Sustainable Development of Electric Vehicle
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Ocktaeck Lim
Prof. Dr. Ocktaeck Lim
 Prof. Dr. Ocktaeck Lim
Prof. Dr. Ocktaeck Lim
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Graduate School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, Ulsan University Mugeo-dong, Nam-gu, Ulsan 680-749 Korea
Interests: vehicle performance; LCA; energy consumption
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Energy security and environmental pollution issues caused by exhaust emissions from transportation vehicles using fossil fuel are motivations for researchers, companies, and institutions to develop alternative vehicles. Electric vehicles (EVs) are the new trend worldwide to replace traditional vehicles using fossil fuel, which allow us to reduce environmental pollution and avoid dependence on fossil fuels, such as gasoline and diesel. Battery, motor, and energy storage technologies, along with advanced control algorithms, contribute to improving the performance of EVs. Safety, performance, convenience, cost, and battery recycling technologies play important roles in the sustainable future of EVs. In addition, it is necessary to develop infrastructure, charging stations, and charging technologies that facilitate the wide application of EVs worldwide. Development and application of advanced control technologies along with artificial intelligence (AI) to improve performance and flexible operation of EVs are new challenges and also big opportunities to develop EVs further. This Special Issue covers present and future perspectives on EVs with respect to sustainability. We are pleased to receive new contributions from researchers, scientists, students from companies, universities, and research institutes all over the world to build an academic network for developing EVs in the future. Topics of interest include (but are not limited to) the following:
- Advanced control algorithms applied to EVs;
- Power electronics for EVs;
- New technologies for developing motor and battery;
- Advanced materials used for EVs;
- Frame design and optimization;
- Topology technologies of EV components (motor, battery, converters, etc.);
- Energy efficiency and energy storage technologies;
- Renewable energy sources;
- EV charging technologies;
- Vehicle-to-everything communication (e.g., V2H, V2G, V2B);
- New technologies using AI for EVs;
- New technologies for smart cities, smart grids, and smart home supported for EVs;
- Autonomous technologies applied to EVs;
- Battery recycling technologies;
- EVs with economic and environmental issues;
- Technologies for safety.
Prof. Dr. Ocktaeck Lim
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- EV
- Optimization
- V2X
- Battery
- Components
- Safety
- Charging
- Control
Published Papers (13 papers)
Open AccessArticle
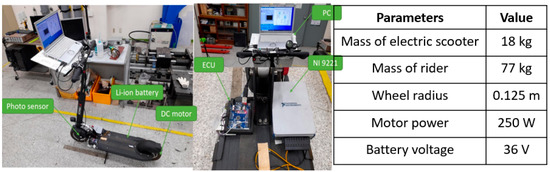
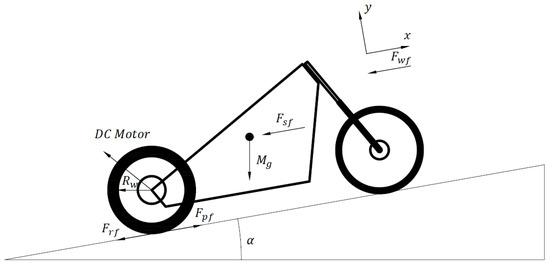
Effects of the Structure and Operating Parameters on the Performance of an Electric Scooter
by
Le Trong Hieu and Ock Taeck Lim
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3067
Abstract
The research objective is to approach the dynamic and consumed electrical energy of an electric scooter by varying the key input parameters, including rider mass, electric scooter mass, wind speed, wheel radius, and slope grade. A simulation model of an electric scooter was
[...] Read more.
The research objective is to approach the dynamic and consumed electrical energy of an electric scooter by varying the key input parameters, including rider mass, electric scooter mass, wind speed, wheel radius, and slope grade. A simulation model of an electric scooter was applied in a MATLAB-Simulink environment to investigate the scooter velocity, required power, battery voltage, and propulsion torque of the e-scooter. It was established by employing mathematical equations during the of electric scooters. The study found that the scooter velocity and electricity consumption were optimized by 3.9% and 0.08%, respectively, when the scooter weight decreased from 26 to 10 kg. The scooter velocity, electricity consumption, and required power decreased by 23.2%, 0.55%, and 8.56%, respectively, when the slope grade decreased from 1.15% to 0%. Following a wind speed reduction from 4 to 0 m/s, the consumed electricity and required power were optimized by 0.2% and 5.5%, respectively. The consumed electricity increased by 0.2% and the scooter velocity and required power significantly increased by 36.5% and 34.3% when the wheel radius increased from 0.105 to 0.185 m. Furthermore, the e-scooter could achieve an effective performance with a weight of 10 kg, wheel radius of 0.185 m, wind speed of 0 km/h, slope grade of 0%, and minimal rider weight. The simulation results showed that the scooter’s effective performance range and consumed electrical energy could be optimized by suitably adjusting the key structures and operating parameters. To support this research, a concurrent experiment investigated the dynamic characteristics and electricity consumption of the electric scooter during operation. The experimental and simulated results had the same patterns in similar initial conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Safety Assessment and Crash Compatibility of Heavy Quadricycle under Frontal Impact Collisions
by
Suphanut Kongwat, Thonn Homsnit, Chaimongkol Padungtree, Naphon Tonitiwong, Pornkasem Jongpradist and Pattaramon Jongpradist
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 4430
Abstract
An electric heavy quadricycle, categorized as an L7e vehicle, is an alternative solution for sustainable mobility with a lower carbon footprint and high energy consumption efficiency. However, accidental crashes of quadricycles with larger vehicle opponents can cause extensive damage to their structures and
[...] Read more.
An electric heavy quadricycle, categorized as an L7e vehicle, is an alternative solution for sustainable mobility with a lower carbon footprint and high energy consumption efficiency. However, accidental crashes of quadricycles with larger vehicle opponents can cause extensive damage to their structures and fatal injury to the occupants due to their geometry drawback in limited space in the front crumple zone. This work investigates the crashworthiness performance and safety assessment of the L7e vehicle under rigid wall crash tests and crash compatibility in car-to-car collisions with a sedan and an SUV. Crash scenarios are simulated using a nonlinear finite element analysis via LS-DYNA to evaluate structural crashworthiness and occupant injuries of a hybrid III 50th percentile male dummy. The compatible vertical alignment of the primary energy-absorbing structure substantially affects the safety of the quadricycle under a frontal crash. A secondary energy-absorbing component should be adapted to the L7e vehicle to achieve vertical alignment with different vehicle sizes. In addition, the typical rigid-wall frontal crash test at 50 kph considerably underestimates the structural damage and occupant injury of the L7e vehicle compared to car-to-car collisions. Thus, additional crash tests representing car-to-car collisions that account for the car’s smaller size and lighter mass should be included in the safety regulation for the L7e vehicle.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
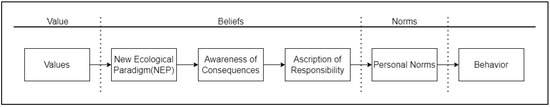
Moderating Effect of Collectivism on Chinese Consumers’ Intention to Adopt Electric Vehicles—An Adoption of VBN Framework
by
Weitao Zhang, Adaviah Mas’od and Zuraidah Sulaiman
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 3376
Abstract
Vehicle electrification has been promoted as an effective way to tackle environmental issues and the energy crisis worldwide. Being the largest auto market, China witnessed a dramatic increase of sale volume and market share of electric vehicles recently, while the incentives kept decreasing.
[...] Read more.
Vehicle electrification has been promoted as an effective way to tackle environmental issues and the energy crisis worldwide. Being the largest auto market, China witnessed a dramatic increase of sale volume and market share of electric vehicles recently, while the incentives kept decreasing. Normative factors have been found to effectively explain consumers’ intention to adopt electric vehicles, but the mechanism remains to be discovered. One of the culture’s orientations, namely collectivism, has been proved to have significant impact on consumption behaviors, but the influence of collectivism on intention to adopt electric vehicles in China needs further discussion. Based on 433 questionnaires collected from Chinese consumers, this study adopted the Value–Belief–Norm (VBN) framework and examined collectivism as a moderator variable on the relationship between personal norms and intention to adopt electric vehicles. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS 27 and PLS-SEM (SmartPLS 3). The results show that the VBN framework successfully explains the intention to adopt electric vehicles of Chinese consumers, and collectivism has a significant positive moderating effect on the relationship between personal norms and intention to adopt electric vehicles. Insights and suggestions from theoretical and managerial perspectives on how to accelerate electric vehicle adoption are discussed for marketers, policymakers and industry practitioners.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
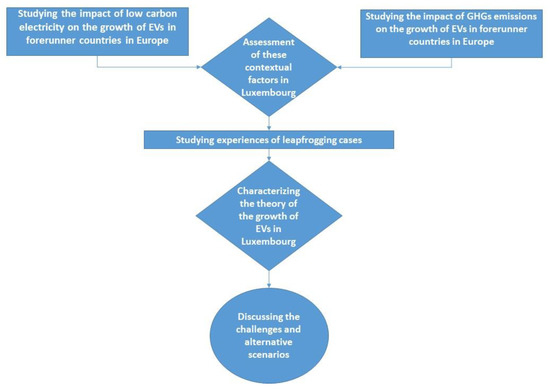
Characterizing the Theory of Spreading Electric Vehicles in Luxembourg
by
Ali Arababadi, Stephan Leyer, Joachim Hansen and Reza Arababadi
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2859
Abstract
The development of electric vehicles (EVs) is happening around the world with different goals. Many researchers have worked on various aspects of EVs from technological and supporting policy issues to the development of required infrastructures. However, arguing the proper time to realize the
[...] Read more.
The development of electric vehicles (EVs) is happening around the world with different goals. Many researchers have worked on various aspects of EVs from technological and supporting policy issues to the development of required infrastructures. However, arguing the proper time to realize the spreading of EVs in each region is neglected. For this purpose, the performance of two contextual factors in each region on the growth of EVs is investigated. Low carbon electricity generation and greenhouse gases emissions are the selected parameters, which are explored in the context of nine European countries, besides Luxembourg, to find their impacts on the issue. These countries have the highest shares of EVs in their energy systems. The achieved results are applied to the Luxembourg case to evaluate how different contextual factors may have hindered the growth of EVs here. In the next step, an analogy between the spreading EVs in Luxembourg and leapfrogging different technologies in the world is made to build a theory of the development of EVs. The theory defines the spreading EVs in Luxembourg as a leapfrogging energy technology to adopt new technology. It is concluded that the development of EVs has a normal priority in Luxembourg.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Blockchain-Based Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading and Charging Payment System for Electric Vehicles
by
Prince Waqas Khan and Yung-Cheol Byun
Cited by 56 | Viewed by 9142
Abstract
The world is moving rapidly from carbon-producing vehicles to green transportation systems. Electric vehicles (EV) are a big step towards a friendly mode of transport. With the constant rise in the number of electric vehicles, we need a widespread and seamless charging infrastructure
[...] Read more.
The world is moving rapidly from carbon-producing vehicles to green transportation systems. Electric vehicles (EV) are a big step towards a friendly mode of transport. With the constant rise in the number of electric vehicles, we need a widespread and seamless charging infrastructure that supports seamless charging and billing. Some users generate electricity using solar panels and charge their electric vehicles. In contrast, some use charging stations, and they pay for vehicle charging. This raises the question of trust and transparency. There are many countries where laws are not strictly enforced to prevent fraud in payment systems. One of the preeminent problems presently existing with any of the trading systems is the lack of transparency. The service provider can overcharge the customer. Blockchain is a modern-day solution that mitigates trust and privacy issues. We have proposed a peer-to-peer energy trading and charging payment system for electric vehicles based on blockchain technology. Users who have excess electricity which they can sell to the charging stations through smart contracts. Electric vehicle users can pay the charging bills through electronic wallets. We have developed the electric vehicle’s automatic-payment system using the open-source platform Hyperledger fabric. The proposed system will reduce human interaction and increase trust, transparency, and privacy among EV participants. We have analyzed the resource utilization and also performed average transaction latency and throughput evaluation. This system can be helpful for the policymakers of smart cities.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
An Investigation on the Effects of Input Parameters on the Dynamic and Electric Consumption of Electric Motorcycles
by
Le-Trong Hieu, Nguyen Xuan Khoa and Ocktaeck Lim
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3082
Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to study how input parameters affect the dynamic characteristics and electric consumption characteristics of an electric motorcycle. To achieve this goal, a simulation model of the electric motorcycle, including dynamic models and battery models were established based
[...] Read more.
The purpose of this paper is to study how input parameters affect the dynamic characteristics and electric consumption characteristics of an electric motorcycle. To achieve this goal, a simulation model of the electric motorcycle, including dynamic models and battery models were established based on mathematical models and using the MATLAB SIMULINK software (Parnas Tower 14th Floor521 Teheran-street Gangnam-district Seoul 06164 Korea). The simulation model was used to determine the velocity, propulsion torque, electric consumption characteristics with variable electric motorcycle mass, driver mass, wheel radius, frontal area, and transmission ratio. Through the simulation study, the paper found that when the electric motorcycle mass was increased from 60 kg to 100 kg, the maximum velocity decreased by 5.45%, the moving distance was reduced by 5.89%, and electric consumption increased by 0.11%. Following increased driver mass from 48 kg to 88 kg, the velocity and moving distance decreased by 5.45% and 5.89%, respectively, while also increasing electric consumption by 0.11%. When the wheel radius was changed from 0.205 m to 0.245 m, the maximum velocity increased by 11%, the moving distance increased by 11.2%, and electric consumption increased by 0.11%. When the frontal area was increased from 0.52 m
2 to 0.92 m
2, the velocity and moving distance decreased by 2.43% and 2.06%, respectively, while electric consumption increased by 0.04%. When the transmission ratio was increased from 2.66 to 4.94, the velocity and moving distance increased from 30.74 km/h to 70.7 km/h and from 303.12 m to 710.44 m, respectively, while electric consumption increased by 0.16%. Finally, an experimental study is conducted to examine the dynamics of the electric motorcycle. The experimental results have the same trend with simulation in the same initial condition. Through combination simulation and experiment, the researcher can optimize the dynamic and electric consumption of an electric motorcycle.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Design and Implementation of Probabilistic Transient Stability Approach to Assess the High Penetration of Renewable Energy in Korea
by
Young-Been Cho, Yun-Sung Cho, Jae-Gul Lee and Seung-Chan Oh
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2328
Abstract
Recently, because of the many environmental problems worldwide, Korea is moving to increase its renewable energy output due to the Renewable 3020 Policy. Renewable energy output can change depending on environmental factors. It is for this reason that institutions should consider the instability
[...] Read more.
Recently, because of the many environmental problems worldwide, Korea is moving to increase its renewable energy output due to the Renewable 3020 Policy. Renewable energy output can change depending on environmental factors. It is for this reason that institutions should consider the instability of renewables when linked to the electric system. This paper describes the methodology of renewable energy capacity calculation based on probabilistic transient stability assessment. Probabilistic transient stability assessment consists of four algorithms: first, to create probabilistic scenarios based on the effective capacity history of renewable energy; second, to evaluate probabilistic transient stability based on transient stability index, interpolation-based transient stability index estimation, reduction-based transient stability index calculation, etc.; third, to implement multiple scenarios to calculate renewable energy capacity using probabilistic evaluation index; and finally, to create a probabilistic transient stability assessment simulator based on Python. This paper calculated renewable energy capacity based on large-scale power system to validate consistency of the proposed paper.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Incentive Policies and Other Socio-Economic Factors on Electric Vehicle Market Share: A Panel Data Analysis from the 20 Countries
by
Chenlei Xue, Huaguo Zhou, Qunqi Wu, Xueying Wu and Xingbo Xu
Cited by 62 | Viewed by 13901
Abstract
Under the strong support of policies and incentives, the global electric vehicle (EV) market has been developing rapidly. However, in the context of the overall EV market boom, the promotion policies and incentives for consumers to adopt EVs differ from country to country.
[...] Read more.
Under the strong support of policies and incentives, the global electric vehicle (EV) market has been developing rapidly. However, in the context of the overall EV market boom, the promotion policies and incentives for consumers to adopt EVs differ from country to country. It is worth exploring the key factors that affect market share and adoption of EVs, such as incentives, policies, and additional socio-economic factors. The data on EV market share and information on policies and incentives in 20 countries were collected from the published reports and online resources from 2015 to 2019. Random effects model analysis was conducted to explore the effect of various factors on EV market share. The innovation of this article is to combine incentive policies with socio-economic factors and use panel data to analyze the actual adoption behavior of the global EV market. Results show that the tax reduction policy, charger density, and income have significantly positive effects on the penetration of EVs. Thus, it suggested that government should still maintain tax incentives and focus on the deployment of charging infrastructure. Household income, as a socio-economic factor, also plays an important role in the adoption of EVs. This will help policymakers adjust and improve policy emphasis to promote the adoption of EVs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Design and Implementation of a Co-Simulation Framework for Testing of Automated Driving Systems
by
Demin Nalic, Aleksa Pandurevic, Arno Eichberger and Branko Rogic
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 3876
Abstract
The increasingly used approach of combining different simulation softwares in testing of automated driving systems (ADSs) increases the need for potential and convenient software designs. Recently developed co-simulation platforms (CSPs) provide the possibility to cover the high demand for testing kilometers for ADSs
[...] Read more.
The increasingly used approach of combining different simulation softwares in testing of automated driving systems (ADSs) increases the need for potential and convenient software designs. Recently developed co-simulation platforms (CSPs) provide the possibility to cover the high demand for testing kilometers for ADSs by combining vehicle simulation software (VSS) with traffic flow simulation software (TFSS) environments. The emphasis on the demand for testing kilometers is not enough to choose a suitable CSP. The complexity levels of the vehicle, object, sensors, and environment models used are essential for valid and representative simulation results. Choosing a suitable CSP raises the question of how the test procedures should be defined and constructed and what the relevant test scenarios are. Parameters of the ADS, environments, objects, and sensors in the VSS, as well as traffic parameters in the TFSS, can be used to define and generate test scenarios. In order to generate a large number of scenarios in a systematic and automated way, suitable and appropriate software designs are required. In this paper, we present a software design for a CSP based on the Model–View–Controller (MVC) design pattern as well as an implementation of a complex CSP for virtual testing of ADSs. Based on this design, an implementation of a CSP is presented using the VSS from IPG Automotive (CarMaker) and the TFSS from the PTV Group (Vissim). The results showed that the presented CSP design and the implementation of the co-simulation can be used to generate relevant scenarios for testing of ADSs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
A Study on State of Charge and State of Health Estimation in Consideration of Lithium-Ion Battery Aging
by
Woongchul Choi
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 4007
Abstract
Due to rapid development of industries around the world, more and more consumption of fossil fuels was unavoidable, resulting in serious environmental problems. The many pollutant emissions—a major contributor to global warming and weather pattern change—have been at the center of concern. In
[...] Read more.
Due to rapid development of industries around the world, more and more consumption of fossil fuels was unavoidable, resulting in serious environmental problems. The many pollutant emissions—a major contributor to global warming and weather pattern change—have been at the center of concern. In order to solve this issue, research and development of electric vehicles and energy storage systems made great progress and successfully introduced products in the market. Nevertheless, accurate measurement of the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of the Li-ion battery, the most popular electric energy storage device, has not yet been fully understood due to the nature of battery aging. In this study, ideas to estimate the capacity and ultimately SOC and SOH of Li-ion batteries are discussed. With these ideas, we expect not only to accommodate the issues with battery aging but also to implement an algorithm for an on-board battery management system. The key idea is to chase and monitor internal resistance continuously in a fast and reliable manner in real time. With further investigation of the key idea, we also fully expect to come up with a reliable SOC and SOH measurement scheme in the near future.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
A Comparative Study of Initial Cost Recuperation Period of Plug-In Series Hybrid Electric Two-Wheel Vehicles in Southeast Asian Countries
by
Woongchul Choi and Seokho Yun
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2803
Abstract
While pollutant emissions from vehicles are under heavy scrutiny all around the world, small two-wheelers have not been under strict regulations until recently. Especially in the region of Southeast Asia, a tremendous number of old, in-house rebuilt and outdated two-wheelers are in operation
[...] Read more.
While pollutant emissions from vehicles are under heavy scrutiny all around the world, small two-wheelers have not been under strict regulations until recently. Especially in the region of Southeast Asia, a tremendous number of old, in-house rebuilt and outdated two-wheelers are in operation and, as a result, pollutant emission problems are one of the most serious concerns of the communities. Since electric grid systems for consistent and stable supply of electricity are not there yet, thus plug-in series hybrid two-wheel vehicles have attracted much attention and are thought to be a meaningful solution for many people in the region. In the current study, an energy simulation tool has been developed to compare the ownership cost of an internal combustion engine (ICE)-based two-wheeler and that of a plug-in series hybrid electric scooter. To estimate annual energy cost (sum of gasoline and electricity cost), gasoline prices and household electricity rates in major Southeast Asian countries were collected. In addition, the nominal initial vehicle prices of ICE-based scooters and those of plug-in series hybrid electric two-wheel vehicles were gathered to estimate the time for the recovery of the initial investment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Energy Management Optimization of Series Hybrid Electric Bus Using an Ultra-Capacitor and Novel Efficiency Improvement Factors
by
Giyeon Hwang, Kyungmin Lee, Jongmyung Kim, Kyu-Jin Lee, Sangyul Lee and Minjae Kim
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2799
Abstract
The existing series hybrid electric bus (SHEB) uses an ultra-capacitor (UC) to extend battery life, mitigate vehicle weight, and reduce cost. However, previous studies did not clearly identify the operation timing and load of the UC for efficiency improvement in an SHEB. This
[...] Read more.
The existing series hybrid electric bus (SHEB) uses an ultra-capacitor (UC) to extend battery life, mitigate vehicle weight, and reduce cost. However, previous studies did not clearly identify the operation timing and load of the UC for efficiency improvement in an SHEB. This paper proposes novel efficiency improvement factors, with their application criteria for the ideal operation timing and load of the UC in an SHEB. The factors are the threshold of the required power of the motor (TRPM), slope of the power split ratio (SPSR), and y-axis intercept of the power split ratio (YPSR). The TRPM determines the duration of using just the battery. The SPSR or YPSR determine the most efficient load ratio between the battery and UC. The criteria for using them are set using particle swarm optimization. Manhattan, Braunschweig, and Orange County driving cycles were used to reflect various road load conditions. The results showed that the proposed factors and their setting criteria guarantee a significant reduction in the fuel consumption and more energy-efficient SHEBs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Design Parameters on Operating Characteristics of an Electric Assisted Bicycle Using Fuel Cell
by
Nguyen Ba Hung and Ocktaeck Lim
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2928
Abstract
A simulation study was conducted to examine the effects of design parameters on the operation of an electric power-assisted bicycle using fuel cell. Bicycle dynamic, electric motor and fuel cell models were built to depict operation of the electric bicycle. These models were
[...] Read more.
A simulation study was conducted to examine the effects of design parameters on the operation of an electric power-assisted bicycle using fuel cell. Bicycle dynamic, electric motor and fuel cell models were built to depict operation of the electric bicycle. These models were solved by Matlab-Simulink to obtain the operating characteristics of the electric bicycle, such as power of fuel cell, propulsion force, moving distance and velocity. The simulation results in motion were compared to experimental results to validate the simulation models. The effects of the number of cells and hydrogen fuel pressure on the operation of the electric bicycle were investigated. In addition, the influences of slope grade on the operating characteristics of the electric-assisted bicycle and fuel cell were investigated in two cases: without and with fuel cell control. The simulation results show that the operating performance of the electric bicycle was improved when the number of cells was increased. The increase in hydrogen fuel pressure helped to increase the operating performance of the electric bicycle; however, this contribution was not significant. When fuel cell control was applied, the velocity of the electric assisted bicycle could be maintained at a stable value, in spite of changing slope grade.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures