Anaerobic Digestion and Sustainable Integrated Biorefinery
A special issue of Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This special issue belongs to the section "Energy Sustainability".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (27 February 2024) | Viewed by 7794
Special Issue Editors
Interests: sustainable energy; biofuels
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
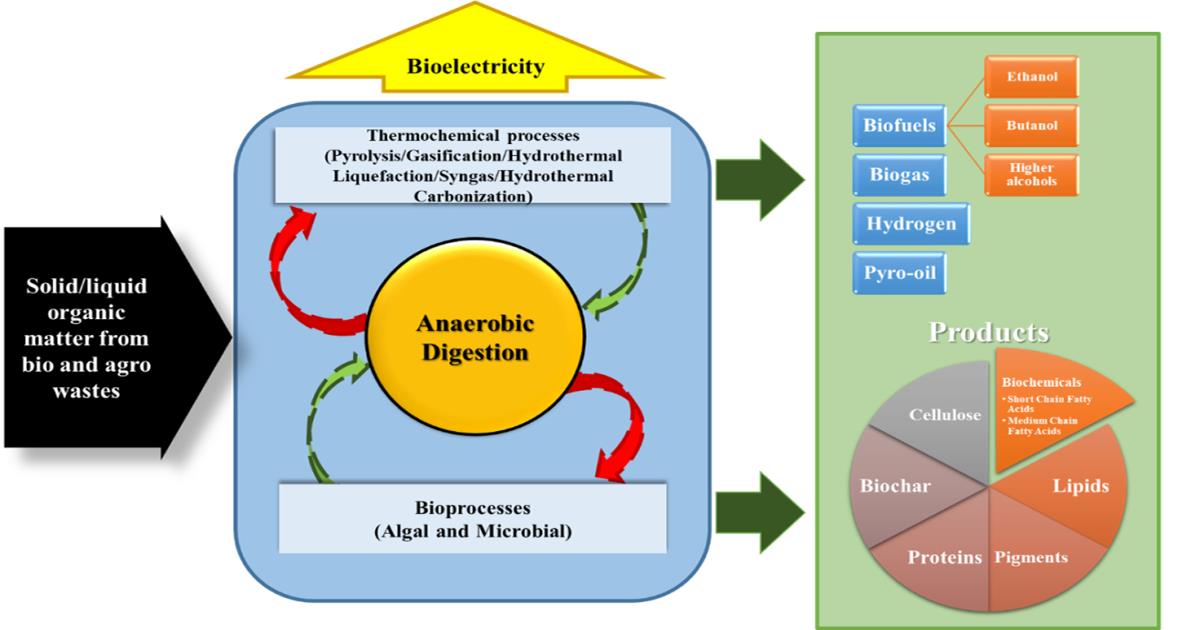
The demand for fossil fuels and subsequent emissions due to their prolonged use have led to investigation of alternative energy resources. With increasing evidence of impending global warming and rising CO2 levels, biomass-based feed stocks have gained significance in recent years. These bio-based materials can be subjected to biochemical, chemical and thermochemical processes to satisfy energy requirements and generate useful by-products like biochar, platform chemicals and other bio products. The concept of biorefinery can be described as a congregation of different unit processes and operations that can be used to derive value-added products such as platform biochemicals and biofuels from biomass-based feed. The concept of biorefineries has been redefined over the years and it has been observed that several other processes such as wastewater treatment, CO2 capture and anaerobic digestion can be integrated into biorefineries, thus helping society to take a step further to adapt to sustainable and zero-waste circular systems. Anaerobic digestion systems have been the backbone of rural waste management in developing countries, with the incentive of utilizing the produced biogas as fuel; simultaneously, the digestate can be repurposed as a soil quality enhancer. Anaerobic digestion (AD) can degrade a large variety of organic wastes, such as food and agro-waste, due to the presence of reactor microbiome. The integration of the anaerobic digestion process with different bioprocesses (microbial, algal etc.) and thermochemical processes has led to the concept of anaerobic digestion-Based biorefineries (ADBB) being developed, strengthening the zero-waste concept of sustainable development. In such a system, the effluent of bioprocesses can be utilized by AD units and the digestate of AD process can in turn be converted into char, syngas, pyro-oil, etc., through thermochemical processes. The upgradation of biogas generated from AD is enabled by the integration of algal bioprocesses, leading to the further generation of biochemicals like lipid, pigment, etc. The generation of hydrogen, ethanol and higher alcohols can be other possibilities through the integration of fermentative and chain elongating bioprocesses into AD. The utilization of liquid effluents, released from bioprocesses in microbial fuel cell for bioelectricity generation, can further strengthen the development of sustainable biorefinery. The biochar generated through pyrolysis of AD digestate can again be introduced into AD for process enhancement. The gases produced during the thermochemical process, namely CO2, can be captured by integrating algal carbon capture and utilization (CCU) units that can remove CO2 and metabolize it same into lipids, fatty acids, proteins and pharmaceuticals. Post-extractions of compounds like leftover biomass, which can be treated as organic waste, can be again fed back into the AD system.
The Guest Editors (GEs) welcome the submission of original research articles and critical review articles incorporating anaerobic digestion process from disciplines related to sustainable biorefineries.
Prof. Dr. Sudipta De
Prof. Dr. Ranjana Chowdhury
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- anaerobic digestion
- biorefinery
- sustainability
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.






