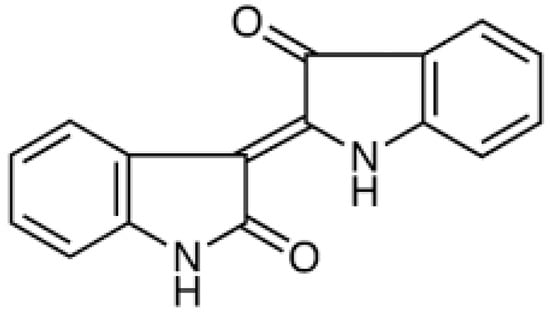
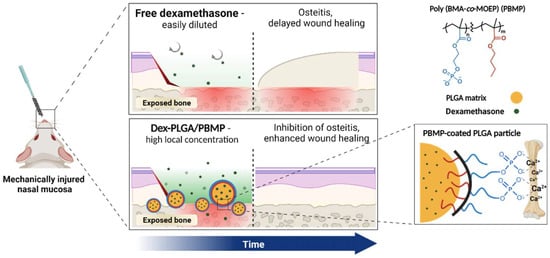
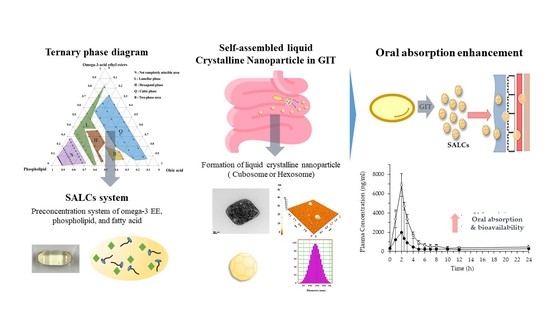
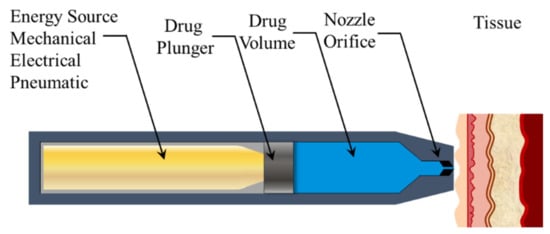
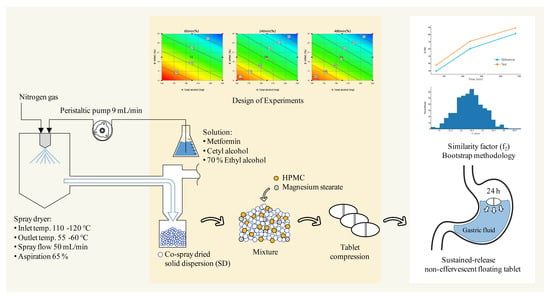
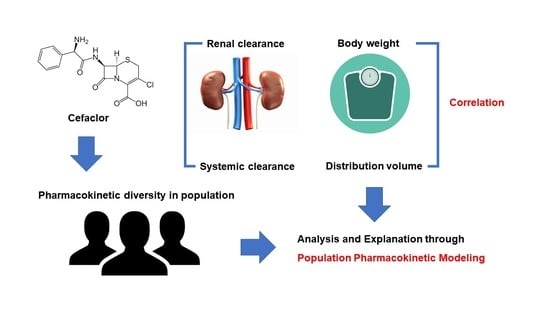
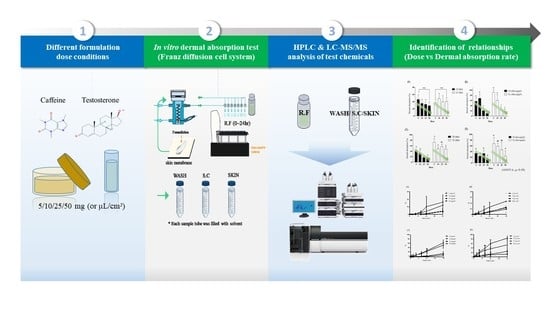
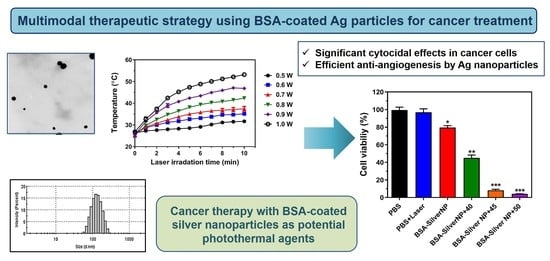
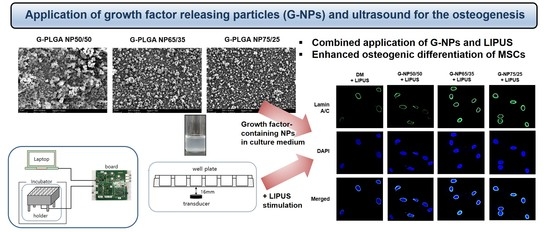
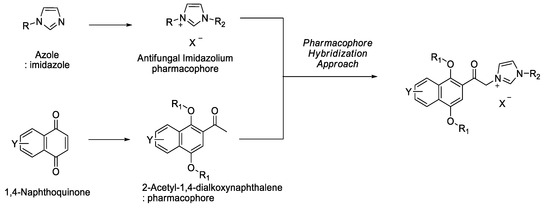
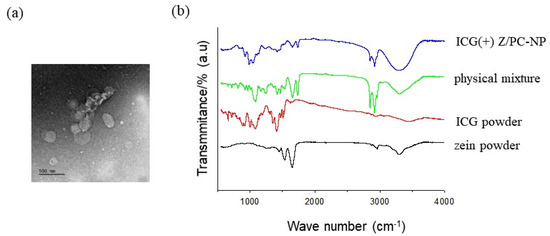
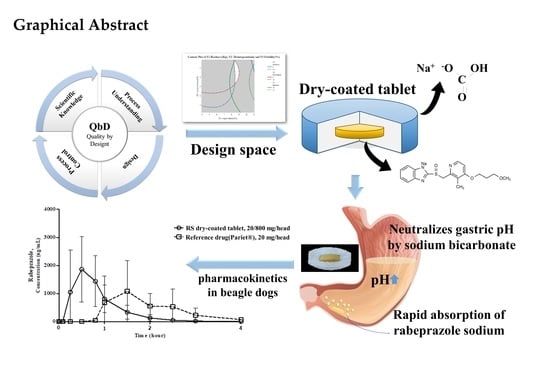
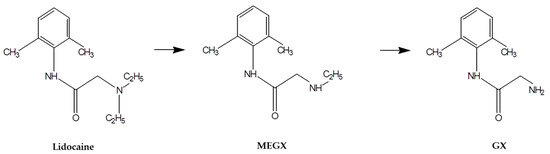
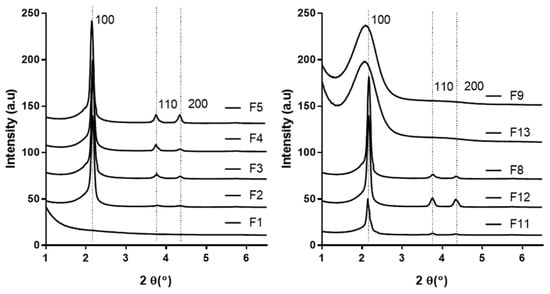
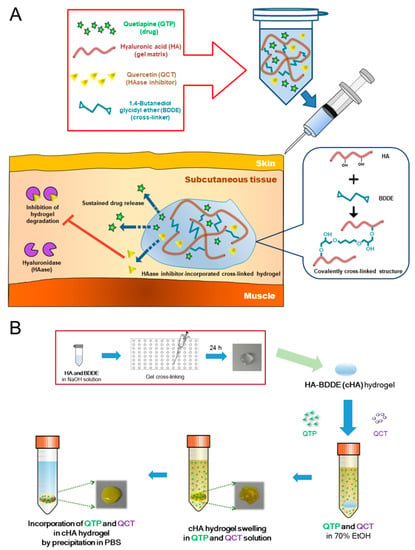
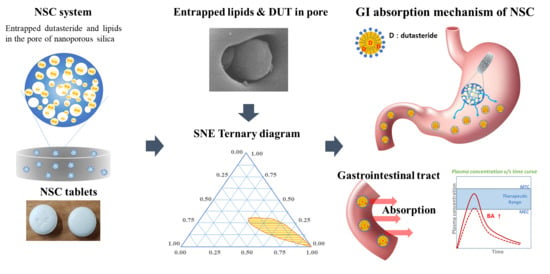
Advanced Pharmaceutical Science and Technology in Korea
A topical collection in Pharmaceutics (ISSN 1999-4923). This collection belongs to the section "Drug Delivery and Controlled Release".
Viewed by 127002Editors
Interests: organic–inorganic hybrid nanocomposites; oral protein delivery; nanomedicine, targeted drug delivery
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: controlled bioavailability of poorly soluble and poorly absorbable drugs; solubilization, formulation, and development of patient-centric dosage forms; advanced nano-based delivery systems using fattigation (fatty acid conjugation) and click chemistry
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
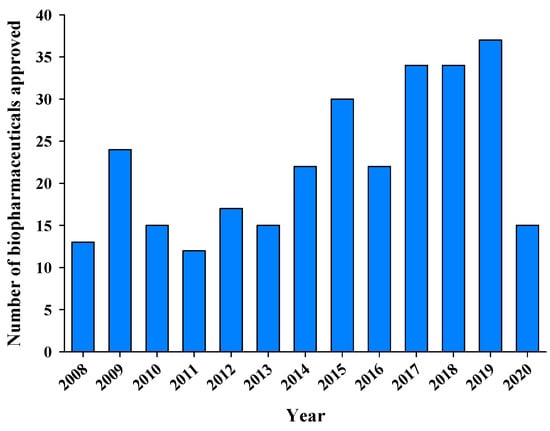
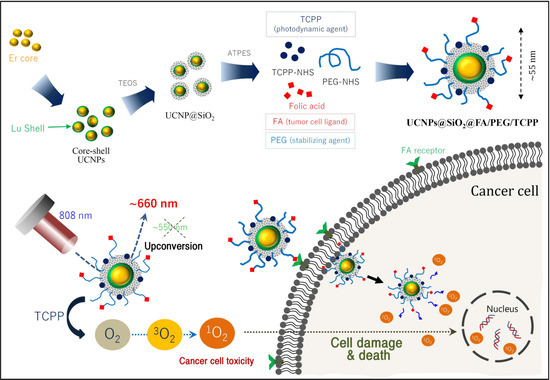
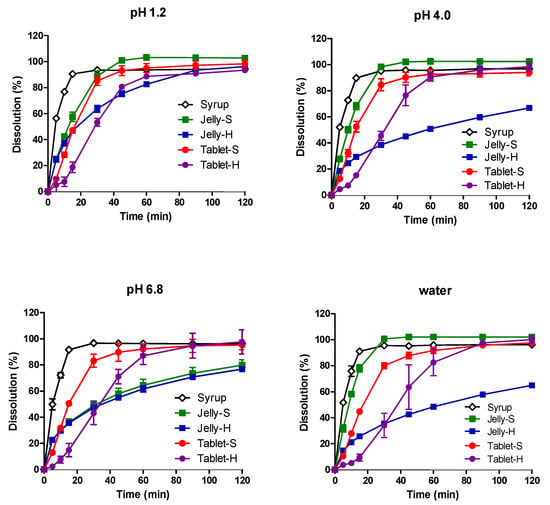
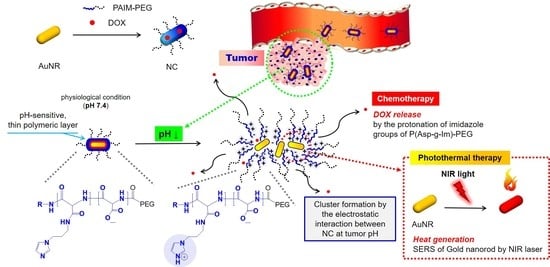
The Korean Society of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Technology (KSPST) is a professional and scholarly organization whose members are actively leading pharmaceutical research and development in academia, the government, and the pharma-bio industries. KSPST members are dedicated to promoting excellence and advancement in the pharmaceutical sciences and technology, mainly working on pioneering topics including novel formulation design, biopharmaceutics and drug delivery, polymer science and materials, pharmacokinetics and drug metabolism, and manufacturing science and biotechnology but not limited to these areas. In addition, pharmaceutical applications of nanomaterials and nanotechnology have made significant progress over the past 10 years, in particular, the drug delivery of small synthetic drugs as well as macromolecules including proteins, peptides, and antibodies. To share and extend the pharmaceutical expertise and advancement in the pharmaceutical sciences in Korea, this topical collection is intended to present research papers and review articles covering recent progress and achievements in high-end pharmaceutical science.
Prof. Beom-Jin Lee
Prof. Dr. Hyo-Kyung Han
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Pharmaceutics is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Drug delivery
- Biopharmaceutics
- Nanomaterials
- Pharmacokinetics
- Nanomedicine
- Preformulation/formulation
Related Special Issue
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Science and Technology in Pharmaceutics (3 articles)