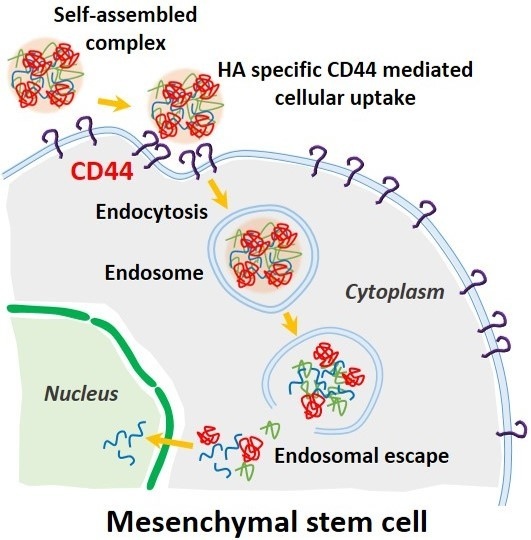
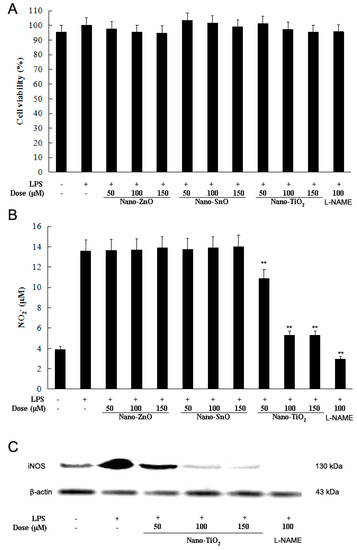
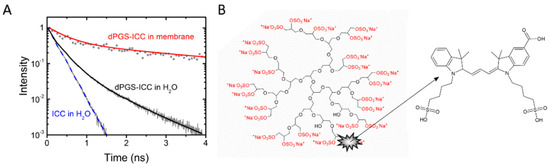
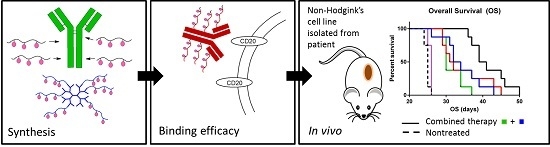
Nanomedicine (Closed)
A topical collection in Molecules (ISSN 1420-3049). This collection belongs to the section "Medicinal Chemistry".
Viewed by 283416Editor
Interests: nanomaterials; functional Au and other transition metal nanoparticles; targeted drug delivery; taxanes; sensors; dendrimers; polymers; catalysis; redox processes
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
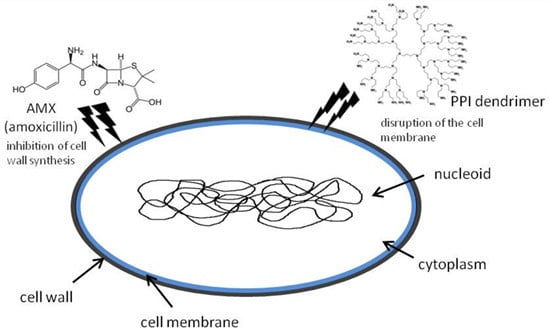
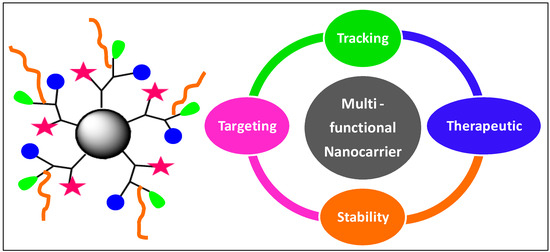
Nanomedicine involves the applications of nanotechnology, controlled mater in the 1–100 nm range, to the diagnosis, and treatment of major diseases using engineered targeted delivery of diagnostic agents and drugs to specific organs in order to maximize efficiency and avoid side effects. An approach for building a drug delivery system is to incorporate the drug within the nanocarrier that results in increased solubility, metabolic stability, and improved circulation time. The precise targets are cells and receptors including phagocytes, dendritic cells, endothelial cells, tumor cells, and tumor neovasculature that guide the rational approach to appropriate nanocarriers. Chemotherapy has limitations due to the lack of selectivity with severe toxicity. Under these circumstances tumor-targeted delivery of anticancer drugs is probably one of the most important steps for cancer chemotherapy. Therefore ongoing research concerns the “magic bullets” that comprises particle design and formulation that are applied to many drugs and are invading industry with huge potential benefits.
The specific properties of such engineered nanomaterials can be used to overcome some of the limitations found in traditional therapeutic and diagnostic agents. In particular, commonly used materials for nanoparticle carriers of nanodrugs for cancer chemotherapy including cisplatin, carboplatin, bleomycin, 5-fluorouracil, doxorubicin, dactinomycin, 6-mercaptopurine, paclitaxel, docetaxel, topotecan, vinblastin and etoposide etc., are dendrimers, polymers, liposomes, micelles, inorganic, organic nanoparticles, whereas the commonly used nano drugs are liposomes. Other nanoparticles such as tailored polymer nananoparticles, gold nanoparticles and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) disclose different properties from those of bulk materials owing to the quantum physics and enhanced surface chemistry related to their nanosize and appear most useful for theranostics, i.e. therapy + diagnostics. Finally, the concept of enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect of solid tumors that involves high drug concentration in tumor compared to that of the blood warrants the development of polymeric drugs, while monoclonal antibody conjugates are another direction with increasing recent interest.
This Topical Collection aims to provide a forum for the dissemination of the latest information on related and new aspects of nanomedicine.
Prof. Dr. Didier Astruc
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Molecules is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- nanomedicine
- cancer
- theranostics
- targeted drug delivery
- diagnosis
- therapy
- disease
- nanocarrier
- metabolic stability
- improved circulation time
- phagocytes
- dendritic cells
- endothelial cells
- tumor cells
- tumor neovasculature
- magic bullet
- cisplatin
- carboplatin
- bleomycin
- 5-fluorouracil
- doxorubicin
- dactinomycin
- 6-mercaptopurine
- paclitaxel
- docetaxel
- topotecan
- vinblastine
- etoposide
- dendrimer
- polymer
- liposome
- micelle
- nanoparticle
- gold
- superparamagnetic iron oxide
- SPION
- plasmon
- enhanced permeability and retention
- EPR