Salt-Tolerant Phenomena, Sequencing and Characterization of a Glyoxalase I (Jojo-Gly I) Gene from Jojoba in Comparison with Other Glyoxalase I Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Salt Concentration
2.2. Culture Condition
2.3. DNA Cloning and Manipulation
2.4. DNA Cloning and DNA Sequencing
2.5. Ligation of the PCR Product with the pSC-A Vector
Preparation of Competent Cells and Transformation
2.6. Purification of DNA Fragment from Agarose Gel
2.7. Qiaquick Gel Extraction Protocol (from Qiagen)
2.8. Homology and Structural Comparison of Jojo-Gly I Gene from Jojoba
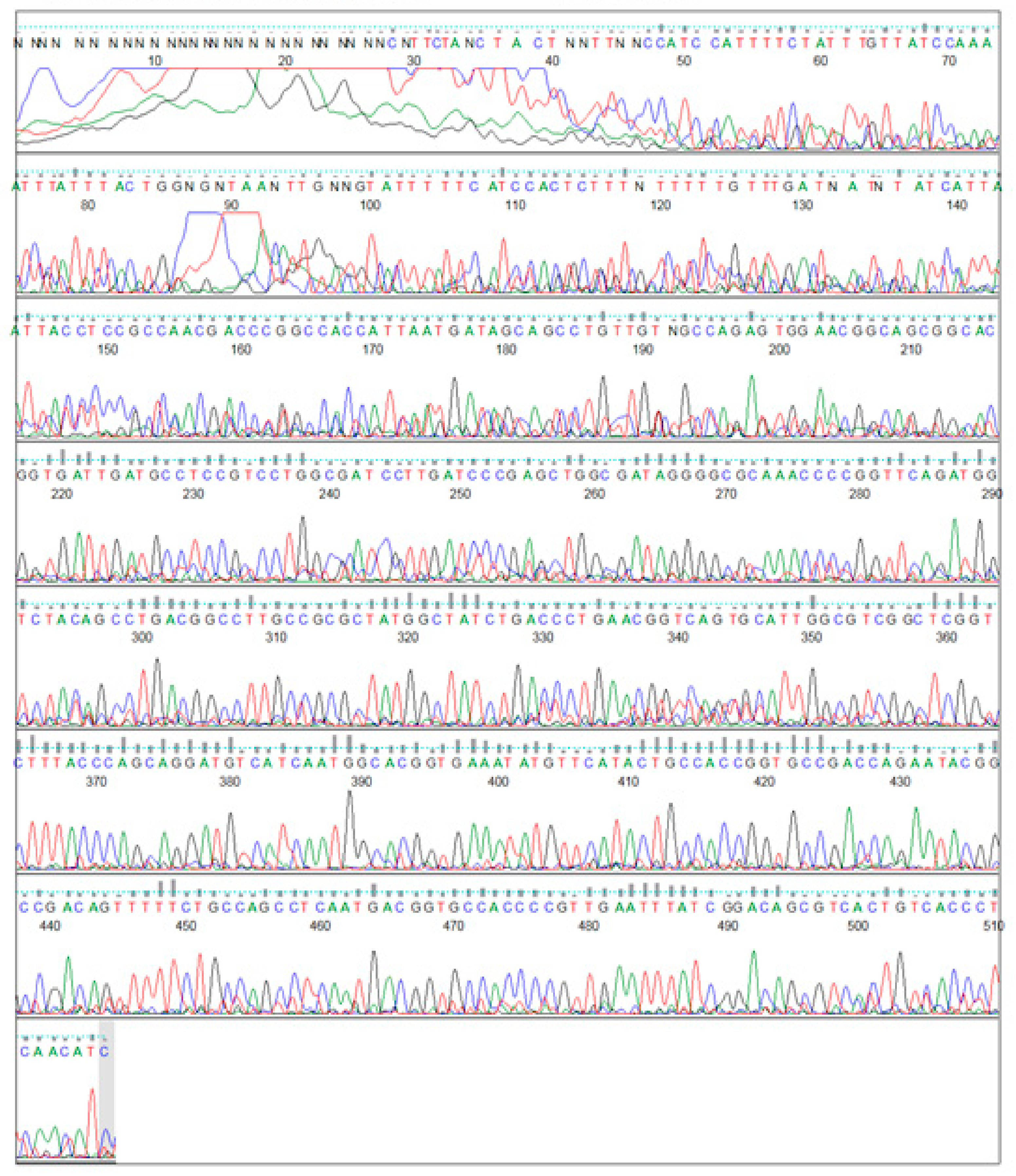
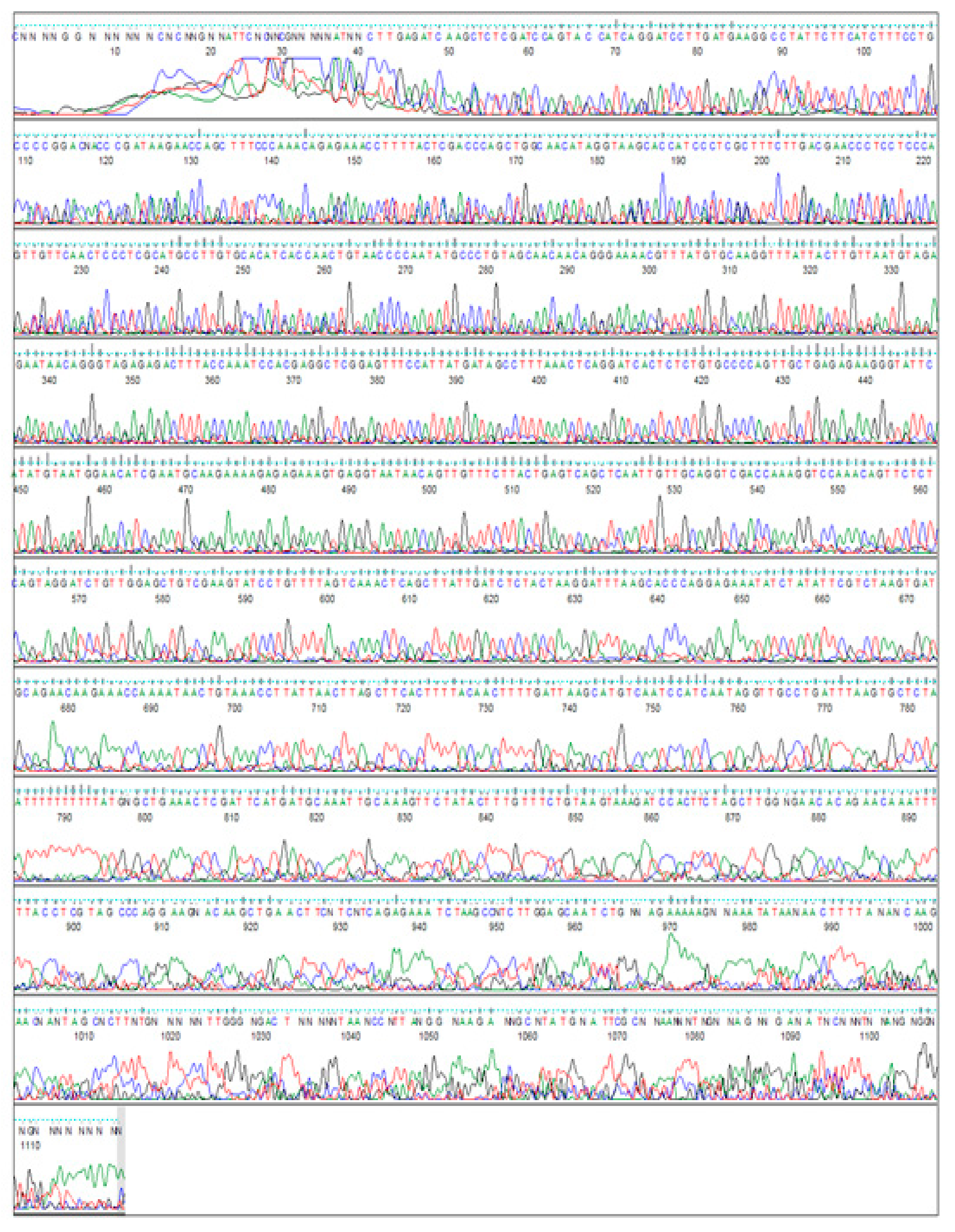
2.9. DNA Sequence Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Abiotic Stress Induced by NaCl on Growth of Jojoba Plant Tissue Culture
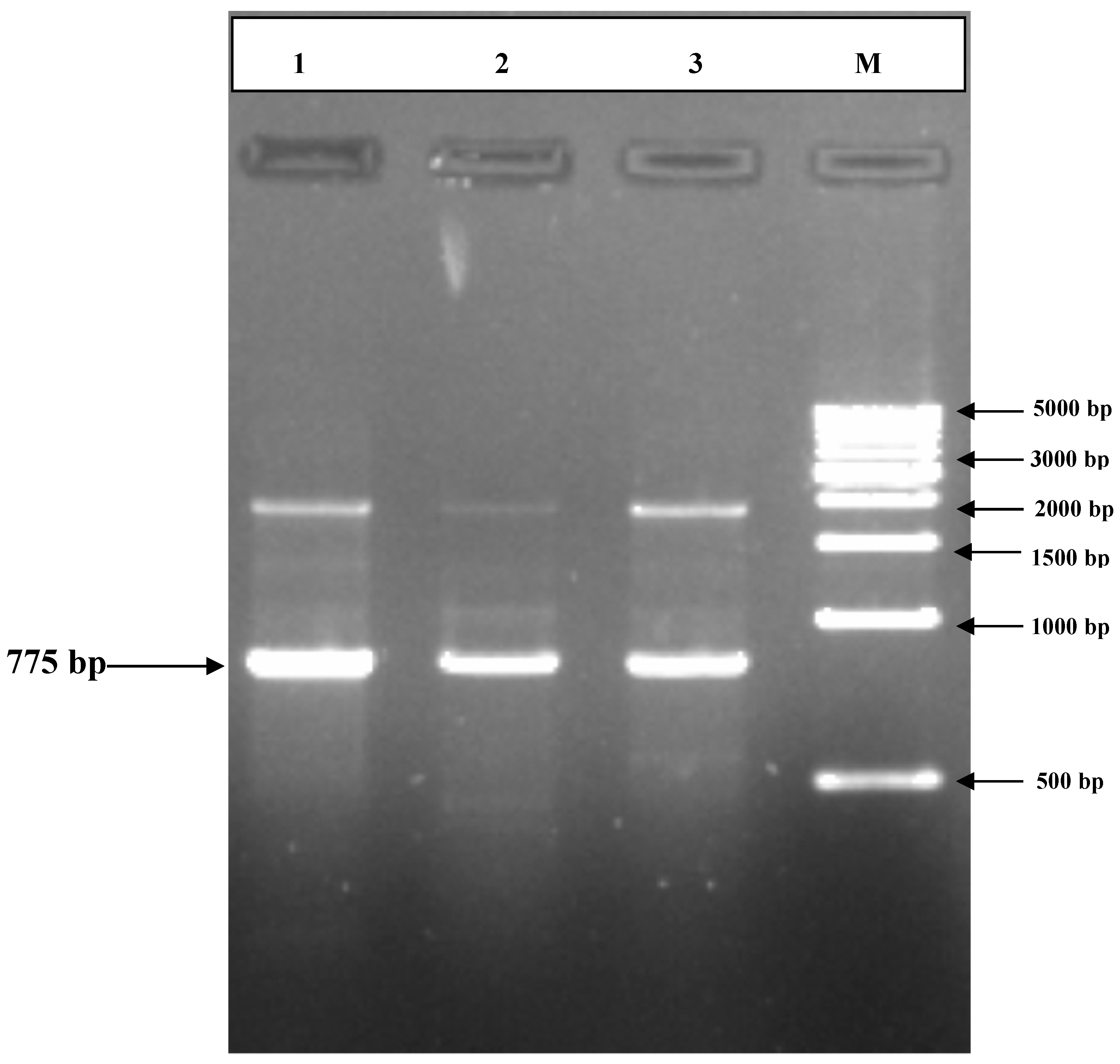
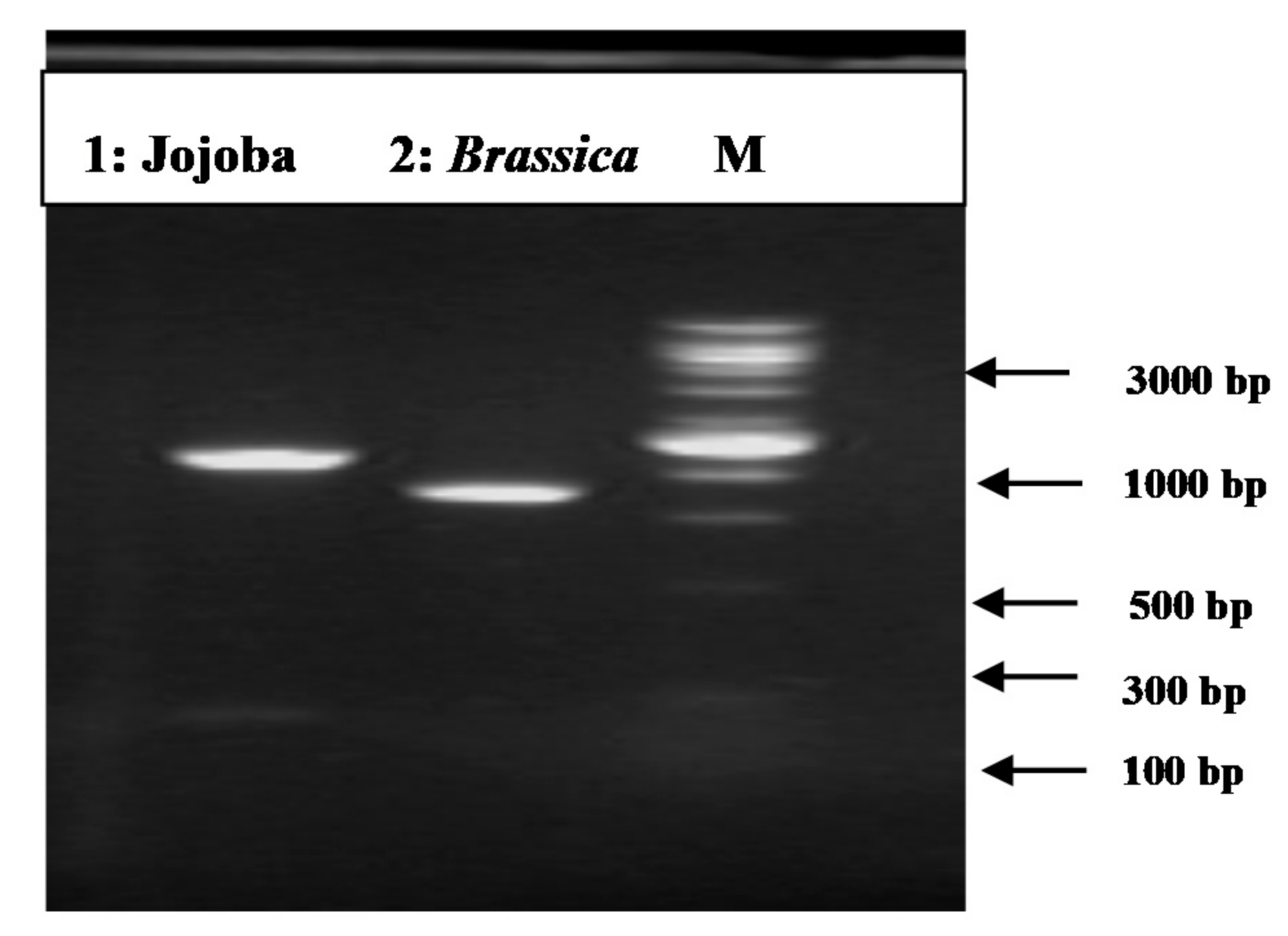
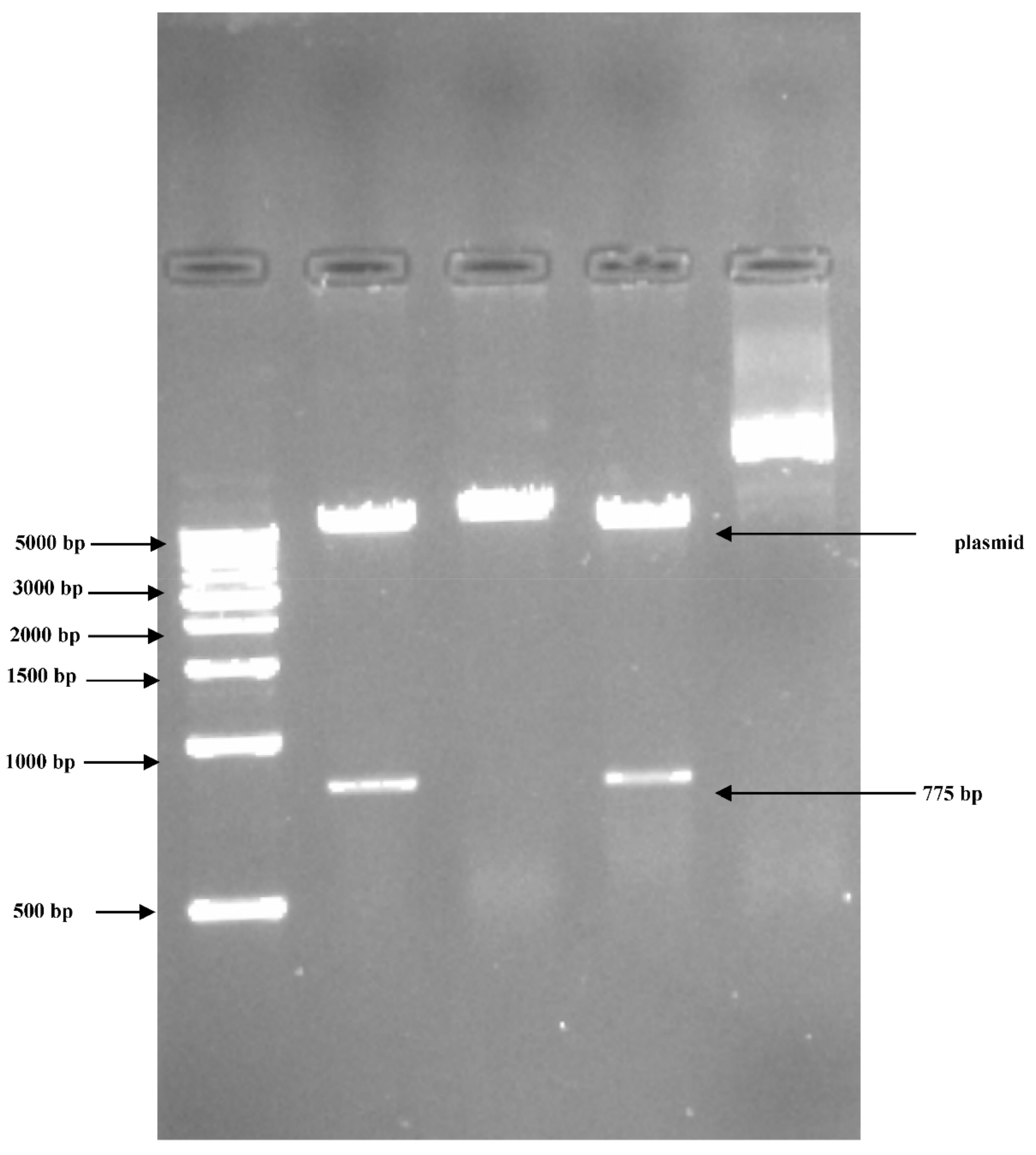
3.2. PCR Amplification of Jojoba Glyoxalase I (Jojo-Gly I) Gene
3.3. Cloning the 5’ End of the Jojo-Gly I
3.4. BLAST Search for Identical Protein Sequences
3.5. Phylogenetic and Glyoxalase I Analyses Show the Origin of Glyoxalase I Plant Genes Derived from Jojoba and Other Plants
3.6. Multiple-Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verbanic, C.J. Jojoba: Answer to sperm whale. Chem. Bus. 1986, 8, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, L.; Bernis, W.P. Buffalo gourd and Jojoba: Potential new crops for arid lands. Adv. Agron. 1983, 36, 317–349. [Google Scholar]
- El-Moguy, N. Jojoba the green gold hope for Egyptian desert development. In Proceedings of the Expert Group Meeting on Enhancing Competitiveness through the Promotion of Innovative Approaches in Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises, Manama, Bahrain, 10–12 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gentry, H.S. The natural history of Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis) and its cultural aspects. Econ. Bot. 1958, 12, 261–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Lv, X.; Gao, G.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Qiao, J.; Xu, K.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Xiao, X.; et al. Identification and characterization of a glyoxalase I gene in a rapeseed cultivar with seed thermotolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yan, B.; Shi, M.; Zhou, W.; Zekria, D.; Wang, H.; Kai, G. Overexpression of a Brassica campestris HSP70 in tobacco confers enhanced tolerance to heat stress. Protoplasma 2015, 253, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, M.; Hara, C.; Matsubayashi, Y.; Lin, L.; Liu, Q.; Tadokoro, F.; Aotsuka, S.; Uchimiya, H. Expressed sequenced tags from cultured cells of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under stressed conditions: Analysis of transcripts of genes engaged in ATP-generating pathways. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 25, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajit, G.; Tahmina, I. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of glyoxalase gene families in soybean (Glycine max) indicate their development and abiotic stress specific response. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, S.; Balasubramanian, K.A. Effect of methylglyoxal on protein thiol and amino groups in isolated rat enterocytes and colonocytes and activity of various brush border enzymes. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 27, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Leoncini, G.; Marsca, M.; Buzi, E. Inhibition of the glycolytic pathway by methylglyoxal in human platelets. Cell Biochem. Funct. 1989, 7, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapos, M.P.; Schaff Zs Garzo, T.; Antonie, F.; Mandl, J. Accumulation of phenols in isolated hepatocytes after pretreatment with methylglyoxal. Toxicol. Lett. 1991, 58, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alscher, R.G. Biosynthesis and antioxidant function of glutathione in plants. Physiol. Plant. 1989, 77, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.J.; Vernoux, T.; Leaver, C.; Montago, M.V.; Inze, D. Glutathione homeostasis in plants: Implications for environmental sensing and plant development. J. Expt. Bot. 1998, 49, 1102–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigellius, R. Oxidative Stress; Sies, H., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 243–272. [Google Scholar]
- Foyer, C.H.; Lelandais, M.; Galap, C.; Kunert, K.J. Effect of elevated cytosolic glutathione reductase activity on the cellular glutathione pool and photosynthesis in leaves under normal and stressed conditions. Plant Physiol. 1991, 97, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aono, M.; Kubo, A.; Saji, H.; Tanaka, K.; Kondo, N. Enhanced tolerance to photooxidative stress of transgenic Nicotiana tabacum with high chloroplastic glutathione reductase activity. Plant Cell Physiol. 1993, 34, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Roxas, V.P.; Smith, R.K.; Allen, E.R.; Allen, R.D. Overexpression of glutathione S-transferase/glutathione peroxidase enhances the growth of transgenic tobacco seedlings during stress. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 988–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noctor, G.; Arisi, A.-C.M.; Jouanin, L.; Kunert, K.J.; Rennenberg, H.; Foyer, C.H. Glutathione: Biosynthesis, metabolism and relationship to stress tolerance explored in transformed plants. J. Exp. Bot. 1998, 49, 623–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, N.; Thornalley, P.J. Glyoxalase in diabetes, obesity and related disorders. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, H.; Thapa, S.; Sangireddy, S.R.; Pei, X.; Liu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, S.; Hui, D.; Bhatti, S.; et al. Al-induced proteomics changes in tomato plants over-expressing a glyoxalase I gene. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, P.V.; Siraj, M.V.; Lalitha, C.R. Identification of partial genomic DNA sequence coding for Glyoxalase I gene in the white mangrove and its associated plant Ipomea Macrantha Roem & Schult: A casual interrelationship. Int. J. Bot. Stud. 2018, 3, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Espartero, J.; Sanchez-Aguayo, I.; Pardo, J.M. Molecular characterization of glyoxalase-I from a higher plant; upregulation by stress. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 29, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-S.; Umezawa, Y.; Ohmura, S.; Kato, S. Human glyoxalase I: cDNA cloning, expression and sequence similarity to glyoxalase I from Pseudomonas putida. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 11217–11221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, S.; Walsh, E.S.; Godwin, A.K.; Tew, K.D. Cloning and characterization of human colon glyoxalase I. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 5661–5667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rhee, H.-I.; Sato, N.; Murata, K.; Kimura, A. Nucleotide sequence of the glyoxalase I gene of Pseudomonas putida. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1987, 52, 2243–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lu, T.; Creighton, D.J.; Antoine, M.; Fenselau, C.; Lovett, P.S. The gene encoding glyoxalase I from Pseudomonas putida: Cloning, overexpression, and sequence comparisons with human glyoxalase I. Gene 1994, 150, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solliman, M.; Mohasseb, H.; Al-khateeb, S.; Al-khateeb, A. Use of date palm syrup as a substituent for sucrose in tissue culture medium of jojoba. PCBMB 2015, 16, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Solliman, M.; Shehata, W.; Mohasseb, H.A.; Aldaej, M.; Al-Khateeb, A.; Al-Khateeb, S.; Hegazy, A.; Abdel-Moneim, H. Induction of biochemical active constituents of Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis (Link) Schneider) callus affected by hormones. J. Med. Plants Res. 2017, 11, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Solliman, M.E.-D.M.; Mohasseb, H.A.A.; Al-Khateeb, A.A.; Al-Khateeb, S.A.; Chowdhury, K.; El-Shemy, H.A.; Aldaej, M.I. Identification and sequencing of date-SRY gene: A novel tool for sex determination of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, W.F.; Solliman, M.M.; Mohasseb, H.A.; Al-Khateeb-AAAldaej, M.I.; Alturki, S.M. Protocol of in vitro jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis (link) schneider) callus induction. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 21, 376–382. [Google Scholar]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, L.; Fritsch, E.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan, D. Techniques for transformation of Escherichia coli. In DNA Cloning, Volume I, A Practical Approach; Glover, D.M., Hrsg, S., Eds.; IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1985; pp. 109–135. [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff, S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene 1984, 28, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, R.A.; Duncan, D.P. A bays rule for symmetric multiple comparison problem. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1969, 64, 1485–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, K.A.; Gomez, A. Statistical Procedure for Agricultural Research—Hand Book; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencingwith chainterminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, J.M.; Martinez, V.; Carvajal, M. Ammonium, bicarbonate and calcium effects on tomato plants grown under saline conditions. Plant Sci. 2000, 157, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, M.V.; Satti, S.M. Calcium and potassium-enhanced growth and. Plant Sci. 1996, 114, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, A.; Pressman, E.; Imas, P.; Miltau, O. Combined effects of KNO3 and salinity on yield and chemical composition of lettuce and Chinese cabbage. Irrig. Sci. 1991, 12, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornalley, P.J. The glyoxalase system in health and disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 1993, 14, 287–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapos, M.P. Methylglyoxal toxicity in mammals. Toxicol. Lett. 1994, 73, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deswal, R.; Chakravarty, T.N.; Sopory, S.K. The glyoxalase system in higher plants: Regulation in growth and differentiation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993, 21, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, C.; Köllner, B.; Jacobsen, H.-J. Physiological and biochemical characterization of glyoxalase I, a general marker for cell proliferation, from a soybean cell suspension. Planta 1993, 189, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, T.N.; Sopory, S.K. Blue light stimulation of cell proliferation and glyoxalase I activity in callus cultures of Amaranthus paniculatus. Plant Sci. 1998, 132, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.D.; Olin, B.; Ridderstrom, M.; Mannervik, B.; Jones, T.A. Crystal structure of human glyoxalase I—Evidence for gene duplication and 3D domain swapping. EMBO J. 1999, 16, 3386–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornalley, P.J.; Edwards, L.G.; Kang, Y.; Wyatt, C.; Davies, N.; Ladan, M.J.; Double, J. Antitumour activity of S-p-bromobenzylglutathione cyclopentyl diester in vitro and in vivo. Inhibition of glyoxalase I and induction of apoptosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1996, 51, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornalley, P.J.; Langborg, A.; Minhas, H.S. Formation of glyoxal, methylglyoxal and 3-deoxyglucosone in the glycation of proteins by glucose. Biochem. J. 1999, 344, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abordo, E.A.; Minhas, H.S.; Thornalley, P.J. Accumulation of alpha- oxoaldehydes during oxidative stress: A role in cytotoxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, M.; Thornalley, P.J.; Giardino, I.; Beisswenger, P.J.; Thorpe, S.R.; Onorato, J.; Brownlee, M. Overexpression of glyoxalase-I in bovine endothelial cells inhibits intracellular advanced glycation endproduct formation and prevents hyperglycemia-induced increases in macromolecular endocytosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Treatments NaCl (mM) | Number of Jars | Shoots per Culture | Number of Shoots | Length of Shoots (cm) | Stem Diameter (mL) | No. of Leaves |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 3 | 5 | 39.33a | 2.40ab | 2.00b | 58.33a |
| 200 | 2 | 5 | 24.00b | 2.50ab | 2.00b | 32.00b |
| 400 | 3 | 5 | 23.67b | 2.93a | 2.00b | 31.67b |
| 600 | 2 | 4 | 10.33d | 1.85c | 1.50c | 18.67c |
| 800 | 2 | 4 | 19.00c | 2.30ab | 3.00a | 29.00b |
| 1000 | 3 | 3 | 17.33c | 2.77a | 3.00a | 26.67b |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohasseb, H.A.A.; Solliman, M.E.-D.; Al-Mssallem, I.S.; Abdullah, M.M.B.; Alsaqufi, A.S.; Shehata, W.F.; El-Shemy, H.A. Salt-Tolerant Phenomena, Sequencing and Characterization of a Glyoxalase I (Jojo-Gly I) Gene from Jojoba in Comparison with Other Glyoxalase I Genes. Plants 2020, 9, 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101285
Mohasseb HAA, Solliman ME-D, Al-Mssallem IS, Abdullah MMB, Alsaqufi AS, Shehata WF, El-Shemy HA. Salt-Tolerant Phenomena, Sequencing and Characterization of a Glyoxalase I (Jojo-Gly I) Gene from Jojoba in Comparison with Other Glyoxalase I Genes. Plants. 2020; 9(10):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101285
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohasseb, Heba Allah A., Mohei El-Din Solliman, Ibrahim S. Al-Mssallem, Mohammed M. Ba Abdullah, Ahmed Saud Alsaqufi, Wael F. Shehata, and Hany A. El-Shemy. 2020. "Salt-Tolerant Phenomena, Sequencing and Characterization of a Glyoxalase I (Jojo-Gly I) Gene from Jojoba in Comparison with Other Glyoxalase I Genes" Plants 9, no. 10: 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101285
APA StyleMohasseb, H. A. A., Solliman, M. E.-D., Al-Mssallem, I. S., Abdullah, M. M. B., Alsaqufi, A. S., Shehata, W. F., & El-Shemy, H. A. (2020). Salt-Tolerant Phenomena, Sequencing and Characterization of a Glyoxalase I (Jojo-Gly I) Gene from Jojoba in Comparison with Other Glyoxalase I Genes. Plants, 9(10), 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101285






