Hemibiotrophic Phytophthora infestans Modulates the Expression of SWEET Genes in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
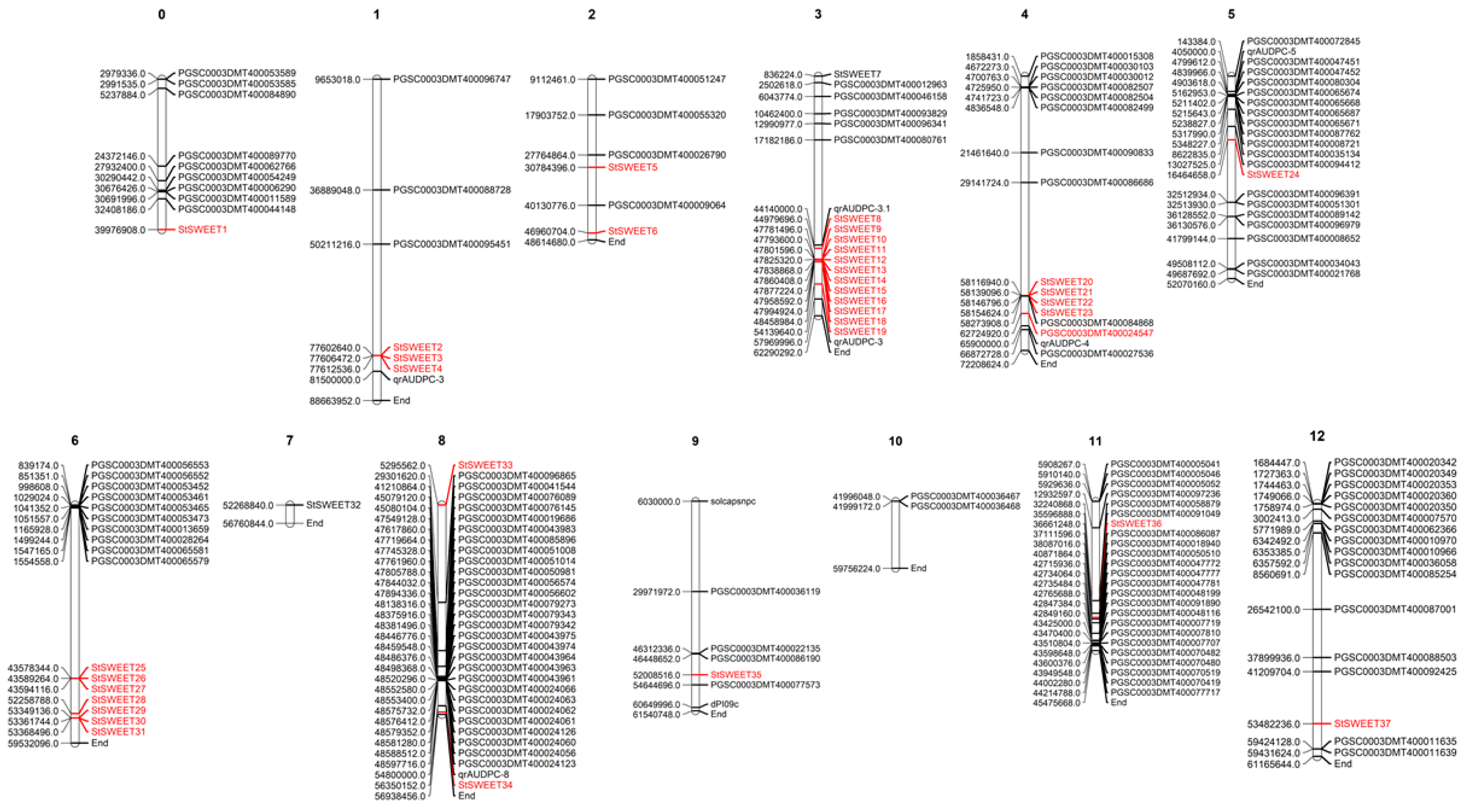
2.1. Distribution of SWEET Genes in Potato Genome and Their Co-Localization with Loci Governing Resistance to P. infestans
2.2. In Sillico Analysis of StSWEET Proteins
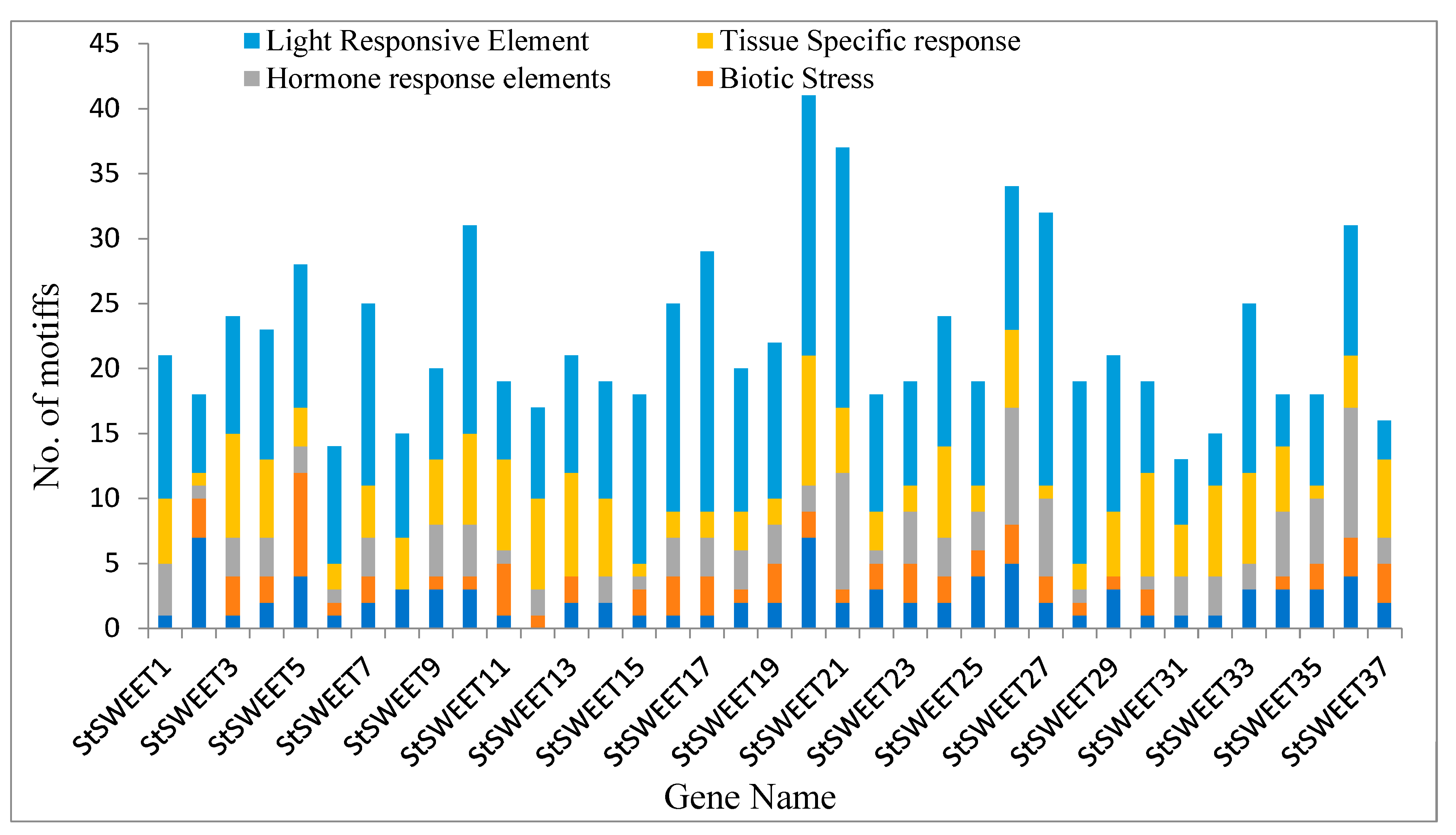
2.3. Prediction of cis-Acting Elements in the Putative Promoter Elements of StSWEET Genes
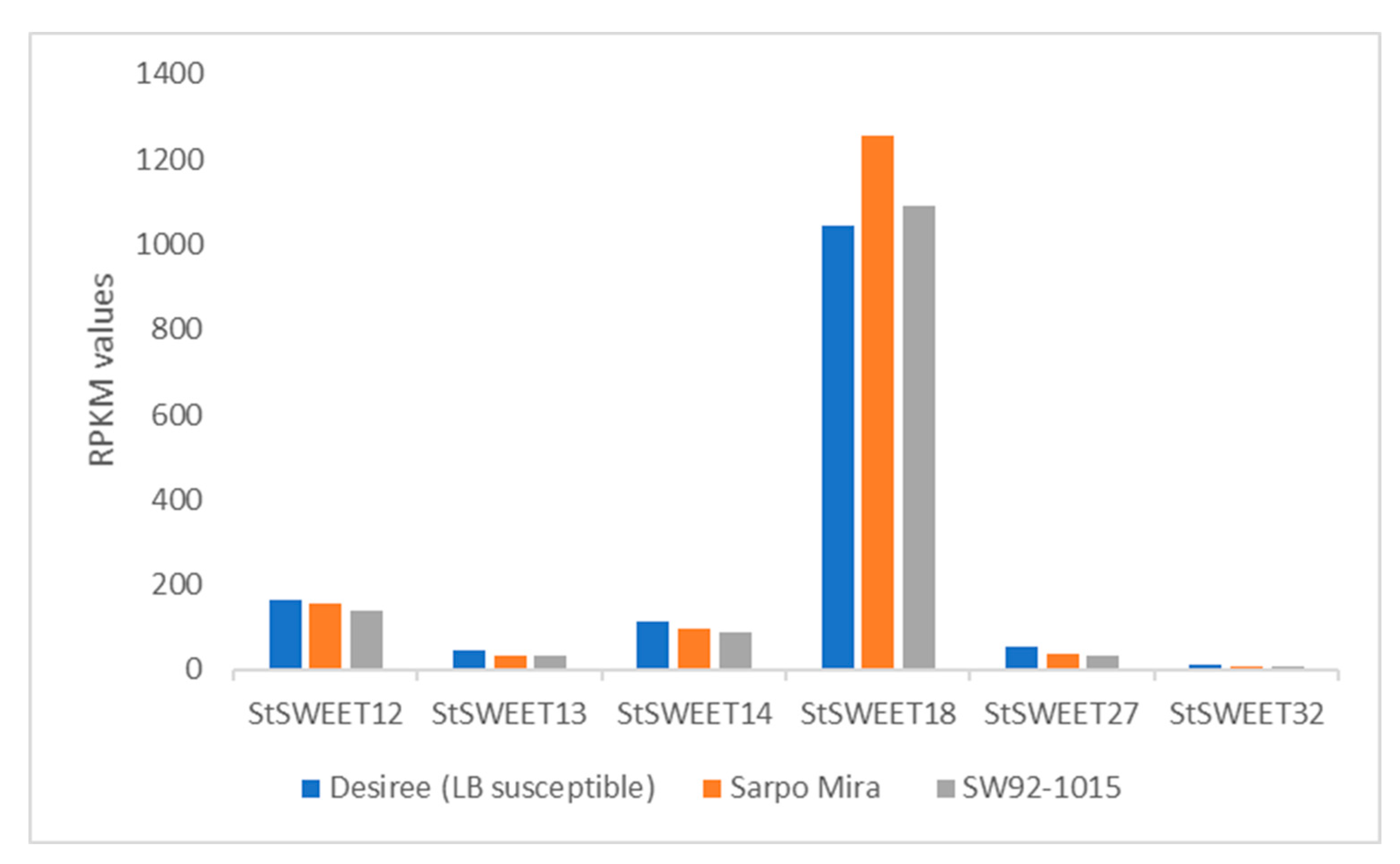
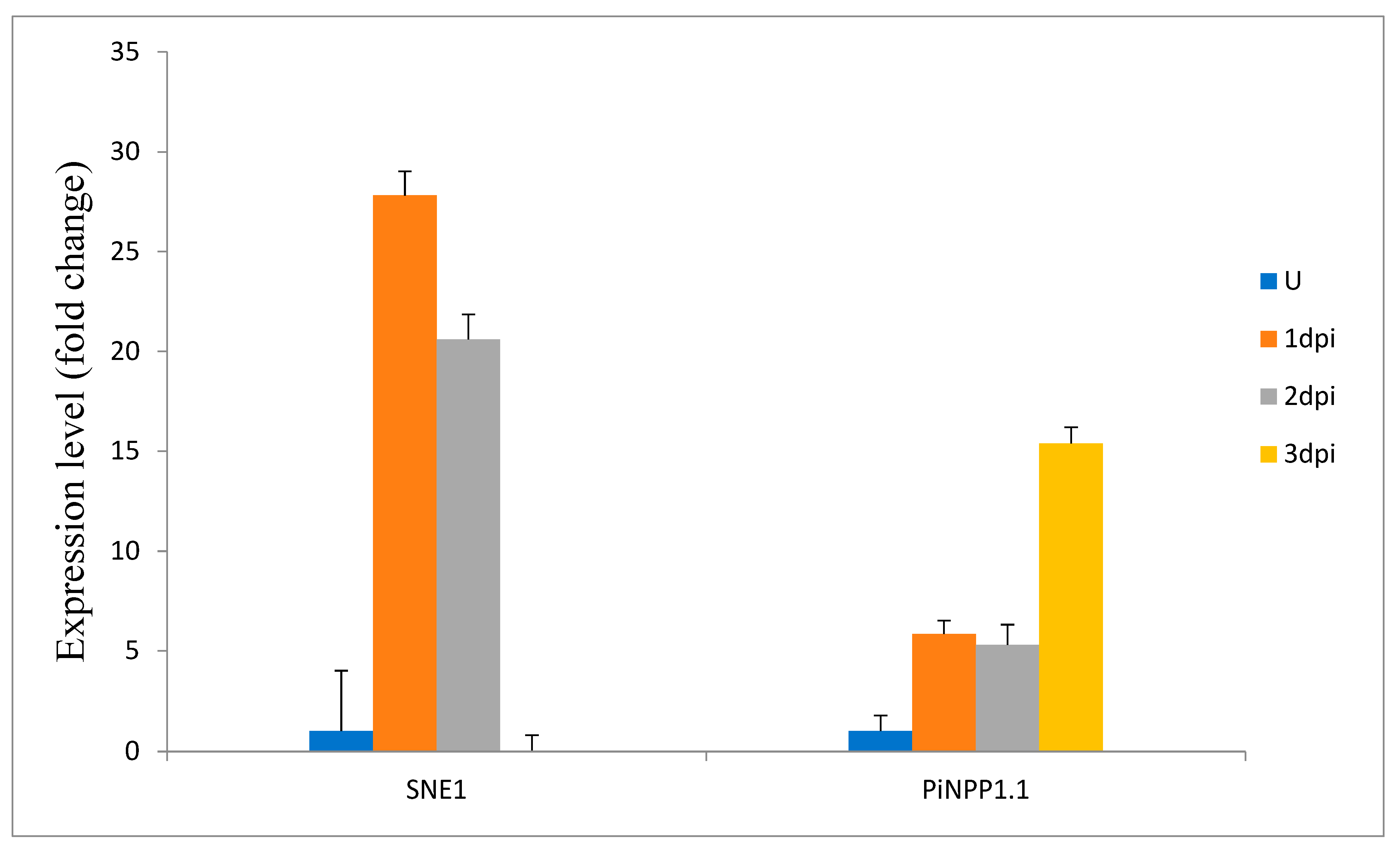
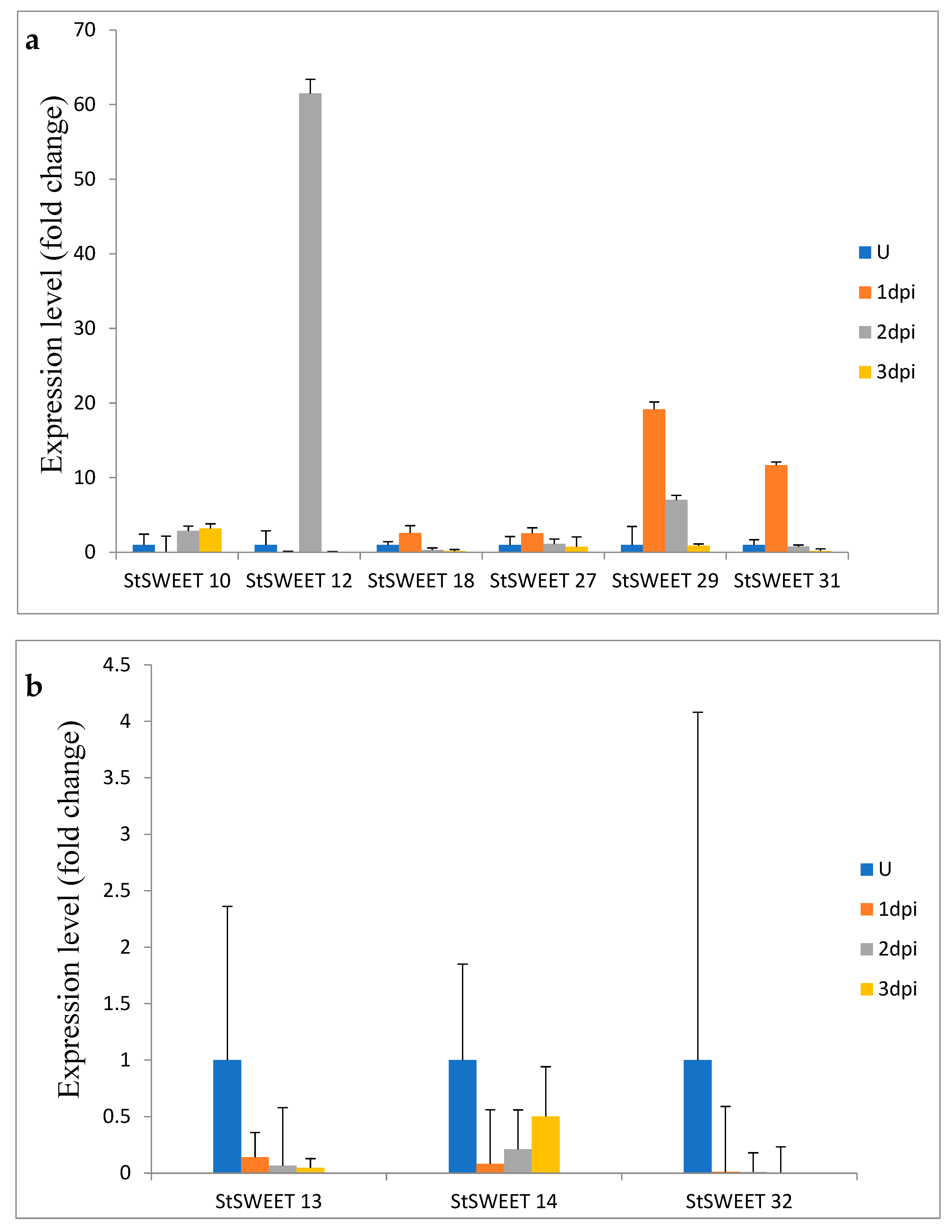
2.4. Expression Profiling of StSWEET Genes under P. infestans Challenge Inoculation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genome-Wide Identification and Phylogenetic Evaluation of SWEET Genes
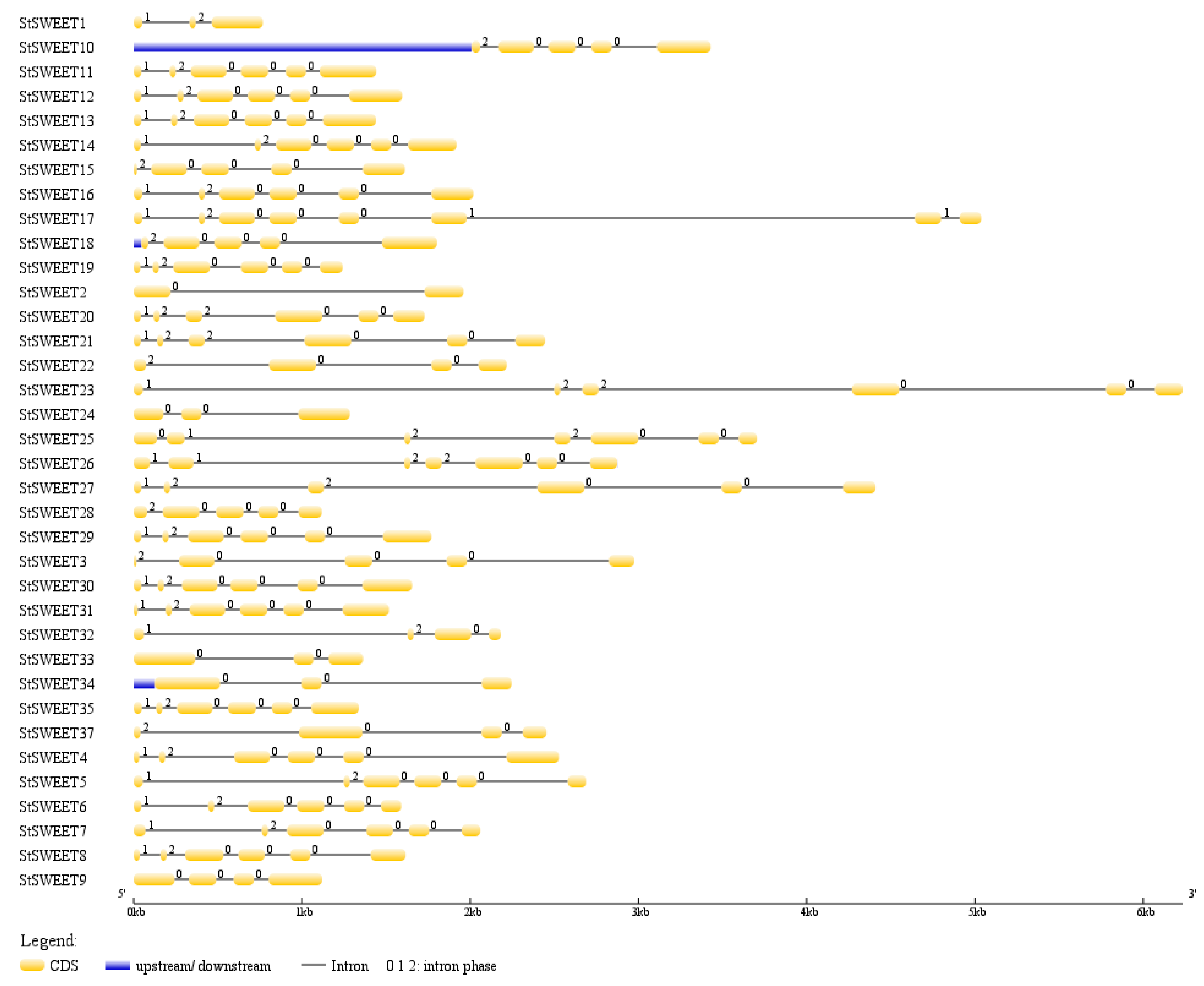
4.2. Gene Structure Analysis
4.3. In Silico Structural Analysis of StSWEET Proteins
4.4. Sub-Cellular Localization, Prediction of Leucine-Rich Nuclear Export Signals (NES), and Gene Ontology (GO) Annotations of StSWEETs
4.5. Identification of cis-Elements in Putative Promoter Elements
4.6. Co-Localization StSWEET and R genes to P infestans
4.7. Expression Dynamics of StSWEET Genes under Late Blight Disease in Potato
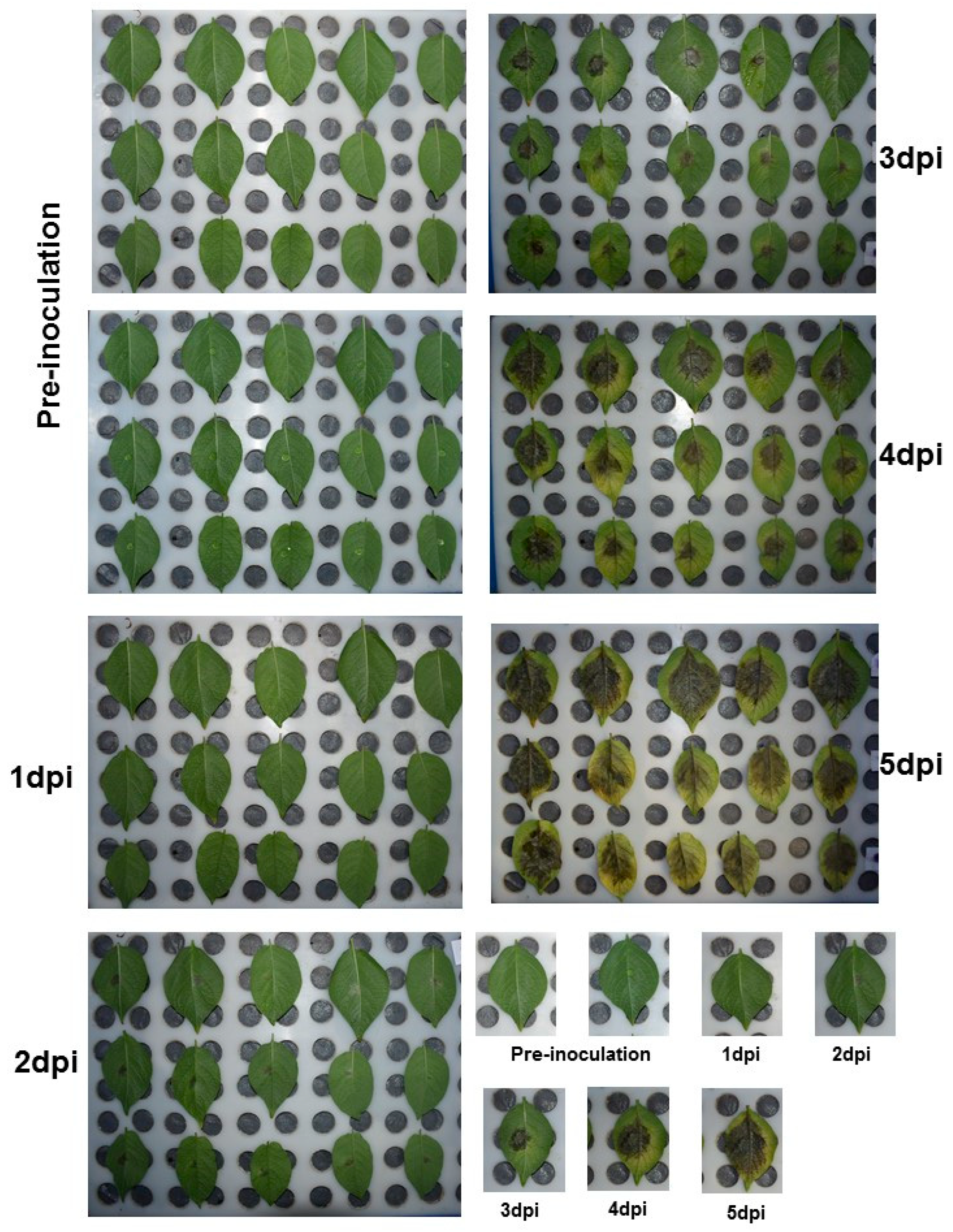
4.8. Detached Leaf Assay for P. infestans
4.9. Plant Material and Validation of StSWEET Gene Expression Profiles along with the Biotrophic and Necrotrophic Markers of P. infestans by Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.10. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.Q.; Qu, X.Q.; Hou, B.H.; Sosso, D.; Osorio, S.; Fernie, A.R.; Frommer, W.B. Sucrose efflux mediated by SWEET proteins as a key step for phloem transport. Science 2012, 335, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Q.; Hou, B.H.; Lalonde, S.; Takanaga, H.; Hartung, M.L.; Qu, X.Q.; Guo, W.J.; Kim, J.G.; Underwood, W.; Chaudhuri, B.; et al. Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange and nutrition of pathogens. Nature 2010, 468, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slewinski, T.L.; Meeley, R.; Braun, D.M. Sucrose transporter1 functions in phloem loading in maize leaves. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streubel, J.; Pesce, C.; Hutin, M.; Koebnik, R.; Boch, J.; Szurek, B. Five phylogenetically close rice SWEET genes confer TAL effector-mediated susceptibility to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denance, N.; Szurek, B.; Noel, L.D. Emerging functions of nodulin-like proteins in non-nodulating plant species. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, M.; Bart, R.S.; Shybut, M.; Dahlbeck, D.; Gomez, M.; Morbitzer, R.; Hou, B.H.; Frommer, W.B.; Lahaye, T.; Staskawicz, B.J. Xanthomonas axonopodis virulence is promoted by a transcription activator-like effector-mediated induction of a SWEET sugar transporter in Cassava. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2014, 27, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Piron, M.; Meyer, S.; Merdinoglu, D.; Bertsch, C.; Mestre, P. The SWEET family of sugar transporters in grapevine: VvSWEET4 is involved in the interaction with Botrytis cinerea. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 6589–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Boevink, P.; McLellan, H.; Armstrong, M.; Bukharova, T.; Qin, Z.; Birch, P.R. A host KH RNA-binding protein is a susceptibility factor targeted by an RXLR effector to promote late blight disease. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boevink, P.C.; Mclellan, H.; Gilroy, E.M.; Naqvi, S.; He, Q.; Yang, L.; Birch, P.R.J. Oomycetes Seek Help from the Plant: Phytophthora infestans effectors target host susceptibility factors. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Han, J.; Han, X.; Jiang, J. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny, and expression analysis of the SWEET gene family in tomato. Gene 2015, 573, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manck-Götzenberger, J.; Requena, N. Arbuscular mycorrhiza symbiosis induces a major transcriptional reprogramming of the potato SWEET sugar transporter family. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Rose, J.K. Mediation of the transition from biotrophy to necrotrophy in hemibiotrophic plant pathogens by secreted effector proteins. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 769–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lyu, H.M.; Zhu, K.; Van de Peer, Y.; Cheng, Z.M. The emergence and evolution of intron-poor and intronless genes in intron-rich plant gene families. Plant J. 2010, 105, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruivo, R.; Bellenchi, G.C.; Chen, X.; Zifarelli, G.; Sagne, C.; Debacker, C.; Pusch, M.; Supplisson, S.; Gasnier, B. Mechanism of proton/substrate coupling in the heptahelical lysosomal transporter cystinosin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezegou, A.; Llinares, E.; Anne, C.; Kieffer-Jaquinod, S.; O’Regan, S.; Aupetit, J.; Chabli, A.; Sagne, C.; Debacker, C.; Chadefaux-Vekemans, B.; et al. Heptahelical protein PQLC2 is a lysosomal cationic amino acid exporter underlying the action of cysteamine in cystinosis therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3434–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, P.J.; Park, J.M.; Kang, S.K.; Kim, S.G.; Park, C.M. An Arabidopsis senescence-associated SAG29 regulates cell viability under high salinity. Planta 2011, 233, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, H.; Wilson, C.; Wahid, A.; Condamine, P.; Cui, X.; Close, T.J. Expression analysis of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) during salinity stress. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2006, 6, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, E.S.; Kwang-Hyun, B.; Sang-Keun Oh Jo, S.H.; Yi, S.Y.; Park, J.M.; Joung, Y.H.; Lee, S.; Cho, H.S.; Choi, D. Induction of enhanced tolerance to cold stress and disease by overexpression of the pepper CaPIF1 gene in tomato. Physiol. Plant. 2007, 129, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosso, D.; Chen, L.Q.; Frommer, W.B. Encyclopedia of Biophysics; Roberts, G., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 2556–2558. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, Y.H.; Hu, Y.B.; Chen, L.Q.; Sosso, D.; Ducat, D.C.; Hou, B.H.; Frommer, W.B. Functional role of oligomerization for bacterial and plant SWEET sugar transporter family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3685–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cheung, L.S.; Feng, L.; Tanner, W.; Frommer, W.B. Transport of Sugars. Frommer Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 84, 865–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Sugio, A.; White, F.F. Os8N3 is a host disease susceptibility gene for bacterial blight of rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10503–10508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kan, J.A.; Shaw, M.W.; Grant-Downton, R.T. Botrytis species: Relentless necrotrophic thugs or endophytes gone rogue? Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 15, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandil, R.K.; Chakrabarti, S.K.; Singh, B.P.; Sharma, S.; Sundaresha, S.; Kaushik, S.K.; Bhatt, A.K.; Sharma, N.N. Genotypic background of the recipient plant is crucial for conferring RB gene mediated late blight resistance in potato. BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.U.; Vanishree, G.; Pattanayak, D.; Sharma, S.; Bhardwaj, V.; Singh, B.P.; Chakrabarti, S.K. Complete mitogenome mapping of potato late blight pathogen, Phytophthora infestans A2 mating type. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2017, 2, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SWEET Name | Locus ID | Functional Annotation | Protein Length (Molecular Weight) | TM Domain | Sub-Cellular Localization | Hydro-Pathy | SWEET Semi-SWEET |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| StSWEET1 | LOC102591902 | BDST sweet12-like | 14,823.5 | 3 | Plasma membrane | 0.666 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET2 | Sotub01g037650 | BDSTsweet17like | 16,937.6 | 3 | _ | 0.336 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET3 | Sotub01g037660 | BDSTsweet16like | 24,470.8 | 5 | _ | 0.597 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET4 | Sotub01g037670 | BDST sweet2alike | 32,147.2 | 7 | _ | 0.408 | SWEET |
| StSWEET5 | Sotub02g018000 | BDST sweet6alike | 25,571.5 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 1.022 | SWEET |
| StSWEET6 | Sotub02g035970 | BDST sweet2alike | 25,761.9 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.751 | SWEET |
| StSWEET7 | Sotub03g006170 | BDST sweet3like | 26,431.4 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.791 | SWEET |
| StSWEET8 | Sotub03g013630 | BDST sweet12like | 29,775.5 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.418 | SWEET |
| StSWEET9 | Sotub03g018270 | BDST sweet12like | 32,153.5 | 6 | Plasma membrane | 0.552 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET10 | Sotub03g018280 | BDST sweet12like | 32,782.3 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.668 | SWEET |
| StSWEET11 | Sotub03g018290 | BDST sweet12like | 33,762.3 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.661 | SWEET |
| StSWEET12 | Sotub03g018300 | BDST sweet12like | 33,086.8 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.673 | SWEET |
| StSWEET13 | Sotub03g018310 | BDST sweet12like | 33,533.2 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.646 | SWEET |
| StSWEET14 | Sotub03g018320 | BDST sweet14like | 32,061.6 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.734 | SWEET |
| StSWEET15 | Sotub03g018330 | BDST sweet12like | 28,119.5 | 6 | Plasma membrane | 0.567 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET16 | LOC102603273 | BDST sweet14-like | 30,780.5 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.569 | SWEET |
| StSWEET17 | LOC102603614 | BDST sweet14-like | 39,953 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.401 | SWEET |
| StSWEET18 | Sotub03g022530 | BDST sweet5like | 32,415.1 | 6 | Plasma membrane | 0.615 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET19 | Sotub03g027590 | BDST sweet1like | 26,664.8 | 7 | _ | 0.641 | SWEET |
| StSWEET20 | Sotub04g024600 | BDST n3like | 27,791 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.658 | SWEET |
| StSWEET21 | Sotub04g024590 | BDST sweet1like | 27,669 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.604 | SWEET |
| StSWEET22 | Sotub04g024580 | BDST sweet1like | 24,431.5 | 6 | _ | 0.551 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET23 | Sotub04g024570 | BDST sweet1like | 27,967.5 | 7 | _ | 0.746 | SWEET |
| StSWEET24 | Sotub05g020570 | BDST sweet12like | 22,166.2 | 4 | Plasma membrane | 0.621 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET25 | LOC102600141 | BDST sweet1-like | 33,207.1 | 7 | _ | 0.483 | SWEET |
| StSWEET26 | LOC102599475 | BDST sweet1-like | 35,193.5 | 6 | _ | 0.515 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET27 | LOC102599149 | BDST sweet1-like | 28,236.5 | 7 | _ | 0.706 | SWEET |
| StSWEET28 | Sotub06g029710 | BDST sweet2like | 26,672.8 | 7 | _ | 0.739 | SWEET |
| StSWEET29 | Sotub06g028350 | BDST sweet5like | 32,750.1 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.646 | SWEET |
| StSWEET30 | Sotub06g028340 | BDST sweet12like | 33,158.6 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.727 | SWEET |
| StSWEET31 | Sotub06g028330 | BDST sweet12like | 31,290.5 | 7 | Plasma membrane | 0.708 | SWEET |
| StSWEET32 | Sotub07g025190 | BDST sweet7like | 14,442.9 | 3 | _ | 0.401 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET33 | LOC102603968 | BDST sweet4-like | 26,330.8 | 6 | _ | 0.649 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET34 | Sotub08g027480 | BDST sweet14like | 25,698.8 | 6 | Plasma membrane | 0.607 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET35 | Sotub09g022640 | BDST sweet7like | 32,627.5 | 7 | _ | 0.451 | SWEET |
| StSWEET36 | Sotub11g020620 | BDSTsweet4like | 15,062.2 | 3 | _ | 0.983 | Semi-SWEET |
| StSWEET37 | Sotub12g024450 | BDST sweet17like | 25,321.5 | 6 | _ | 0.709 | Semi-SWEET |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kardile, H.B.; Karkute, S.G.; Challam, C.; Sharma, N.K.; Shelake, R.M.; Kawar, P.G.; Patil, V.U.; Deshmukh, R.; Bhardwaj, V.; Chourasia, K.N.; et al. Hemibiotrophic Phytophthora infestans Modulates the Expression of SWEET Genes in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plants 2023, 12, 3433. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193433
Kardile HB, Karkute SG, Challam C, Sharma NK, Shelake RM, Kawar PG, Patil VU, Deshmukh R, Bhardwaj V, Chourasia KN, et al. Hemibiotrophic Phytophthora infestans Modulates the Expression of SWEET Genes in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plants. 2023; 12(19):3433. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193433
Chicago/Turabian StyleKardile, Hemant B., Suhas Gorakh Karkute, Clarissa Challam, Nirmal Kant Sharma, Rahul Mahadev Shelake, Prashant Govindrao Kawar, Virupaksh U. Patil, Rupesh Deshmukh, Vinay Bhardwaj, Kumar Nishant Chourasia, and et al. 2023. "Hemibiotrophic Phytophthora infestans Modulates the Expression of SWEET Genes in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.)" Plants 12, no. 19: 3433. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193433
APA StyleKardile, H. B., Karkute, S. G., Challam, C., Sharma, N. K., Shelake, R. M., Kawar, P. G., Patil, V. U., Deshmukh, R., Bhardwaj, V., Chourasia, K. N., & Valluri, S. D. (2023). Hemibiotrophic Phytophthora infestans Modulates the Expression of SWEET Genes in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plants, 12(19), 3433. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12193433








