Nanotechnology Applied to the Effects of Nutrients on Chronic Diseases
A special issue of Nutrients (ISSN 2072-6643). This special issue belongs to the section "Nutrition and Public Health".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (1 October 2022) | Viewed by 12483
Special Issue Editor
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
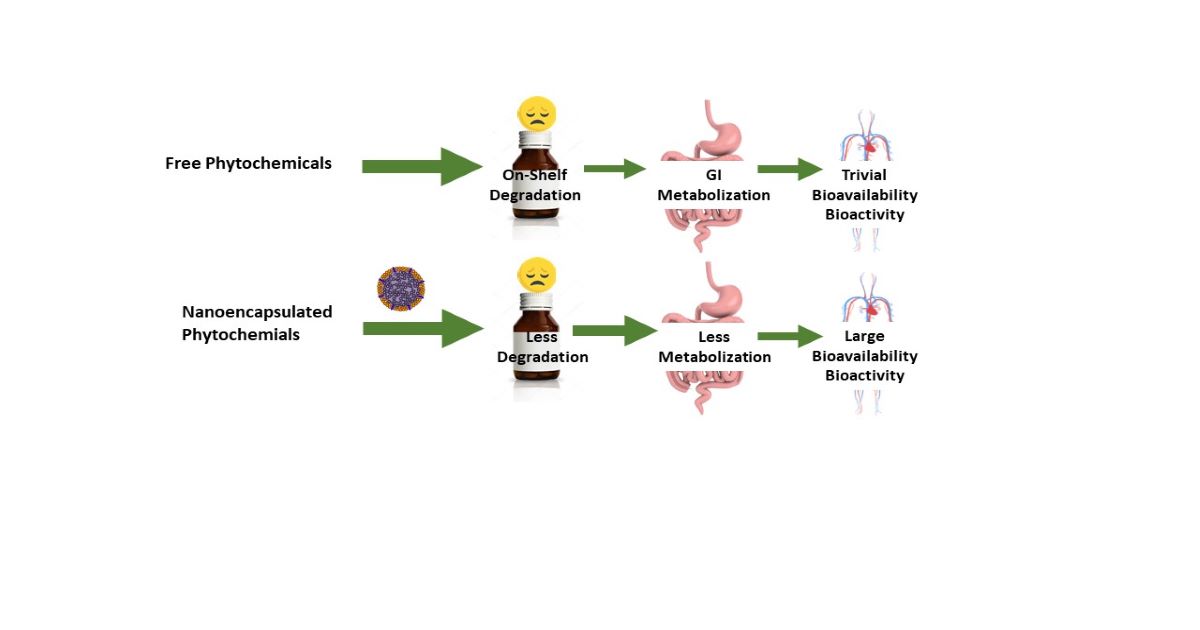
Many nutrients, phytochemicals, and bioactive compounds have the potential to prevent or even treat chronic diseases including obesity, cardiovascular diseases, type II diabetes, certain cancers, chronic respiratory disease, chronic liver disease, chronic inflammatory conditions, and more. However, their low levels of aqueous solubility, stability, bioavailability, and target specificity, and high levels of side effects including hepatic metabolism, and toxicity if taken at high doses, restrict their applications in combating chronic diseases that need regular doses for long periods. Encapsulation of these nutrients and compounds into biocompatible and biodegradable nanoparticles provides a very promising route to overcome these limitations. Nanoencapsulation can significantly increase their aqueous solubility and stability, improve their absorption and bioavailability, protect them from degradation, render their sustained release, prolong their circulation time, and enhance the permeation and retention effect in disease tissues. More importantly, nanoparticles coated with targeting ligands can deliver the encapsulated payload into specific cells or tissues, resulting in a high level of preventive or therapeutic efficacy and a low level of toxicity and side effects.
This Special Issue of Nutrients, entitled “Nanotechnology Applied to the Effects of Nutrients on Chronic Diseases”, welcomes the submission of manuscripts reporting original research or reviewing the scientific literature. Articles investigating effects of nanoparticle-assisted delivery of nutrients, phytochemicals and bioactive compounds on any type of chronic diseases are welcome.
Prof. Dr. Shu Wang
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Nutrients is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- nanotechnology
- nutrients
- nanoparticles
- nutraceuticals
- bioactivities
- bioavailability
- chronic diseases
- obesity
- diabetes
- cardiovascular disease
- fatty liver disease
- metabolic disorders
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.






