Journal Description
Diseases
Diseases
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access, multidisciplinary journal which focuses on the latest and outstanding research on diseases and conditions published monthly online by MDPI. The first issue is released in 2013.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Medicine, Research and Experimental)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 8 topical sections.
Impact Factor:
2.9 (2023)
Latest Articles
Clinical Heterogeneity of Early-Onset Autoimmune Gastritis: From the Evidence to a Pediatric Tailored Algorithm
Diseases 2025, 13(5), 133; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13050133 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Autoimmune gastritis (AIG) is an uncommon and often underestimated condition in children, characterized by chronic stomach inflammation leading to the destruction of oxyntic glands with subsequent atrophic and metaplastic changes. This condition is associated with hypo-/achlorhydria, impairing iron and vitamin B12 absorption. The
[...] Read more.
Autoimmune gastritis (AIG) is an uncommon and often underestimated condition in children, characterized by chronic stomach inflammation leading to the destruction of oxyntic glands with subsequent atrophic and metaplastic changes. This condition is associated with hypo-/achlorhydria, impairing iron and vitamin B12 absorption. The pathogenesis involves the activation of helper type 1 CD4+/CD25-T-cells against parietal cells. Clinical manifestations in children are not specific and include abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and iron deficiency anemia (IDA). The disease is also linked to an increased risk of pernicious anemia, intestinal-type gastric cancer, and type I neuroendocrine tumors. AIG is often diagnosed through the presence of autoantibodies in the serum, such as parietal cell (APCA) and intrinsic factor (IF) antibodies. However, therapeutic recommendations for pediatric AIG are currently lacking. We aim to present two clinical cases of pediatric-onset AIG, highlighting the heterogeneous clinical manifestations and the challenges in diagnosis with the support of an updated literature review. A 9-year-old girl presented with refractory IDA, initial hypogammaglobulinemia, and a 12-year-old boy was initially diagnosed with eosinophilic esophagitis. Both cases underline the importance of considering AIG in children with chronic gastrointestinal symptoms and gastric atrophy. Diagnostic workup, including endoscopy and serological tests, is crucial for accurate identification. A better understanding of this condition is imperative for timely intervention and regular monitoring, given the potential long-term complications, including the risk of malignancy. These cases contribute to expanding the clinical spectrum of pediatric AIG and highlight the necessity for comprehensive evaluation and management in affected children.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Beneficial Effects of White Grape Pomace in Experimental Dexamethasone-Induced Hypertension
by
Raluca Maria Pop, Paul-Mihai Boarescu, Corina Ioana Bocsan, Mădălina Luciana Gherman, Veronica Sanda Chedea, Elena-Mihaela Jianu, Ștefan Horia Roșian, Ioana Boarescu, Floricuța Ranga, Maria Doinița Muntean, Maria Comșa, Sebastian Armean, Ana Uifălean, Alina Elena Pârvu and Anca Dana Buzoianu
Diseases 2025, 13(5), 132; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13050132 - 24 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Grape pomace (GP), a by-product of winemaking, is a rich source of bioactive polyphenols known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. While the cardiovascular benefits of red grape pomace have received significant scientific attention, the therapeutic potential of white grape pomace remains
[...] Read more.
Background: Grape pomace (GP), a by-product of winemaking, is a rich source of bioactive polyphenols known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. While the cardiovascular benefits of red grape pomace have received significant scientific attention, the therapeutic potential of white grape pomace remains largely unexplored, particularly in glucocorticoid-induced hypertension. Given the rising prevalence of hypertension and the oxidative-inflammatory mechanisms underlying its progression, this study investigates the effects of white GP on blood pressure regulation, oxidative stress, and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in an experimental model of dexamethasone (DEXA)-induced hypertension (HTN). By focusing on white GP, this research addresses a significant gap in current knowledge and proposes a novel, sustainable approach to managing hypertension through valorising winemaking by-products. Methods: The first concentration used, GP1, was 795 mg polyphenols/kg bw, while the second concentration, GP2, was 397.5 mg polyphenols/kg bw. Results: White GP polyphenols extract in the DEXA_GP1 group had reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The extract with a higher content of polyphenols (GP1) prevented the elevation of serum levels of total oxidative stress (TOS), malondialdehyde (MDA), and oxidative stress index (OSI), while the extract with a lower content of polyphenols (GP2) slightly reduced serum levels of MDA. Both concentrations of GP increased serum levels of NO and Total Thiols, significantly higher (p < 0.05) than in the group treated with lisinopril. The serum levels of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) increased in all groups where HTN was induced. Both doses of GP extract prevented the elevation of TNF-α. Heart tissue levels of the studied cytokines (TNF-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6 were not influenced (p > 0.05) by either the HTN induction or the treatment administered. Conclusions: These findings suggest that grape pomace may serve as a promising nutraceutical intervention for hypertension management, particularly in conditions associated with oxidative stress.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Desmocollin-3 and Bladder Cancer
by
Chandreshwar P. Shukla, Nayan K. Jain, Michael A. O’Donnell, Kapil V. Vachhani, Rashmi Patel, Janki Patel, Rajiv Modi, Arpit Dheeraj, Jee Min Lee, Annah Rolig, Sanjay V. Malhotra and Bakulesh Khamar
Diseases 2025, 13(5), 131; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13050131 - 23 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Desmocollin3, a transmembrane protein, is expressed in the basal/suprabasal layer of normal stratified epithelium. DSC3 gene expression is described in muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). DSC3-protein-expressing recurrent non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) had a durable response to CADI-03, a DSC3-specific active immunotherapy. Methods: We
[...] Read more.
Background: Desmocollin3, a transmembrane protein, is expressed in the basal/suprabasal layer of normal stratified epithelium. DSC3 gene expression is described in muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). DSC3-protein-expressing recurrent non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) had a durable response to CADI-03, a DSC3-specific active immunotherapy. Methods: We evaluated DSC3 protein expression and its correlation with tumor-infiltrating immune cells in bladder cancer. DSC3 gene expression and its correlation with 208 immune encoding genes, treatment outcome, and survival were evaluated using the “ARRAYEXPRESS” and “TCGA” datasets. Immune genes were grouped as tumor-controlling immune genes (TCIGs) and tumor-promoting immune genes (TPIGs) as per their functions. Results & conclusions: NMIBC had higher DSC3 expression compared to MIBC. More immune genes were correlated with DSC3 in MIBC (21) compared to NMIBC (11). Amongst the TCIGs, six in NMIBC and one in MIBC had a negative correlation while two in NMIBC and nine in MIBC had a positive correlation with DSC3. Amongst the TPIGs, nine in NMIBC and five in MIBC had a negative correlation. Seven TPIGs had a positive correlation with DSC3 in MIBC and none in NMIBC. Of the T cell exhaustion markers, none were correlated with DSC3 in MIBC. Among NMIBC, CTLA4 and TIGIT were the only markers of exhaustion that demonstrated a negative correlation with DSC3. DSC3 expression was also higher in p53 mutant compared to wild p53, non-papillary MIBC compared to papillary MIBC, and in basal, squamous molecular subtype compared to luminal MIBC. MIBC with lower DSC3 expression had better outcomes (response, survival) compared to those with higher DSC3 expression.
Full article
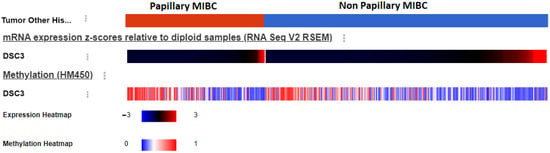
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prevalence of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Asthma in the Community of Pathumthani, Thailand
by
Narongkorn Saiphoklang, Pitchayapa Ruchiwit, Apichart Kanitsap, Pichaya Tantiyavarong, Pasitpon Vatcharavongvan, Srimuang Palungrit, Kanyada Leelasittikul, Apiwat Pugongchai and Orapan Poachanukoon
Diseases 2025, 13(5), 130; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13050130 - 23 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Airway diseases, particularly asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pose significant respiratory problems. The prevalence and risk factors of these diseases among community dwellers vary geographically and because of underdiagnosis. This study aims to determine the prevalence and factors associated
[...] Read more.
Background: Airway diseases, particularly asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pose significant respiratory problems. The prevalence and risk factors of these diseases among community dwellers vary geographically and because of underdiagnosis. This study aims to determine the prevalence and factors associated with these diseases in a provincial-metropolitan area in Thailand. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted between April 2023 and November 2023 on individuals aged 18 years or older residing in Pathumthani, Thailand. Data on demographics, pre-existing diseases, respiratory symptoms, and pulmonary functions assessed by spirometry, including forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and bronchodilator responsiveness (BDR), were collected. COPD was defined as having respiratory symptoms, a risk factor, and post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC < 70%. Asthma was defined as having respiratory symptoms and a positive bronchodilator responsiveness. Results: A total of 1014 subjects (71.7% female) were included, with a mean age of 56.6 years. The smoking history was 10.4% (13.4 pack-years). Common symptoms included cough (18.4%), sputum production (14.5%), and dyspnea (10.0%). COPD was found in 8.3%, while asthma was found in 10.3%. Logistic regression analysis indicated that these diseases were significantly associated with older age (odds ratio [OR] 1.023; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.007–1.039 for every 1-year increase in age), smoking (OR 2.247; 95% CI 1.068–4.728), heart disease (OR 2.709; 95% CI 1.250–5.873), wheezing (OR 3.128; 95% CI 1.109–8.824), runny nose (OR 1.911; 95% CI 1.050–3.477), and previous treatment for dyspnea (OR 6.749, 95% CI 3.670–12.409). Conclusions: COPD and asthma were relatively prevalent in our study. Being elderly, smoking, having heart disease, and experiencing any respiratory symptoms with a history of treatment are crucial indicators for these airway diseases. Pulmonary function testing might be needed for active surveillance to detect these respiratory diseases in the community.
Full article
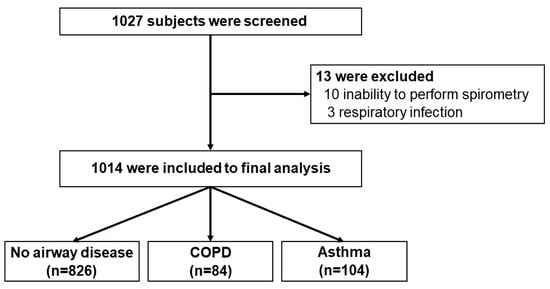
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Current and Emerging Parenteral and Peroral Medications for Weight Loss: A Narrative Review
by
Abdullah Al Lawati, Ayman Alhabsi, Rhieya Rahul, Maria-Luisa Savino, Hamed Alwahaibi, Srijit Das and Hanan Al Lawati
Diseases 2025, 13(5), 129; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13050129 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Obesity is a growing global health challenge, necessitating effective treatment options beyond lifestyle interventions. This narrative review explores established and emerging pharmacotherapies for weight management, including parenteral agents like Liraglutide, Semaglutide, Setmelanotide, and Tirzepatide, as well as peroral medications such as Phentermine, Phentermine/Topiramate,
[...] Read more.
Obesity is a growing global health challenge, necessitating effective treatment options beyond lifestyle interventions. This narrative review explores established and emerging pharmacotherapies for weight management, including parenteral agents like Liraglutide, Semaglutide, Setmelanotide, and Tirzepatide, as well as peroral medications such as Phentermine, Phentermine/Topiramate, Bupropion/Naltrexone, Orlistat, and Metformin. Newer treatments like Cagrilintide and Bimagrumab show promise for enhancing weight loss outcomes. Parenteral GLP-1 receptor agonists demonstrate superior efficacy compared to traditional peroral medications, with gastrointestinal side effects being the most common. Artificial intelligence presents intriguing opportunities to enhance weight loss strategies; however, its integration into clinical practice remains investigational and requires rigorous clinical validation. While current anti-obesity medications deliver significant benefits, future research must determine the efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness of AI-driven approaches. This includes exploring how AI can complement combination therapies and tailor personalized interventions, thereby grounding its potential benefits in robust clinical evidence. Future directions will focus on integrating AI into clinical trials to refine and personalize obesity management strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Body Composition, Energy Expenditure and Lifestyle During Obesity Management)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Ultrasound Relationship of Plantar Fat and Predislocation Syndrome
by
Ana María Rayo Pérez, Rafael Rayo Martín, Rafael Rayo Rosado, Joao Miguel Costa Martiniano and Raquel García-de-la-Peña
Diseases 2025, 13(5), 128; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13050128 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Plantar fat plays a crucial role in protecting and cushioning the metatarsals. Its degeneration is a risk factor for the development of metatarsalgia and, consequently, predislocation syndrome. Objectives: To evaluate the relationship between plantar fat thickness and predislocation syndrome in an adult
[...] Read more.
Background: Plantar fat plays a crucial role in protecting and cushioning the metatarsals. Its degeneration is a risk factor for the development of metatarsalgia and, consequently, predislocation syndrome. Objectives: To evaluate the relationship between plantar fat thickness and predislocation syndrome in an adult population, and to determine a possible association between a decrease in forefoot plantar fat and the presence of symptoms. Material and Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted, including records of patients who visited the podiatry clinic between December 2022 and December 2023. Fifty complete records were selected, divided into two groups, one healthy and one pathological, aged between 18 and 70 years. An ultrasound examination of the plantar area of the second metatarsophalangeal joint was performed to assess the thickness of the fat and plantar plate. Results: The analysis of the 50 records, divided into healthy and pathological groups, reveals significant differences in the thickness of plantar fat and the plantar plate between the two groups. Subjects with predislocation syndrome have a significantly lower plantar fat thickness (0.566 cm) compared to the healthy group (0.941 cm) and also show a greater thickness of the plantar plate (0.359 cm vs. 0.244 cm). Statistical tests confirm these differences with high significance (p < 0.001). The ROC curve shows that plantar fat thickness is a good predictor of predislocation syndrome, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.923, emphasizing the utility of this measure in identifying the condition. Conclusions: Preliminary studies suggest that a reduction in plantar fat increases the predisposition to develop predislocation syndrome at the level of the second metatarsophalangeal joint.
Full article
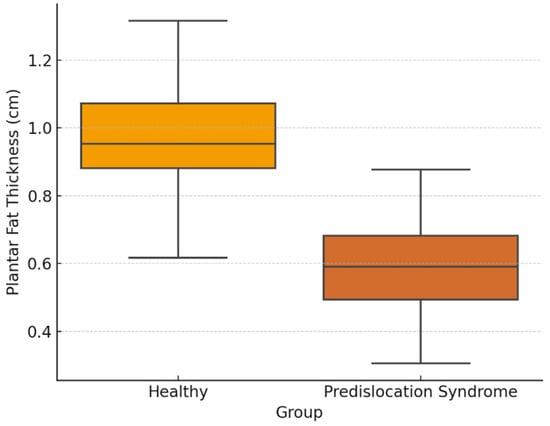
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
A Closer Look at the Dermatological Profile of GLP-1 Agonists
by
Calista Persson, Allison Eaton and Harvey N. Mayrovitz
Diseases 2025, 13(5), 127; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13050127 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/objectives: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are widely used in treating type 2 diabetes and obesity, offering established metabolic and cardiovascular benefits. Emerging evidence suggests these agents also exert direct dermatologic effects. This systematic review categorizes these effects and explores their role in
[...] Read more.
Background/objectives: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are widely used in treating type 2 diabetes and obesity, offering established metabolic and cardiovascular benefits. Emerging evidence suggests these agents also exert direct dermatologic effects. This systematic review categorizes these effects and explores their role in inflammatory skin diseases. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was performed across EMBASE, PubMed, Web of Science, and Google Scholar for studies published from 2014 to 2025. Inclusion criteria were English-language, peer-reviewed original research involving human subjects that linked GLP-1RAs to dermatologic effects. Animal and in vitro studies were excluded. PRISMA guidelines were followed. Results: Fifty-one studies met inclusion criteria. Thirty-four reported adverse effects, including hypersensitivity, injection-site reactions, pruritus, urticaria, angioedema, and immune-mediated conditions like bullous pemphigoid. Seventeen studies described beneficial outcomes, such as improvements in psoriasis, reduced hidradenitis suppurativa flares, enhanced wound healing, anti-aging potential, and decreased inflammation. GLP-1RAs showed cytokine modulation in psoriasis, though their role in hidradenitis suppurativa remains uncertain. Cosmetic concerns, such as “Ozempic Face” due to rapid weight loss, were also noted. Conclusions: GLP-1RAs have a broad spectrum of dermatologic effects, from immunomodulatory benefits to adverse cutaneous reactions. Their impact on inflammatory skin disorders suggests a novel therapeutic avenue. However, adverse reactions and aesthetic changes warrant vigilance. Future research should focus on mechanistic studies, long-term safety, and identifying biomarkers to predict dermatologic responses, ultimately guiding personalized treatment approaches.
Full article
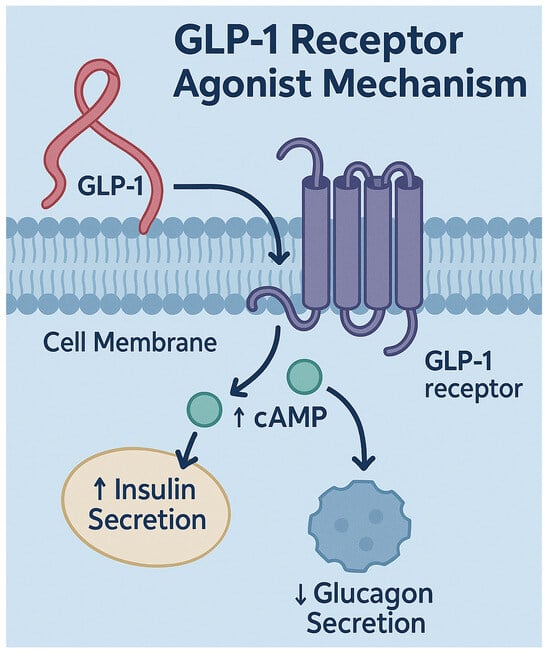
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Clinical Importance of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Levels in Sinus Rhythm at 3 Months After Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Ablation
by
Jumpei Saito, Toshihiko Matsuda, Yui Koyanagi, Katsuya Yoshihiro, Yuma Gibo, Soichiro Usumoto, Wataru Igawa, Toshitaka Okabe, Naoei Isomura and Masahiko Ochiai
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 126; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040126 - 21 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels after ablation have been associated with a risk of arrhythmia recurrence (AR) after atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation. In addition, baseline BNP levels were also predictors of AR after AF ablation. However, previous studies have not been clear
[...] Read more.
Background: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels after ablation have been associated with a risk of arrhythmia recurrence (AR) after atrial fibrillation (AF) ablation. In addition, baseline BNP levels were also predictors of AR after AF ablation. However, previous studies have not been clear about whether sinus rhythm (SR) or AF was present at the time of BNP measurement. In this study, we investigated BNP levels in SR at 1,3 months after persistent AF ablation. Methods: We followed up 178 patients with persistent AF undergoing first-time arrhythmia ablation. BNP levels were measured before 1 and 3 months later after AF ablation in SR. The correlation between AR within 1 year after AF ablation and measured BNP levels was examined. Results: A total of 178 cases (81 males, mean age 69 (60, 74), mean CHA2DS2 Vasc score 2 (0, 4)) with persistent AF were included for ablation. BNP levels before AF ablation were not significantly different between AR and not AR patients. The BNP levels of AR patients were significantly elevated from 1 month to 3 months after the procedure compared with those without (−11.1 pg/mL (−53, 5.7) vs. 17.8 pg/mL (−58.3, 180.5), p < 0.0001). Elevated BNP levels in SR after AF ablation were a significant predictor of AR. Conclusions: Elevated BNP levels in SR 3 months after AF ablation compared with BNP levels 1 month after persistent AF ablation might be a significant prognostic factor in AR.
Full article
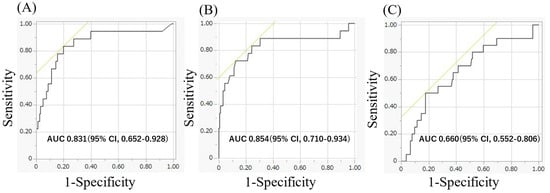
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Patient with Secondary Amyloidosis Due to Crohn’s Disease on Hemodialysis Effectively Treated with Ferric Carboxymaltose Injections: A Case Report and Literature Review
by
Masayo Ueno, Fumihito Hirai, Asami Fuji, Yuko Shimomura, Keiko Uemoto, Kosuke Masutani and Takao Saito
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 125; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040125 - 21 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Almost all patients undergoing dialysis develop renal anemia and receive medicines such as erythropoietin and iron preparations. However, the conventional intravenous treatment with saccharated ferric oxide (SFO) is insufficient for these patients when they have incurable and persistent iron deficiency anemia due
[...] Read more.
Background: Almost all patients undergoing dialysis develop renal anemia and receive medicines such as erythropoietin and iron preparations. However, the conventional intravenous treatment with saccharated ferric oxide (SFO) is insufficient for these patients when they have incurable and persistent iron deficiency anemia due to secondary amyloidosis. Therefore, we administered 500 mg of ferric carboxymaltose (FCM) to such a patient with Crohn’s disease. Case presentation: A 56-year-old man on maintenance hemodialysis had secondary amyloidosis due to Crohn’s disease. Additionally, he was anemic and received 40 mg of SFO weekly; however, his hemoglobin (Hb) level remained low at 7 g/dL. Therefore, 500 mg of FCM was administered bimonthly from the first to the fourth dose, and the Hb level temporarily increased compared to that after the previous SFO administration. Since bimonthly administration did not adequately maintain the Hb level, FCM was administered monthly from the 5th to 12th dose, which stabilized the Hb level at 10–12 g/dL. No side effects, such as hypophosphatemia, were observed. Conclusions: A single dose of 500 mg FCM administered once every 1–2 months stabilizes the Hb level and contributes to efficient iron utilization in patients with incurable anemia undergoing hemodialysis.
Full article
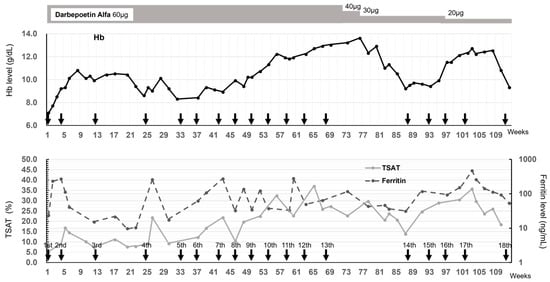
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Rabies Vaccination and Public Health Insights in the Extended Arabian Gulf and Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Scoping Review
by
Helal F. Hetta, Khalid S. Albalawi, Amal M. Almalki, Nasser D. Albalawi, Abdulmajeed S. Albalawi, Suleiman M. Al-Atwi, Saleh E. Alatawi, Mousa J. Alharbi, MeshaL F. Albalawi, Ahmad A. Alharbi, Hassabelrasoul Elfadil, Abdullah S. Albalawi and Reem Sayad
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 124; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040124 - 21 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background and Aim: This systematic scoping review examines rabies-related incidents, interventions, and post-exposure immunoprophylaxis in the Arabian Gulf region and Saudi Arabian Peninsula. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in databases including PubMed, Scopus, WoS, MedLine, and Cochrane Library up to July
[...] Read more.
Background and Aim: This systematic scoping review examines rabies-related incidents, interventions, and post-exposure immunoprophylaxis in the Arabian Gulf region and Saudi Arabian Peninsula. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in databases including PubMed, Scopus, WoS, MedLine, and Cochrane Library up to July 2024. Studies were included discussing the reported cases of rabies that received the PEP in all countries of the Arabian Gulf, their epidemiological data, the received schedules of vaccination, and their safety. The search was done by using the following terminologies: rabies vaccine, rabies human diploid cell vaccine, vaccine, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Iraq, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Southwest Asia, Iran, West Asia, Western Asia, Persian Gulf, Arabian Gulf, Gulf of Ajam, Saudi Arabian Peninsula, and The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Results: The systematic scoping review included 36 studies, synthesizing findings from diverse research designs, including large-scale cross-sectional studies and case reports, spanning nearly three decades. Findings indicated that young males in urban areas are most at risk for animal bites, predominantly from domestic dogs and cats. While post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) was generally administered within recommended timeframes, vaccination completion rates varied. Conclusions: The review highlighted gaps in public awareness about rabies risks and prevention. Vaccine safety profiles were generally favorable, with mostly mild-to-moderate side effects reported. The study underscores the need for enhanced public health education, standardized PEP protocols, and a One Health approach to rabies prevention.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Infectious Disease Epidemiology 2024)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Correlation of Inflammatory Biomarkers and IgG4 Antibodies with Malaria in Cameroon’s Buea Municipality Children
by
Jerome Nyhalah Dinga, Flora Ayah, Emmanuel Fondungallah Anu, Haowen Qin, Stanley Dobgima Gamua, Anthony Kukwah Tufon, Magloire Essissima Amougou and Rameshbabu Manyam
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 123; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040123 - 21 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: In recent decades, malaria has become a major worldwide public health problem in endemic countries, especially with children below five years. Malaria causes inflammation, and inflammatory biomarkers like α-1-glycoprotein (AGP) and C-reactive protein (CRP) are elevated in serum during malaria. This work
[...] Read more.
Background: In recent decades, malaria has become a major worldwide public health problem in endemic countries, especially with children below five years. Malaria causes inflammation, and inflammatory biomarkers like α-1-glycoprotein (AGP) and C-reactive protein (CRP) are elevated in serum during malaria. This work aimed at assessing the serum levels of AGP (chronic inflammation) and CRP (acute inflammation) biomarkers and IgG4 and their correlation with malaria in children below five years in the Buea Health District of the South West Region of Cameroon. Methods: This cross-sectional study was carried out between February and April, 2024. AGP and CRP were measured using Q-7plex Human Micronutrient Measurement Kit while IgG4 levels were measured using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay with 80 samples. Results: Serum AGP and CRP biomarker levels were significantly higher in malaria-positive children compared to malaria-negative children (p < 0.001 and p < 0.001, respectively). IgG4 levels were high in malaria-negative children (mean OD = 0.51) compared to children infected with the malaria parasite (mean OD = 0.29), in a manner that was statistically significant (p < 0.03). Hemoglobin (Hb) had a strong negative correlation with AGP (−0.62) and CRP (−0.46), meaning that as Hb levels increased, AGP and CRP levels decreased. CRP had a strong positive correlation with both age (0.3) and AGP (0.5), suggesting that as age increased or as AGP levels rose, CRP levels tended to increase as well. Conclusions: This study revealed that malaria causes alterations in the serum levels of AGP, CRP, and IgG4 in children below the age of 5 in the Buea municipality of Cameroon. It impacts immune responses by increasing the level of inflammation biomarkers like AGP and CRP and decreasing IgG4, a marker associated with immune regulation. Thus, this study helps the understanding of the inflammatory nature of malaria and could be expanded to aid in the broader public health efforts to control and prevent malaria, reduce its complications, and improve overall health outcomes in children in the Buea municipality.
Full article
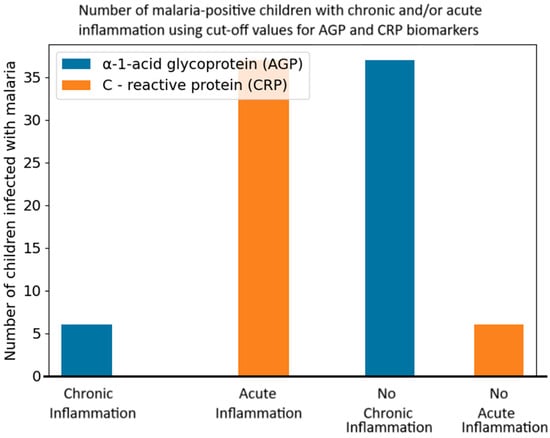
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Clinical Trial: Effects of Autologous Dendritic Cell Administration on Renal Hemodynamics and Inflammatory Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
by
Endang Drajat, Aziza Ghanie Icksan, Jonny Jonny, Aditya Pratama Lokeswara, Bhimo Aji Hernowo, Elvita Rahmi Daulay and Terawan Agus Putranto
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 122; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040122 - 21 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a significant risk factor for End-Stage Renal Disease, with a high global incidence and mortality rate. Hyperglycemia in DKD induces inflammation, contributing to glomerular hyperfiltration, fibrosis, and impaired renal function. Current therapies, including SGLT2 inhibitors, ACE inhibitors,
[...] Read more.
Background: Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a significant risk factor for End-Stage Renal Disease, with a high global incidence and mortality rate. Hyperglycemia in DKD induces inflammation, contributing to glomerular hyperfiltration, fibrosis, and impaired renal function. Current therapies, including SGLT2 inhibitors, ACE inhibitors, and ARBs, show limited efficacy. Autologous dendritic cells (DCs) offer potential anti-inflammatory effects by reducing cytokine activity and fibrosis biomarkers. Methods: A quasi-experimental pretest–post-test design was conducted involving 29 DKD patients. Baseline blood and urine samples were collected for MMP-9, TGF-β, and Doppler ultrasound (PSV, EDV) measurements. The subjects received subcutaneous injections of autologous DCs, and follow-up measurements were conducted four weeks after treatment. The statistical analyses included paired t-tests, Wilcoxon signed-rank tests, and linear regression. Results: After treatment, there were a significant decrease in PSV (from 47.1 ± 23.87 cm/s to 27.85 ± 20.53 cm/s, p = 0.044) and a significant increase in EDV (from 13 ± 5.32 cm/s to 15.7 ± 12.55 cm/s, p = 0.039). A strong correlation was observed between the TGF-β and MMP-9 levels (p = 0.001). Linear regression analysis showed reduced MMP-9 influence on the TGF-β after treatment, suggesting potential fibrosis reduction. Gender and UACR subgroup analyses revealed significant PSV and EDV improvements in females and the microalbuminuria group. Conclusion: Autologous dendritic cell therapy significantly improved renal hemodynamics and showed potential to reduce fibrosis by modulating TGF-β and MMP-9 levels in DKD patients, warranting further investigation.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Self-Perceived Stress and Anxiety Throughout Pregnancy: A Longitudinal Study
by
Mar Miguel Redondo, Cristina Liebana-Presa, Javier Pérez-Rivera, Cristian Martín-Vázquez, Natalia Calvo-Ayuso and Rubén García-Fernández
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 121; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040121 - 19 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Anxiety and stress are common during pregnancy and can impact the health of the pregnant woman and the newborn. There is a lack of research focused on identifying weaknesses that promote equity in the care of pregnant women. The objective of this
[...] Read more.
Background: Anxiety and stress are common during pregnancy and can impact the health of the pregnant woman and the newborn. There is a lack of research focused on identifying weaknesses that promote equity in the care of pregnant women. The objective of this study was to describe the levels of anxiety and stress during the three trimesters of pregnancy and to compare whether there are differences according to obstetric and gynecological variables. Methods: A descriptive prospective longitudinal and correlational observational study was carried out. Non-probability sampling was carried out with 176 women. The Pregnancy-Related Anxiety Questionnaire and the Perceived Stress Scale were used. Results: The prevalence of anxiety was 23.9%, 17%, and 17.6%, and mean stress scores reached 32.24, 33.02, and 49.74 in the first, second, and third trimesters, respectively. In comparison, without miscarriages, anxiety was higher during the first trimester. In multiparous women who had suffered a miscarriage, anxiety was higher in the first trimester. Conclusions: Anxiety is higher during the first trimester. Mean stress levels are higher during the third trimester compared to the other two trimesters. Care for these vulnerable pregnant women can impact society’s health system and align with the Sustainable Development Goals of Health and Well-being and Gender Equality in others.
Full article
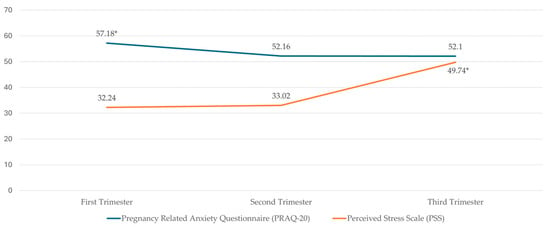
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Factors Influencing Physical Performance and Quality of Life in Post-COVID-19 Patients
by
Ajchamon Thammachai, Patchareeya Amput and Sirima Wongphon
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 120; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040120 - 19 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: This study aims to identify the factors related to demographic variables and physical performance associated with quality of life (QoL) in post-COVID-19 pa-tients who have recovered from mild infection and were not hospitalized. Methods: Seventy-four post-COVID-19 individuals who recovered from
[...] Read more.
Background: This study aims to identify the factors related to demographic variables and physical performance associated with quality of life (QoL) in post-COVID-19 pa-tients who have recovered from mild infection and were not hospitalized. Methods: Seventy-four post-COVID-19 individuals who recovered from mild COVID-19 infec-tion were assessed for the baseline demographic variables (age, sex, height, weight, body mass index; BMI) and clinical information (comorbidities, duration of COVID-19 infection, and exercise habits). Vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen sat-uration; SpO2) were measured. Physical performance was evaluated for upper- and lower-limb muscle strength, ability of balance, and cardiorespiratory performance. All participants were assessed for QoL. Results: Hand grip strength was negatively asso-ciated with gender and age while positively associated with the duration of COVID-19. Quadricep strength also showed a negative association with gender and duration of COVID-19. Age was positively associated with multiple quality of life dimensions, while emotional role limitations were negatively associated with the duration of COVID-19 and waist circumference. Mental health was negatively linked to BMI. Conclusions: This study highlights the complex impact of COVID-19 on physical per-formance and QoL, revealing that older adults often report better QoL despite reduced muscle strength, particularly in women. The findings emphasize the need for targeted rehabilitation programs addressing both physical and emotional health for vulnerable groups.
Full article
Open AccessBrief Report
Possible Significance of Neutrophil–Hemoglobin Ratio in Differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy from Depression: A Pilot Study
by
Michał Markiewicz, Natalia Madetko-Alster, Dagmara Otto-Ślusarczyk, Karolina Duszyńska-Wąs, Bartosz Migda, Patryk Chunowski, Marta Struga and Piotr Alster
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 119; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040119 - 18 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Research has associated chronic inflammation with the evolution of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s Disease (PD), Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), and less common ones such as Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP), are commonly linked to depression. However, the pathomechanisms and the
[...] Read more.
Background: Research has associated chronic inflammation with the evolution of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s Disease (PD), Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), and less common ones such as Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP), are commonly linked to depression. However, the pathomechanisms and the role of neuroinflammation in these disorders remain unclear; therefore, interest is increasing in easily accessible inflammatory morphological assessments of blood samples, such as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), the neutrophil-to-monocyte ratio (NMR), and the neutrophil-to-hemoglobin ratio (N/HGBR). Methods: The authors analyzed 15 age-matched controls and 21 patients with PSP; the PSP group was additionally divided into 11 patients without depression (PSP) and 10 with depression (Beck Depression Inventory [BDI] ≥ 14) (PSP-D). Results: In the PSP-D group, the level of N/HGBR was significantly lower than in the controls (p = 0.01), but there were no significant differences in any other neutrophil-derived parameters or comparisons of morphological blood assessment. Patients with PSP-D exhibited a marginally significant decrease in neutrophil levels compared to the controls. Conclusions: This is the first study highlighting the possible significance of peripheral inflammatory factors in patients with PSP affected by depression. It highlights possible tendencies in the area of non-specific inflammatory markers and suggests their relation to affective disorders in PSP.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research Progress in Neurodegenerative Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
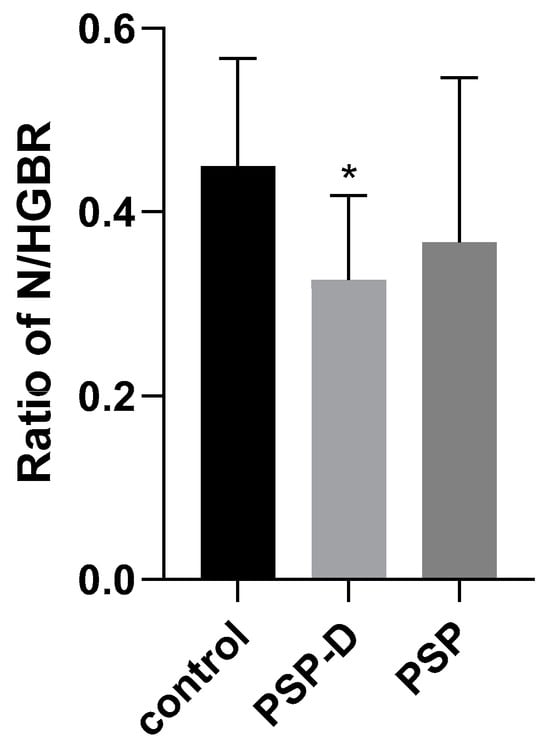
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
False-Positive Galactomannan Test Results in Multiple Myeloma
by
Shingen Nakamura, Yusaku Maeda, Ryohei Sumitani, Masahiro Oura, Kimiko Sogabe, Hikaru Yagi, Shiro Fujii, Takeshi Harada, Ken-ichi Matsuoka and Hirokazu Miki
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 118; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040118 - 17 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IA) is a common infectious disease in patients with hematological diseases. The prevention, early detection, and establishment of treatment strategies for IA are important. The serum galactomannan antigen (GM) mycological test for IA diagnosis, included in the mycology criteria
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IA) is a common infectious disease in patients with hematological diseases. The prevention, early detection, and establishment of treatment strategies for IA are important. The serum galactomannan antigen (GM) mycological test for IA diagnosis, included in the mycology criteria of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycosis Study Group (EORTC/MSG), is widely used because of its high sensitivity and specificity. However, false-positive results are a concern. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed all GM tests performed at our department in the clinical practice setting between April 2003 and January 2012. Results: Of the 330 cases and 2155 samples analyzed, 540 (25%) were positive (≥0.5). Among the underlying diseases, positivity rates were the highest for multiple myeloma (MM), with 61.3%. By type, positivity rates for IgG, IgA, Bence-Jones protein, and IgD were 71.7%, 33.3%, 57.1%, and 34.6%, respectively. Seventeen out of eighteen cases that were GM-positive at MM diagnosis were false positives, according to the 2008 EORTC/MSG criteria. The IgG and GM values were not directly correlated. Of the seventeen false-positive cases identified, two developed IA during anti-myeloma treatments, and GM values did not become negative during the treatment in most cases. Conclusions: Although subclinical IA may be included in a higher GM index, the results may be prone to false positives; particularly in IgG-type MM, the results should thus be interpreted cautiously.
Full article
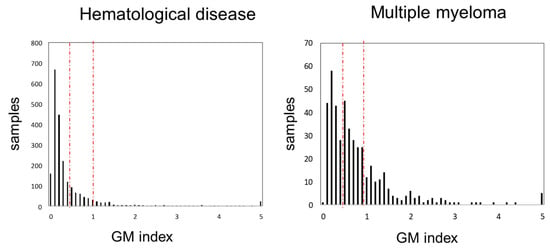
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Neurogenic Bladder in Children with Myelomeningocele
by
Aleksandar Sič, Borko Stojanović and Miroslav Đorđević
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 117; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040117 - 17 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Myelomeningocele (MMC), a severe congenital anomaly resulting from neural tube closure defects, poses significant urological challenges necessitating specialized care. This review explores the intricate landscape of MMC within urological practice, advocating for a multidisciplinary approach to optimize patient outcomes. By surveying diverse treatment
[...] Read more.
Myelomeningocele (MMC), a severe congenital anomaly resulting from neural tube closure defects, poses significant urological challenges necessitating specialized care. This review explores the intricate landscape of MMC within urological practice, advocating for a multidisciplinary approach to optimize patient outcomes. By surveying diverse treatment modalities, this review aims to offer insights into enhancing urological management strategies for MMC and guiding future research directions. At the heart of the conversation lies the pathophysiology of neurogenic bladder dysfunction in children with MMC, with a particular focus on the complexities of diagnosis and the various paradigms guiding urological management. Common complications such as recurrent urinary tract infections are examined alongside non-surgical interventions like intermittent catheterization (CIC) and pharmacotherapy, notably oxybutynin. Additionally, surgical options including botulinum toxin injection and reconstructive procedures are explored to enhance urological outcomes for affected children. By unpacking the complexities of neurogenic bladder dysfunction in MMC, this review emphasizes the imperative of a collaborative, multidisciplinary approach in urological care, ultimately aiming to enhance patient well-being and functional outcomes.
Full article
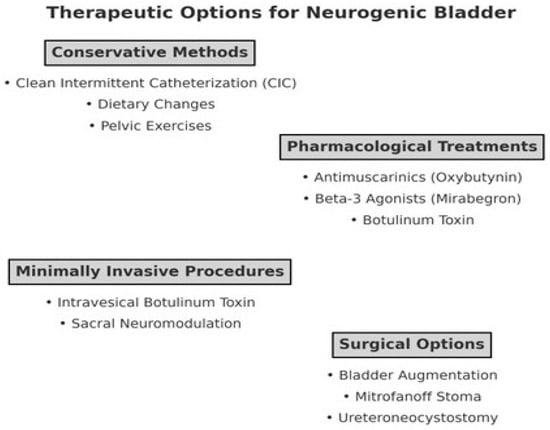
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Autologous Dendritic Cell Therapy on Renal Perfusion in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Analysis of Doppler Ultrasound and Angiogenesis Biomarkers
by
Ardianto Pramono, Jonny, Djuwita Adi Wahyono, Aditya Pratama Lokeswara, Enda Cindylosa Sitepu, Ermi Girsang and Terawan Agus Putranto
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 116; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040116 - 16 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a global health challenge with a severe health burden. Approximately 40% of diabetic patients develop diabetic kidney disease (DKD), leading to kidney failure. Autologous dendritic cell therapy may enhance renal function by modulating vascular markers. Methods: Involving 35
[...] Read more.
Background: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a global health challenge with a severe health burden. Approximately 40% of diabetic patients develop diabetic kidney disease (DKD), leading to kidney failure. Autologous dendritic cell therapy may enhance renal function by modulating vascular markers. Methods: Involving 35 patients, this quasi-experimental study assessed the pulsatility index (PI), resistive index (RI), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and endothelin levels before and four weeks following autologous dendritic cell administration. Results: A significant reduction in median PI was found from 1.61 ± 0.63 to 1.21 ± 0.26 (p < 0.001). The increase in mean RI was insignificant from 0.74 ± 0.07 to 0.75 ± 0.06 (p = 0.17). The median VEGF showed a slight reduction from 522.10 ± 608.6 to 473.70 ± 550 (p = 0.589) and endothelin from 1.74 ± 0.71 to 1.63 ± 0.76 (p = 0.554). Conclusions: This study shows that autologous dendritic cell therapy may improve kidney perfusion in DKD patients, indicated by a significant reduction in the PI. These findings suggest potential therapeutic benefits for renal perfusion in DKD.
Full article
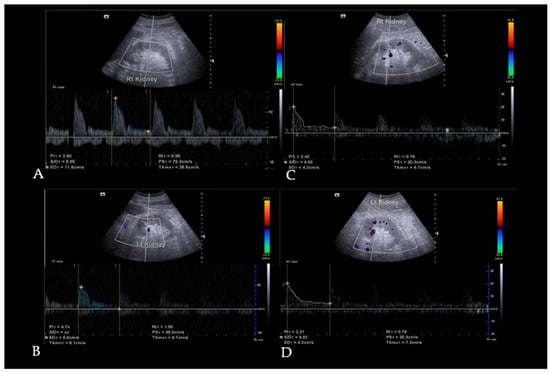
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Artificial Sweeteners: A Double-Edged Sword for Gut Microbiome
by
Helal F. Hetta, Nizar Sirag, Hassabelrasoul Elfadil, Ayman Salama, Sara F. Aljadrawi, Amani J. Alfaifi, Asma N. Alwabisi, Bothinah M. AbuAlhasan, Layan S. Alanazi, Yara A. Aljohani, Yasmin N. Ramadan, Noura H. Abd Ellah and Abdelazeem M. Algammal
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 115; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040115 - 15 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background and Aim: The human gut microbiome plays a crucial role in maintaining health. Artificial sweeteners, also known as non-nutritive sweeteners (NNS), have garnered attention for their potential to disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome. This review explores the complex relationship
[...] Read more.
Background and Aim: The human gut microbiome plays a crucial role in maintaining health. Artificial sweeteners, also known as non-nutritive sweeteners (NNS), have garnered attention for their potential to disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome. This review explores the complex relationship between NNS and the gut microbiome, highlighting their potential benefits and risks. By synthesizing current evidence, we aim to provide a balanced perspective on the role of AS in dietary practices and health outcomes, emphasizing the need for targeted research to guide their safe and effective use. Methods: A comprehensive literature review was conducted through searches in PubMed and Google Scholar, focusing on the effects of artificial sweeteners on gut microbiota. The search utilized key terms including “Gut Microbiome”, “gut microbiota”, “Eubiosis”, “Dysbiosis”, “Artificial Sweeteners”, and “Nonnutritive Sweeteners”. Results: NNS may alter the gut microbiome, but findings remain inconsistent. Animal studies often report a decrease in beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, and an increase in harmful strains such as Clostridium difficile and E. coli, potentially leading to inflammation and gut imbalance. Disruptions in short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production and gut hormone signaling have also been observed. However, human studies generally show milder or no significant changes, highlighting the limitations in translating animal model findings directly to humans. Differences in study design, dosage, exposure time, and sweetener type likely contribute to these varied outcomes. Conclusions: While NNS offer certain benefits, including reduced caloric intake and improved blood sugar regulation, their impact on gut microbiome health raises important concerns. The observed reduction in beneficial bacteria and the rise in pathogenic strains underscore the need for caution in NNS consumption. Furthermore, the disruption of SCFA production and metabolic pathways illustrates the intricate relationship between diet and gut health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microbiota in Human Disease)
►▼
Show Figures
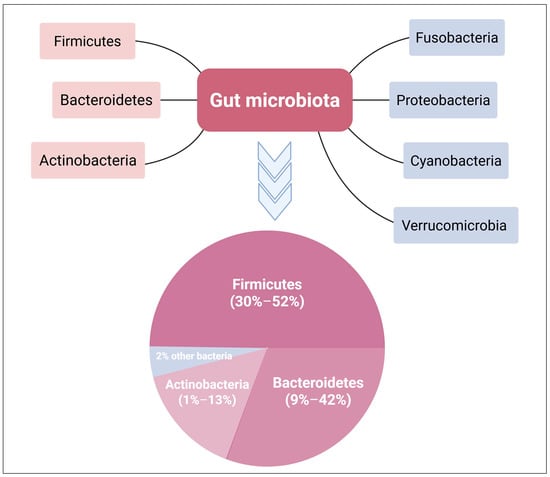
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Seroprevalence and Serotypes of Dengue Virus Infection in Ghana: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Isaac Boamah, Alex Odoom, Kwamena W. C. Sagoe and Eric S. Donkor
Diseases 2025, 13(4), 114; https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases13040114 - 14 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Dengue virus (DENV) infection poses a serious and growing public health threat in many tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, including Ghana. Despite the heightened risks due to suitable climatic conditions and the presence of competent vectors, the epidemiology of DENV in Ghana
[...] Read more.
Background: Dengue virus (DENV) infection poses a serious and growing public health threat in many tropical and subtropical regions worldwide, including Ghana. Despite the heightened risks due to suitable climatic conditions and the presence of competent vectors, the epidemiology of DENV in Ghana remains poorly understood, underscoring the critical need for a comprehensive assessment of the burden and circulation of the virus in the country. Methods: The review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. A literature search was conducted using the PubMed, Web of Science, and Scopus databases from inception to 24 September 2024. Studies presenting primary DENV seroprevalence data among Ghanaian populations were included. Quality was assessed using JBI tools. Meta-analyses estimated pooled prevalence with 95% CIs using random-effects models. Heterogeneity was evaluated using I2 statistic. Results: A total of nine studies met the selection criteria, with eight studies involving febrile patients and one involving blood donors. The pooled seroprevalence rates were 33.3% (95% CI: 16.2–50.4%) for IgG, 5.9% (95% CI: 0–12.5%) for IgM, 1.5% (95% CI: 0.4–2.6%) for DENV RNA, and 32.3% (95% CI: 0–68.5%) for IgG/IgM combined. Notably, the IgG seroprevalence exhibited substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 99%). DENV-2 and DENV-3 were the predominant serotypes identified. There was potential bias in seroprevalence estimates from hospital-based febrile samples. Conclusions: This review has established the prevalence and circulation of DENV serogroups in Ghana. The higher seropositivity and heterogeneity underscore the need for standardized large-scale surveillance to optimize disease characterization and guide control. Integrating dengue prevention into existing vector control programs could help reduce risks in Ghana.
Full article
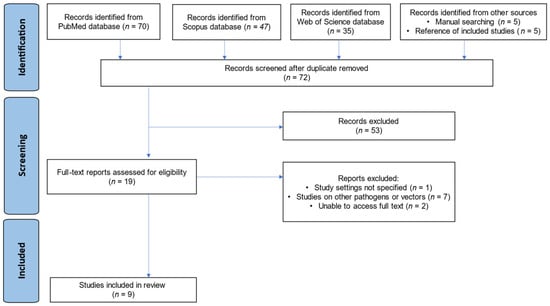
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Cancers, Current Oncology, Diagnostics, Diseases, Onco
Artificial Intelligence in Cancer Pathology and Prognosis
Topic Editors: Hamid Khayyam, Ali Hekmatnia, Rahele Kafieh, Ali JamaliDeadline: 1 May 2025
Topic in
Biomolecules, Cancers, Diseases, Neurology International, Biomedicines
Brain Cancer Stem Cells and Their Microenvironment
Topic Editors: Maria Patrizia Stoppelli, Luca Colucci-D'Amato, Francesca BianchiniDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Biomedicines, Diseases, JCM, JPM, Uro, Reports
Clinical, Translational, and Basic Research and Novel Therapy on Functional Bladder Diseases and Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunctions
Topic Editors: Hann-Chorng Kuo, Yao-Chi Chuang, Chun-Hou LiaoDeadline: 31 December 2026
Topic in
Cancers, Current Oncology, Diseases, IJMS, Cells
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Obesity-Associated Cancer Development and Treatments
Topic Editors: Ming Yang, Chunye ZhangDeadline: 31 August 2027

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Diseases
Treatment Strategies and Immune Responses in Rheumatic Diseases
Guest Editor: Rita Aguiar MouraDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Diseases
Feature Papers in the 'Respiratory Diseases' Section in 2024–2025
Guest Editors: Gaetano Caramori, Andrea BiancoDeadline: 1 May 2025
Special Issue in
Diseases
Targeted Therapies for Acute Leukemias
Guest Editor: Eleftheria HatzimichaelDeadline: 31 May 2025
Special Issue in
Diseases
Cancers of the Genitourinary System: Pathophysiology, Modeling, and Treatment
Guest Editors: Hisham Bahmad, Wassim Abou-KheirDeadline: 9 June 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Diseases
Effects of Food Antioxidants on Cardiovascular Diseases and Human Cancers
Collection Editors: Esra Capanoglu, Maurizio Battino
Topical Collection in
Diseases
Lysosomal Storage Diseases
Collection Editors: José A. Sánchez-Alcázar, Luis Jiménez Jiménez










