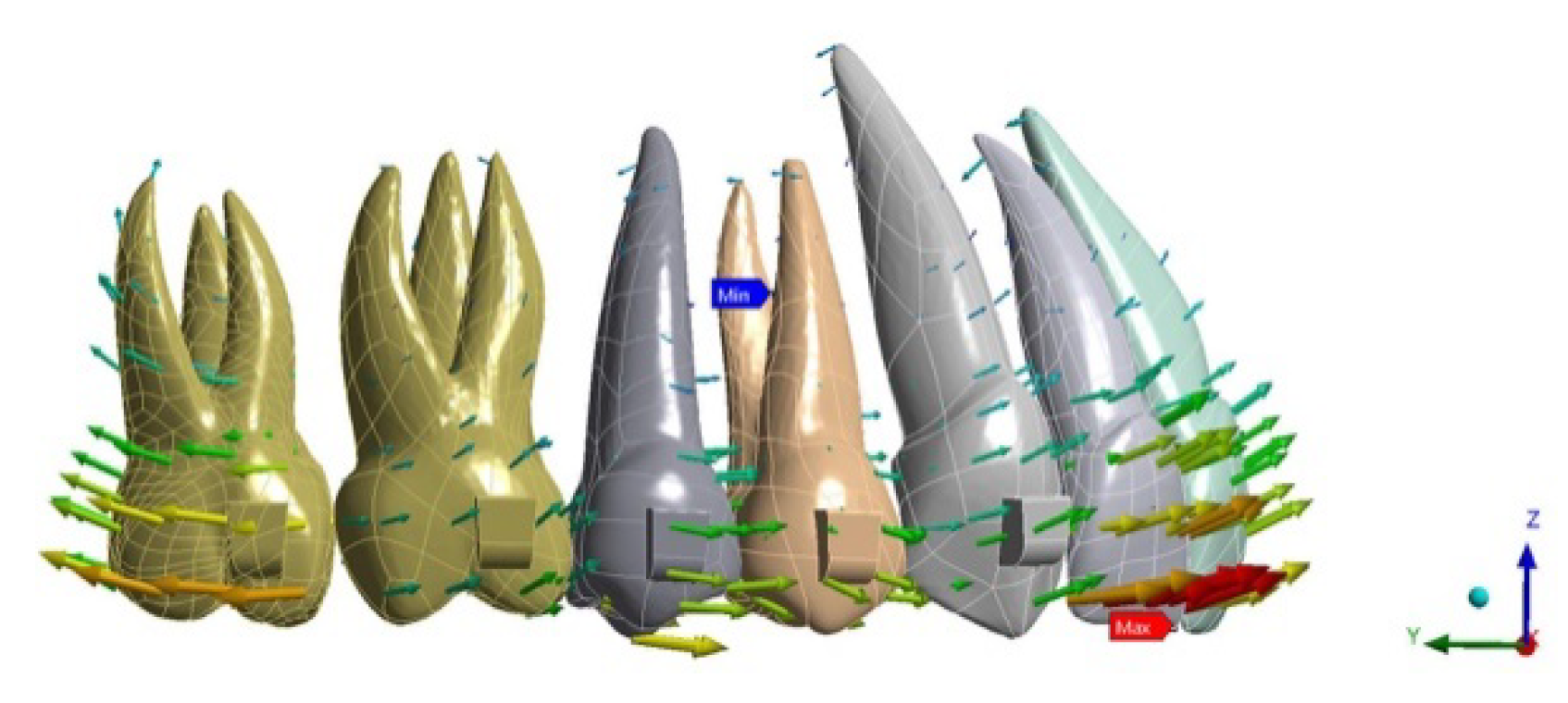
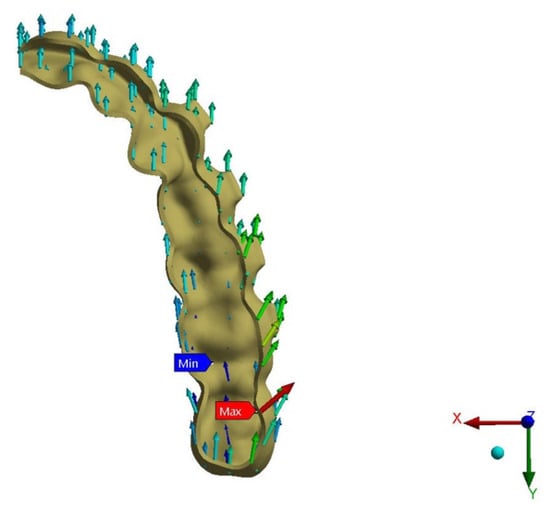
Figure 4.
Aligner deformation.
Figure 4.
Aligner deformation.
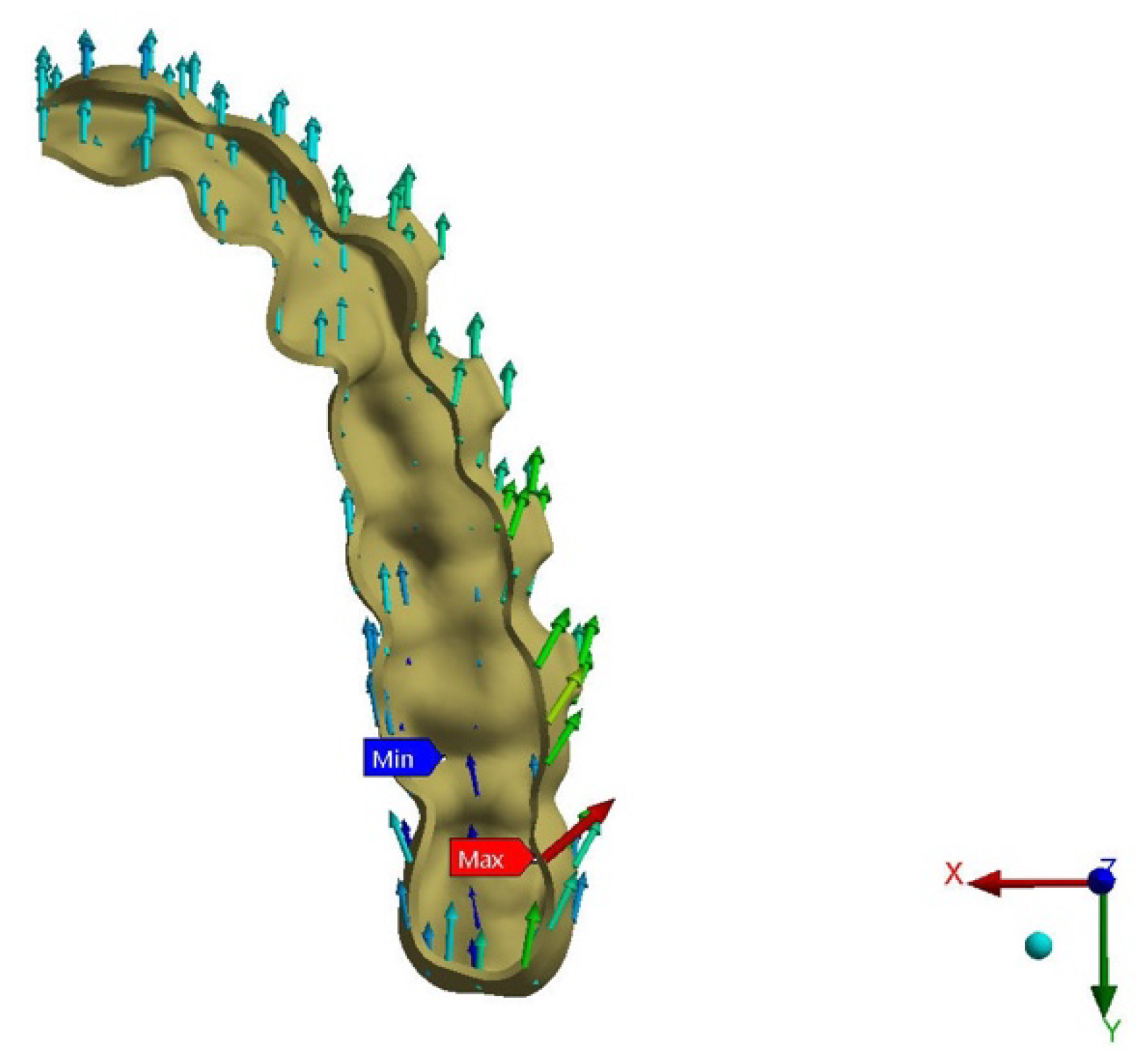

Figure 5.
NO ATT contact pressure.
Figure 5.
NO ATT contact pressure.
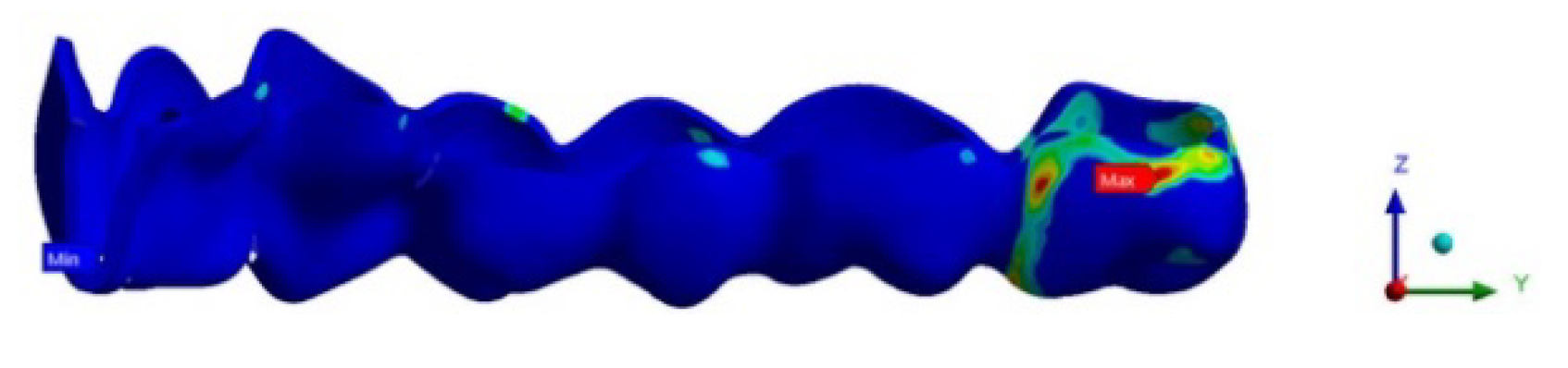

Figure 6.
ATT 3–6 contact pressure.
Figure 6.
ATT 3–6 contact pressure.
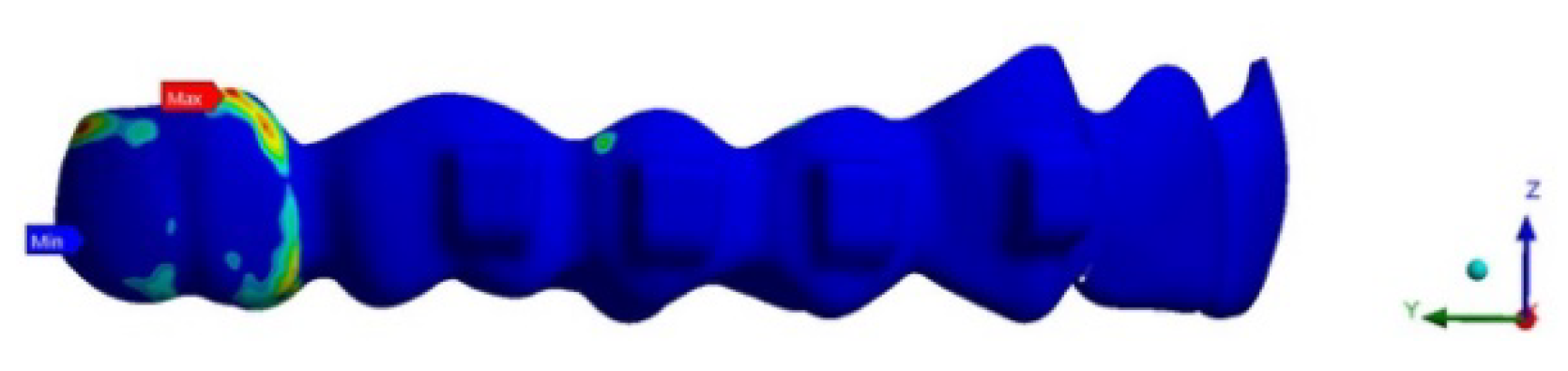

Figure 7.
ATT 3–7 contact pressure.
Figure 7.
ATT 3–7 contact pressure.
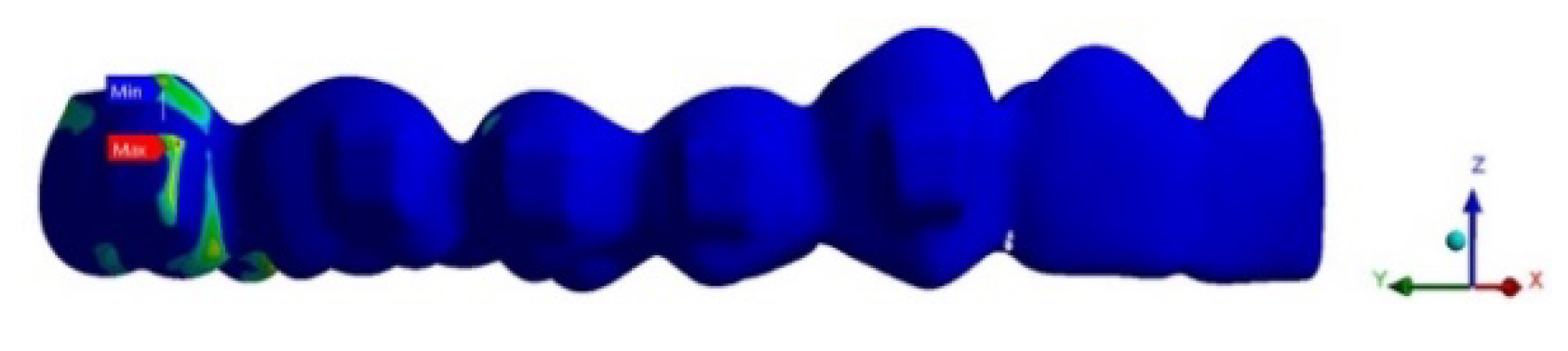
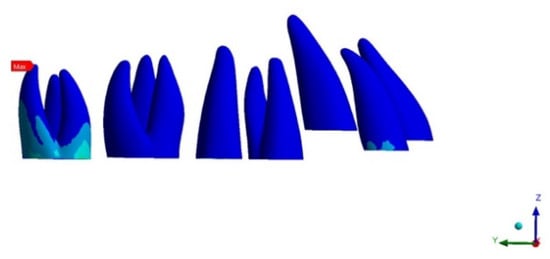
Figure 8.
PDL pressure (lateral view).
Figure 8.
PDL pressure (lateral view).
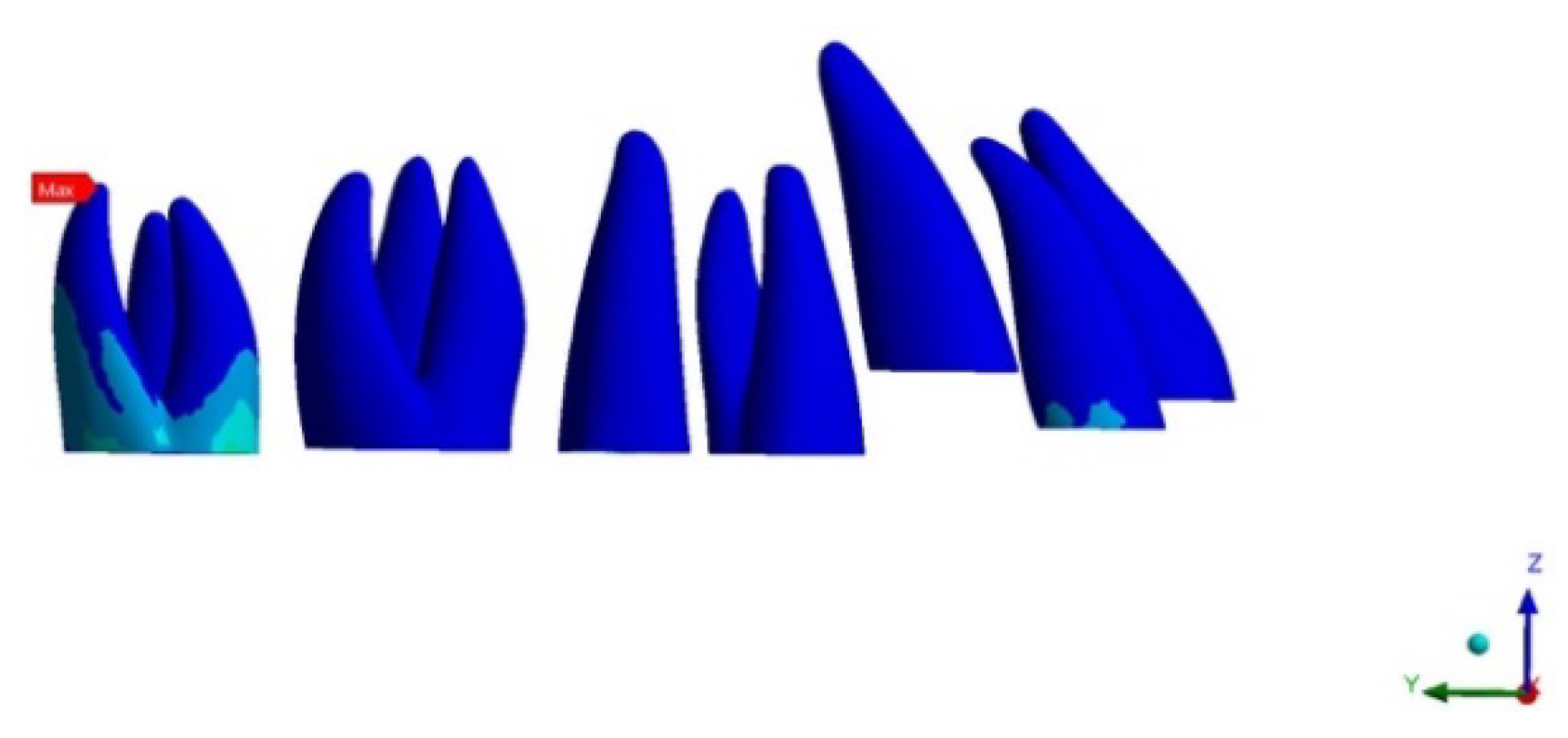
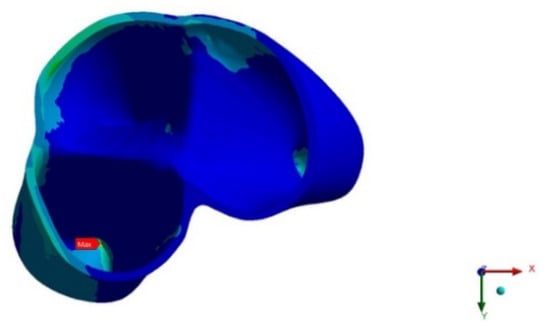
Figure 9.
Upper second molar PDL pressure (occlusal view).
Figure 9.
Upper second molar PDL pressure (occlusal view).
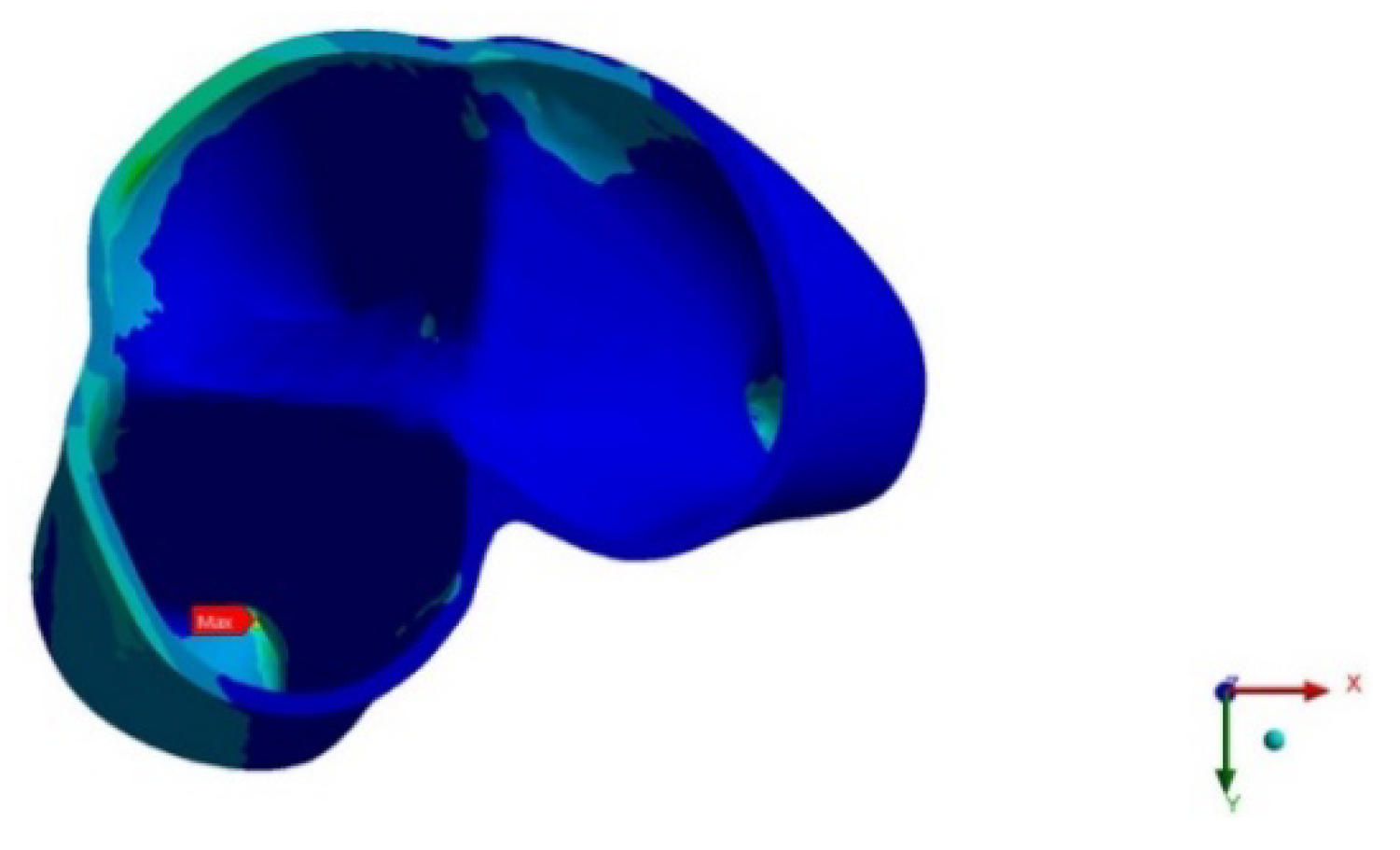
4. Discussion
Garino et al. and Ravera et al. demonstrated that upper molar distalization efficiency is strictly dependent on the use of attachments, as well as Class II elastics [6,7]. Within this research, Class II elastics were not considered since the aim was to test the actual efficacy of aligners only in distalizing upper molars. Based on our results, one could state that attachments have an influence on the force level and tooth displacement. However, in all the analyzed configurations, the amount of molar distalization reached was not enough to establish that aligners alone are effective at performing this kind of movement. Such findings are consistent with what was demonstrated in previous clinical trials [6,7].
This study is the first attempt to uncover the force system and biomechanical behavior of aligners during distalization. In our opinion, one shall focus on aligner deformation: the obtained results demonstrated that even with a full set of attachments, the majority of programmed tooth movement (0.2 mm) would be lost in mesio-buccal deformation of aligners upon insertion. Even if limited in time, this information could help us interpret clinical conditions in which the amount of space between molars generated from the replacement of aligners, as well as the amount of sagittal correction, does not match the ClinCheck® simulation. Another effect of the mesial deformation of aligner upon insertion is the buccal shift of lateral incisor, which represents the maximum displacement area in NO ATT and ATT 3–7 setups, while in ATT 3–6 present almost an equal amount of movement with respect to the second molar. Thus, this biomechanical study seems to confirm the clinical experiences of several experts that report this tooth as the most difficult to control with orthodontic aligners.
In analyzing the obtained results, it should be highlighted that the configurations with attachments are more effective in terms of the amount of displacement and PDL stress compared to a NO ATT configuration. The best performing model for tooth displacement appears to be ATT 3–6, which also presents the highest-pressure value at the PDL level. A similar study by Simon et al. that analyzed force systems during distalization reported that the presence of attachments increased the measured force on the upper molar, although the authors reported it to be not statistically significant [15].
The slight differences in terms of tooth displacement and PDL stress between ATT 3–7 and ATT 3–6 could be explained on the basis of different aligner stiffnesses resulting from the number of applied attachments. In the ATT 3–6 configuration, the attachment units from tooth 1.6 to tooth 1.3 should act as an anchorage against the desired force (producing molar distalization) and the undesired effect (incisors buccal flaring). However, this assumption is true to a limited extent since anchorage preservation on lateral incisor still remains poor. The second molar, on which the aligner is acting to produce the distalization movement, is covered by a more elastic aligner section with respect to the anchorage unit; therefore, more displacement could be expected.
On the other hand, the increased number of attachments in ATT 3–7 aligner could reduce the amount of second molar distalization, compared to the previous configuration, since the aligner section covering this tooth presents increased stiffness due to its anchorage to a rectangular attachment. However, these results are in contrast with the one published by Garino et al. [7] in their 2016 study. The obtained results resemble the type of tooth movement obtained by placing an open spring between second and first molar braces in conventional orthodontics; so, as it would be done with fixed appliances, anchorage reinforcement with auxiliaries is a mandatory choice to improve the efficiency of the system. These assumptions may help do clarify the different results obtained in our study and in the one by Garino et al. [7]. Furthermore, it should be remembered that registered efficiency in FEM simulations is limited to the insertion time and first reaction of the system to the aligner mismatch. Probably, in the clinical environment, in time, the force system will be modified, bringing to different results, as demonstrated by Yokoi et al. in their 2019 study [16]. However, different activation techniques of aligners from our model still could not allow for time-dependent results. Simulations with time effect are solicited to clarify this point.
Regarding contact pressure on the aligner, it seems that the effective pressure area for molar distalization is located on the mesio-buccal surface of the second molar. Our results demonstrate that attachments on active units are actively involved in producing tooth movement, since in the ATT 3–7 configuration, the maximum stress area is located on the buccal surface of the attachment, differently from other configurations where the active area is located on gingival surfaces of aligners. Aligner fitting depends on the selected material and the thermoforming technique [17]. However, the aligners’ gingival margin is known to be the most elastic section of the aligner and, consequently, the one with more chances to lose fitting [18]. Therefore, it could be postulated that active areas at the gingival edges of the aligners could reduce their efficiency within the clinical setting.
Thus, it could be stated that ATT 3–7 and ATT 3–6 configurations present, in an in silico environment, almost equal effectiveness at distalizing the upper second molar. However, translating such evidence in a clinical setting, the ATT 3–7 configuration is indicated because of the distribution of active surfaces on the aligner and as a means of reducing the risk of a loose fitting of the aligner on the last molar, thanks to the higher elasticity of the aligner’s terminal portion. However, if due to patient-related issues (anatomical factors, bad compliance, e.g., bonding of attachments on upper second molar results to be a very difficult procedure, ATT 3–6 may represent an efficient choice for upper distalization with clear aligners.
It should always be kept in mind that this FEM analysis describes the force system during the insertion of the aligner and not the results of its elastic return.
5. Limitations of the Study
FEM studies represent one of the best ways to analyze force systems delivered by orthodontic appliances. However, in vitro and in vivo study results may differ. When analyzing aligner deformations, we should always keep in mind that polymer material, friction phenomena, thermoplastic material properties, thermoforming procedures and insertion and removal of the appliance are all factors acting on aligner mechanical properties. Unfortunately, most of those factors are patented and not disclosed by companies and, therefore, cannot be used to increase the complexity of FEM analyses.
Occlusal forces deriving from functional and parafunctional contacts affect the applied orthodontic force [2]. Therefore, future FEM analyses should also consider those effects in orthodontic tooth movement control.
High-quality clinical trials are required to confirm FEM-derived force systems. Additionally, the study could be improved and integrated by examining other possibilities, such as attachments placed on every maxillary tooth or repeated simulations with other attachment designs.
6. Conclusions
On the basis of this study and within the limitations of the applied methodology, it can be concluded that:
- (1)
- attachments are mandatory to control the bodily movement of a second molar;
- (2)
- attachments should be used to reinforce anchorage units and to function as active units on distalizing molars;
- (3)
- considering the location of the aligner’s active surfaces and the clinical feasibility of attachment configuration, it can be stated that ATT 3–7 represents the most promising model for the clinical setting when Class II correction is planned via maxillary molar distalization.
Author Contributions
G.R.—FEM analysis, writer; M.S.—writer; S.P.—FEM analysis; A.S.—writer, A.D.—study design; T.C.—study design. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to acknowledge Michele Camposaragna, for his precious help in designing the FEM framework adopted in this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
Castroflorio reports grants and personal fees from Align Technology, grants and non-financial support from 3M Unitek, grants and non-financial support from Sweden&Martina, outside the submitted work. Andrea Deregibus reports grants and non-financial support from 3M Unitek, grants and non-financial support from Sweden&Martina, outside the submitted work.
Abbreviations
| CAT | clear aligners treatment |
| FEM | finite element method |
| FEA | finite element analysis |
| PDL | periodontal ligament |
| NO ATT | no attachments |
| ATT 3–6 | 3 mm vertical rectangular attachment positioned on the buccal crown surface, from the right canine to the right first molar |
| ATT 3–7 | 3 mm vertical rectangular attachments on the buccal crown surface, from the right canine to the right second molar |
References
- Boyd, R.L. Esthetic orthodontic treatment using the Invisalign appliance for moderate to complex malocclusions. J. Dent. Educ. 2008, 72, 948–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossini, G.; Parrini, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Deregibus, A.; Debernardi, C.L. Efficacy of clear aligners in controlling orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic review. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossini, G.; Parrini, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Deregibus, A.; Debernardi, C.L. Periodontal health during clear aligners treatment: A systematic review. Eur. J. Orthod. 2015, 37, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, K. Invisalign treatment of dental Class II malocclusions without auxiliaries. J. Clin. Orthod. 2010, 44, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schupp, W.; Haubrich, J.; Neumann, I. Class II correction with the Invisalign system. J. Clin. Orthod. 2010, 44, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ravera, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Garino, F.; Daher, S.; Cugliari, G.; Deregibus, A. Maxillary molar distalization with aligners in adult patients: A multicenter retrospective study. Prog. Orthod. 2016, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garino, F.; Castroflorio, T.; Daher, S.; Ravera, S.; Rossini, G.; Cugliari, G.; Deregibus, A. Effectiveness of composite attachments in controlling upper-molar movement with aligners. J. Clin. Orthod. 2016, 50, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barone, S.; Paoli, A.; Razionale, A.V.; Savignano, R. Computational design and engineering of polymeric orthodontic aligners. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2017, 33, e2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.W.; Julien, K.C.; Jacob, H.; Campbell, P.M.; Buschang, P.H. Discomfort associated with Invisalign and traditional brackets: A randomized, prospective trial. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, J.P.; Peña, F.M.; Martínez, V.; Giraldo, D.C.; Cardona, C.I. Initial force systems during bodily tooth movement with plastic aligners and composite attachments: A three-dimen-sional finite element analysis. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konda, P.; Sa, T. Basic principles of finite element method and its applications in orthodontics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 16, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Papageorgiou, S.N.; Keilig, L.; Hasan, I.; Jäger, A.; Bourauel, C. Effect of material variation on the biomechanical behaviour of orthodontic fixed appliances: A finite element analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2016, 38, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Su, M.-Z.; Chang, H.-H.; Chiang, Y.C.; Tao, S.H.; Cheng, J.H.; Fuh, L.J.; Lin, C.P. Tension-compression viscoelastic behaviors of the periodontal ligament. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2012, 111, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.-Z.; Chang, H.-H.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Cheng, J.H.; Fuh, L.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Lin, C.P. Modeling viscoelastic behavior of periodontal ligament with nonlinear finite element analysis. J. Dent. Sci. 2013, 8, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Keilig, L.; Schwarze, J.; Jung, B.A.; Bourauel, C. Forces and moments generated by removable thermoplastic aligners: Incisor torque, premolar derotation, and molar distalization. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2014, 145, 728–736, published correction appears in 2014, 146, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, Y.; Arai, A.; Kawamura, J.; Uozumi, T.; Usui, Y.; Okafuji, N. Effects of Attachment of Plastic Aligner in Closing of Diastema of Maxillary Dentition by Finite Element Method. J. Healthc. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1075097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, E.; Castroflorio, E.; Rossini, G.; Garino, F.; Cugliari, G.; Deregibus, A.; Castroflorio, T. Scanning electron microscopy evaluation of aligner fit on teeth. Angle Orthod. 2018, 88, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, W.; Dathe, H.; Fialka-Fricke, J.; Fricke-Zech, S.; Zapf, A.; Kubein-Meesenburg, D.; Sadat-Khonsari, R. Influence of thermoplastic appliance thickness on the magnitude of force delivered to a maxillary central incisor during tipping. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 136, 12.e1–12.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
