Optimal Planting Density Increases the Seed Yield by Improving Biomass Accumulation and Regulating the Canopy Structure in Rapeseed
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Plot Seed Yield
2.2. Yield Components
2.3. Biomass Accumulation and Partitioning
2.4. Yield Performance of Main Raceme and Branch Raceme
2.4.1. Yield Components of Main Raceme and Branch Raceme
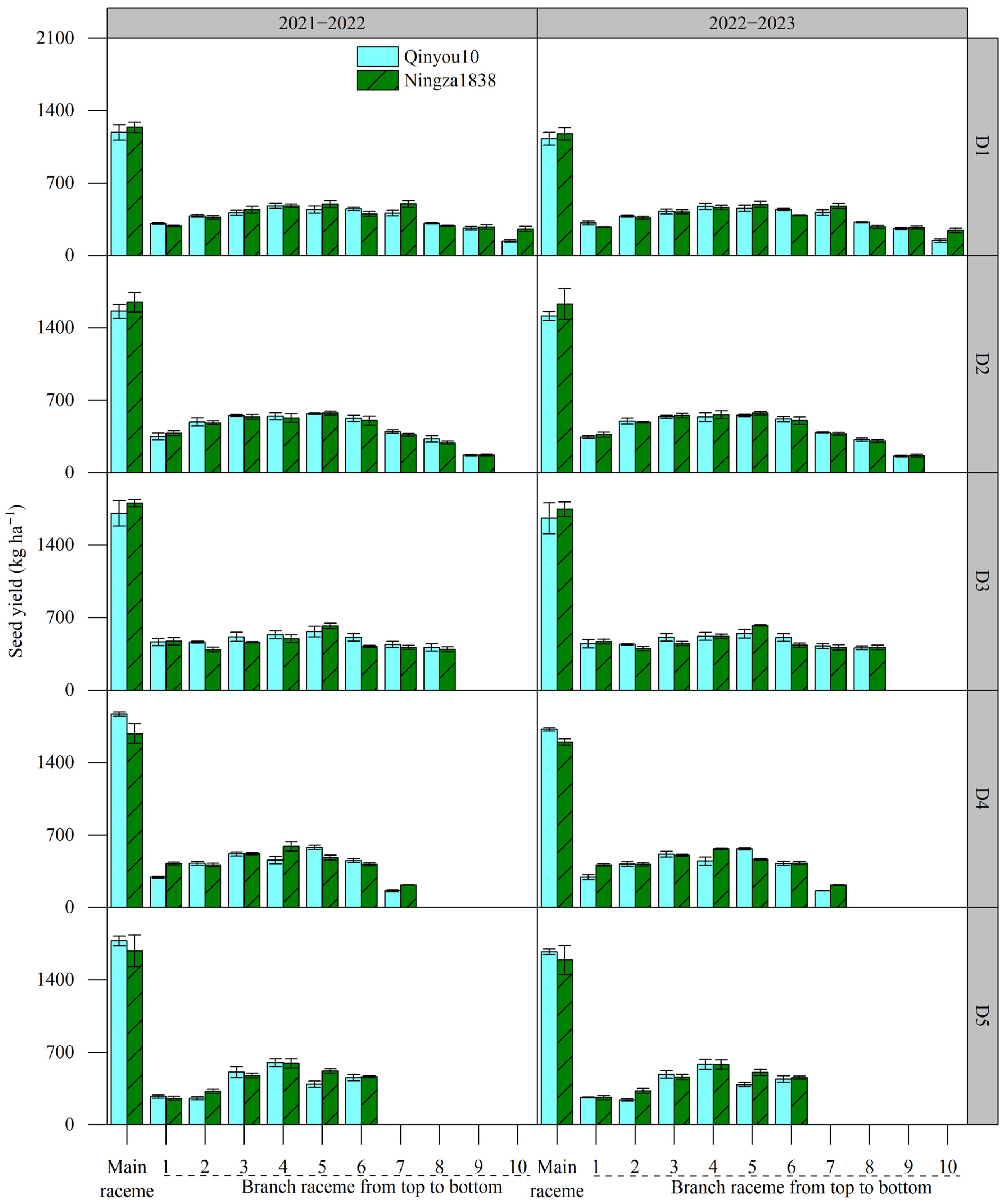
2.4.2. Seed Yield of Main Raceme and Branch Raceme
2.4.3. Yield Distribution of Main Raceme and Branch Raceme
2.5. Canopy Structure
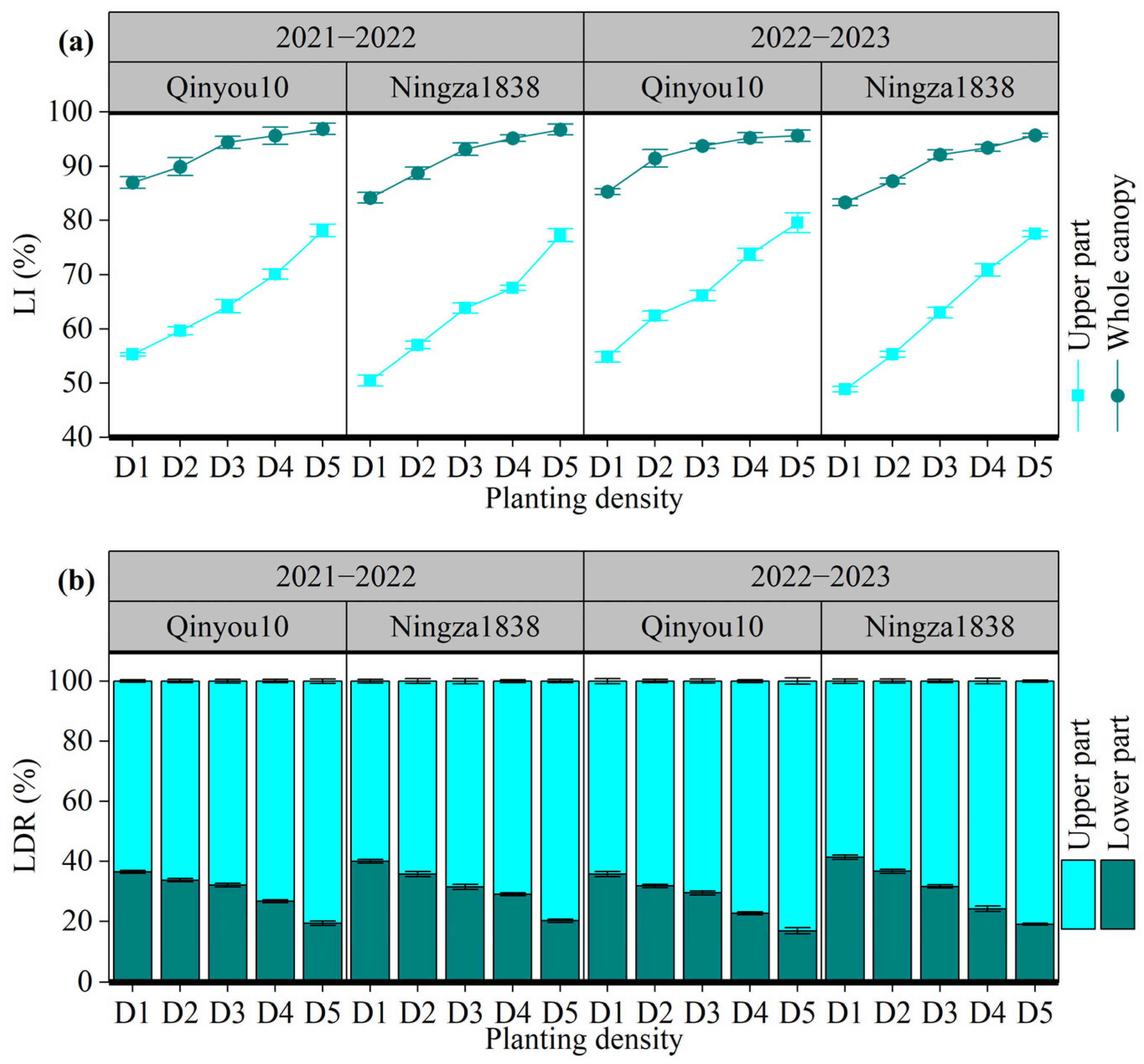
2.5.1. PAI and Light Interception
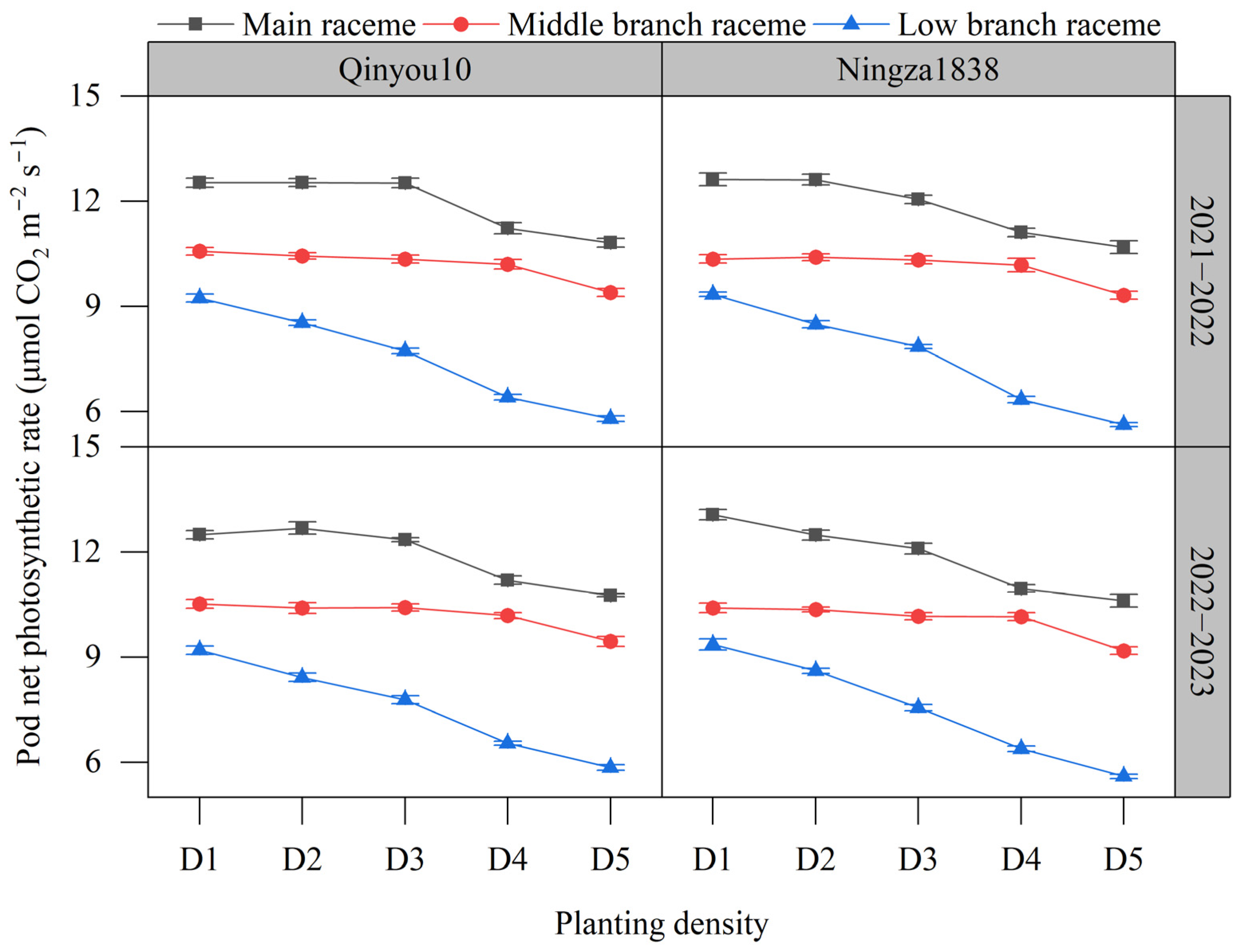
2.5.2. Pod Photosynthesis
3. Discussion
3.1. Effects of Planting Density on Yield and Yield Components
3.2. Effects of Planting Density on Biomass
3.3. Effects of Planting Density on Canopy Structure
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Site and Design
4.2. Sampling and Measurement
4.2.1. Plot Seed Yield and Seedling Survival Rate
4.2.2. Yield Components
4.2.3. Biomass Accumulation and Partitioning
4.2.4. PAI and Pod Photosynthesis
4.2.5. Light Interception and Distribution
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, Z.; Kong, J.; Tang, M.; Luo, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, R.; Feng, S.; Zhang, C. Modelling Winter Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Growth and Yield under Different Sowing Dates and Densities Using AquaCrop Model. Agronomy 2023, 13, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. Available online: https://data.stats.gov.cn/adv.htm?m=advquery&cn=C01 (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Li, Q.; Wang, C. An Evaluation of Chinese Rapeseed Production Efficiency Based on Three-Stage DEA and Malmquist Index. Sustain. Sci. 2022, 14, 15822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riar, A.; Gill, G.; McDonald, G.K. Rate of Nitrogen Rather Than Timing of Application Influence Yield and NUE of Canola in South Australian Mediterranean Environments. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Watts, D.B.; Torbert, H.A.; Howe, J.A. Influence of Nitrogen Rate on Winter Canola Production in the Southeastern United States. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 2978–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, J.; Sun, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Huang, H.; Liao, Q.; Wu, C.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, G. The Yield of Mechanically Harvested Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Can Be Increased by Optimum Plant Density and Row Spacing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganj-Abadi, F.; Shirani Rad, A.H.; Sani, B.; Mozafari, H. Grain Yield and Qualitative of Rapeseed Genotypes Change in Response to Exogenous Application of Salicylic Acid and Planting Density. Gesunde Pflanz. 2021, 73, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Yu, C.B.; Zhu, S.; Xie, L.H.; Hu, X.J.; Liao, X.; Liao, X.S.; Che, Z. High Planting Density Benefits to Mechanized Harvest and Nitrogen Application Rates of Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.). Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 60, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, A.; Samdaliri, M.; Rad, A.S.; Shahsavari, N.; Jabbari, H. Effect of Plant Density on Yield and Physiological Characteristics of Six Canola Cultivars. J. Sci. Agric. 2017, 1, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Friedman, S.P. Relationships between Combined and Individual Field Crops’ Biomass and Planting Density. Field Crops Res. 2024, 305, 109188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, S.; Du, B.; Zhou, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, J. Tillage Intensity and Planting Density Significantly Affected Photosynthesis, Growth, and Yield of Rice. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 2662–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Liao, Z.; Lai, Z.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Fan, J. Interactive Effects of Planting Pattern, Supplementary Irrigation and Planting Density on Grain Yield, Water-Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Economic Benefit of Winter Wheat in a Semi-Humid but Drought-Prone Region of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 287, 108438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Huang, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, L. Optimizing Irrigation and Planting Density of Spring Maize under Mulch Drip Irrigation System in the Arid Region of Northwest China. Field Crops Res. 2021, 266, 108141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, J.; Li, X.; Ji, J.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhou, G. Response of Leaf Carbon Metabolism and Dry Matter Accumulation to Density and Row Spacing in Two Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Genotypes with Differing Plant Architectures. Crop J. 2022, 10, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Wang, L.; Ali, S.; Tung, S.A.; Hafeez, A.; Yang, G. Optimal Planting Density and Sowing Date Can Improve Cotton Yield by Maintaining Reproductive Organ Biomass and Enhancing Potassium Uptake. Field Crops Res. 2017, 214, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.; van der Werf, W.; Evers, J.B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Song, X.; Li, Z. Use of the Beta Growth Function to Quantitatively Characterize the Effects of Plant Density and a Growth Regulator on Growth and Biomass Partitioning in Cotton. Field Crops Res. 2018, 224, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlangue, T.; Andrade, F.H.; Calvino, P.A.; Purcell, L.C. Why Do Maize Hybrids Respond Differently to Variations in Plant Density? Agron. J. 2007, 99, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmel, C.; D’Odorico, P.; Revill, A.; Hortnagl, L.; Ammann, C.; Buchmann, N.; Eugster, W. Canopy Photosynthesis of Six Major Arable Crops Is Enhanced under Diffuse Light Due to Canopy Architecture. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 5164–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zheng, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, D.; Peng, W. Effects of a Range of Phosphorus Levels on Yield, Phosphorus Efficiency, and Canopy Sunlight Interception in Direct-Seeded Winter Rapeseed. Agron. J. 2023, 115, 2058–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zuo, Q.; Chang, H.; Bai, G.; Kuai, J.; Zhou, G. Higher Density Planting Benefits Mechanical Harvesting of Rapeseed in the Yangtze River Basin of China. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammelvind, L.H.; Schjoerring, J.K.; Mogensen, V.O.; Jensen, C.R.; Bock, J.G.H. Photosynthesis in Leaves and Siliques of Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.). Plant Soil 1996, 186, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuai, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, P.; Zuo, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhou, G. The Effect of Nitrogen Application and Planting Density on the Radiation Use Efficiency and the Stem Lignin Metabolism in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Field Crops Res. 2016, 199, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrell, A.K.; Hammer, G.L. Nitrogen Dynamics and the Physiological Basis of Stay-Green in Sorghum. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Kuai, J.; Li, Z.; Bai, R.; Zhou, G. Planting Density and Variety Intercropping Improve Organ Biomass Distribution of Rapeseed to Alleviate the Trade-off between Yield and Lodging Resistance. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 2696–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, P.M.; Spink, J. Predicting Yield Losses Caused by Lodging in Wheat. Field Crops Res. 2012, 137, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wang, B.; Kuai, J.; Zhou, G. An Improvement in Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.) Productivity through Optimization of Rice-Straw Quantity and Plant Density. Field Crops Res. 2021, 273, 108290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; El-Badri, A.M.; Batool, M.; Anwar, S.; Wang, X.; Bai, M.; You, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; et al. Moderately Deep Tillage Enhances Rapeseed Yield by Improving Frost Resistance of Seedling during Overwintering. Field Crops Res. 2023, 304, 109173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ren, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Cong, R.; Liu, S.; Fan, X.; Lu, J. Evaluating the Application of Controlled Release Urea for Oilseed Rape on Brassica napus in a Regional Scale: The Optimal Usage, Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency Responses. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 140, 111560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Yuan, J.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Naeem, M.S.; Zhang, C. Ideotype Population Exploration: Growth, Photosynthesis, and Yield Components at Different Planting Densities in Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieling, K.; Christen, O.; Nemati, B.; Hanus, H. Effects of Previous Cropping on Seed Yield and Yield Components of Oil-Seed Rape (Brassica napus L.). Eur. J. Agron. 1997, 6, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepenbrock, W. Yield Analysis of Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.): A Review. Field Crops Res. 2000, 67, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasari, E.; Patwardhan, A.M.; Ghole, V.S.; Omid, G.C.; Ahmad, A. Relationship of Growth Parameters and Nutrients Uptake with Canola (Brassica napus L.) Yield and Yield Contribution at Different Nutrients Availability. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 11, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momoh, E.J.J.; Zhou, W. Growth and Yield Responses to Plant Density and Stage of Transplanting in Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L). J. Agron. Crop Sci.-Z. Acker Pflanzenbau 2001, 186, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Q.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Song, H.; Ding, Z.; Zhran, M.A.; Eissa, M.A.; Kheir, A.M.S.; et al. Increasing Yield, Quality and Profitability of Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus) under Combinations of Nutrient Levels in Fertiliser and Planting Density. Crop Pasture Sci. 2020, 71, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, M.M.; Adak, M.S.; Kocabas, Z. An Investigation on the Relationship Between Yield and Canopy Components in Wheat (Triticum aestivum). J. Agric. Sci.-Tarim Bilim. Derg. 2008, 14, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingra, P.K.; Mahey, R.K.; Gill, K.K.; Mukherjee, J.; Bal, S.K. Prediction of Grain Yield of Wheat Using Canopy Temperature Based Indices. J. Agrometeorol. 2010, 12, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Su, S.; Ma, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of Canopy Microclimate on Fruit Yield and Quality of Camellia Oleifera. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 235, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wu, W.; Cheng, X.; Peng, W. High Plant Density Increases Sunlight Interception and Yield of Direct-Seeded Winter Canola in China. Exp. Agric. 2023, 59, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Naeem, M.S.; Ali, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Ma, N.; Zhang, C. Leaf Senescence, Root Morphology, and Seed Yield of Winter Oilseed Rape (Brassica napus L.) at Varying Plant Densities. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8581072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Year | Variety | Planting Density | Seedling Survival Rate (%) | Yield per Plant (g) | Number of Pods per Plant | Number of Pods in Population (×106 ha−1) | Number of Seeds per Pod | 1000-Seed Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021–2022 | Qinyou10 | D1 | 97.8 a | 19.48 a | 333.0 a | 78.16 d | 17.5 a | 3.502 b |
| D2 | 97.2 a | 14.50 b | 243.4 b | 85.15 c | 17.8 a | 3.626 a | ||
| D3 | 96.7 a | 11.24 c | 203.0 c | 94.23 a | 16.2 b | 3.663 a | ||
| D4 | 93.6 b | 7.76 d | 170.8 d | 95.92 a | 15.6 c | 3.182 c | ||
| D5 | 91.6 b | 5.86 e | 138.4 e | 91.26 b | 15.1 d | 3.099 d | ||
| Ningza1838 | D1 | 97.4 a | 19.55 a | 333.2 a | 77.89 d | 17.6 a | 3.674 a | |
| D2 | 97.1 a | 15.18 b | 236.6 b | 82.67 c | 17.7 a | 3.750 a | ||
| D3 | 95.9 a | 11.44 c | 195.8 c | 90.13 b | 16.1 b | 3.766 a | ||
| D4 | 94.5 ab | 7.89 d | 167.4 d | 94.86 a | 15.1 c | 3.313 b | ||
| D5 | 92.0 b | 5.93 e | 140.3 e | 92.98 ab | 14.9 c | 3.114 c | ||
| 2022–2023 | Qinyou10 | D1 | 97.9 a | 18.61 a | 331.9 a | 77.96 d | 17.6 a | 3.466 b |
| D2 | 97.1 a | 13.95 b | 244.0 b | 85.30 c | 17.5 a | 3.599 a | ||
| D3 | 94.8 b | 10.97 c | 204.4 c | 92.96 a | 16.2 b | 3.614 a | ||
| D4 | 92.0 c | 7.66 d | 170.5 d | 94.13 a | 15.5 c | 3.128 c | ||
| D5 | 89.5 d | 5.74 e | 136.9 e | 88.18 b | 14.9 d | 3.096 c | ||
| Ningza1838 | D1 | 97.9 a | 19.19 a | 328.3 a | 77.11 d | 17.3 a | 3.620 b | |
| D2 | 96.5 b | 14.84 b | 239.1 b | 83.02 c | 17.6 a | 3.777 a | ||
| D3 | 95.4 c | 11.04 c | 196.5 c | 89.96 b | 16.1 b | 3.777 a | ||
| D4 | 92.3 d | 7.73 d | 167.4 d | 92.64 a | 15.1 c | 3.293 c | ||
| D5 | 89.0 e | 5.93 e | 138.1 e | 88.48 b | 14.9 c | 3.172 d | ||
| ANOVA | ||||||||
| Year | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ns | ||
| Variety | ns | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | ||
| Planting density | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| Year × variety | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| Year × planting density | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | ns | ||
| Variety × planting density | ns | ns | ** | ** | ns | * | ||
| Year × variety × planting density | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| Year | Variety | Planting Density | Root | Stem | Pod | Seed | Total Plant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021–2022 | Qinyou10 | D1 | 1772.7 b | 8021.2 b | 4823.7 bc | 4785.9 b | 19,403.4 b |
| D2 | 1856.9 ab | 8678.7 a | 5367.3 a | 5495.7 a | 21,398.6 a | ||
| D3 | 1882.3 a | 8832.5 a | 5553.8 a | 5606.4 a | 21,875.0 a | ||
| D4 | 1580.4 c | 7631.8 b | 4976.6 b | 4764.3 b | 18,953.0 b | ||
| D5 | 1412.0 d | 6868.7 c | 4563.9 c | 4264.2 c | 17,108.8 c | ||
| Ningza1838 | D1 | 1835.6 a | 8040.5 b | 5123.4 b | 5022.6 b | 20,022.1 b | |
| D2 | 1852.5 a | 8447.8 ab | 5331.7 ab | 5489.0 a | 21,121.0 a | ||
| D3 | 1854.0 a | 8512.6 a | 5544.2 a | 5469.8 a | 21,380.6 a | ||
| D4 | 1589.9 b | 7490.6 c | 5127.1 b | 4746.7 c | 18,954.3 c | ||
| D5 | 1430.5 c | 6874.1 d | 4702.1 c | 4315.2 d | 17,321.8 d | ||
| 2022–2023 | Qinyou10 | D1 | 1748.0 b | 7922.4 b | 4739.8 c | 4756.3 b | 19,166.5 c |
| D2 | 1828.4 a | 8480.4 a | 5156.8 b | 5379.5 a | 20,845.0 b | ||
| D3 | 1834.9 a | 8612.2 a | 5497.8 a | 5454.4 a | 21,399.3 a | ||
| D4 | 1513.9 c | 7330.8 c | 4793.9 c | 4553.7 c | 18,192.4 d | ||
| D5 | 1351.3 d | 6537.4 d | 4354.1 d | 4079.8 d | 16,322.7 e | ||
| Ningza1838 | D1 | 1771.8 b | 7735.1 b | 4905.9 b | 4842.9 b | 19,255.7 b | |
| D2 | 1860.2 a | 8575.9 a | 5423.9 a | 5529.3 a | 21,389.4 a | ||
| D3 | 1853.3 a | 8427.3 a | 5460.3 a | 5462.2 a | 21,203.1 a | ||
| D4 | 1534.5 c | 7382.9 b | 5011.4 b | 4610.9 c | 18,539.8 c | ||
| D5 | 1381.0 d | 6630.2 c | 4404.8 c | 4188.4 d | 16,604.3 d |
| Year | Variety | Planting Density | Root | Stem | Pod | Seed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021–2022 | Qinyou10 | D1 | 9.14 a | 41.33 a | 24.85 c | 24.68 b |
| D2 | 8.68 b | 40.55 ab | 25.09 c | 25.68 a | ||
| D3 | 8.61 bc | 40.38 ab | 25.39 bc | 25.63 a | ||
| D4 | 8.34 cd | 40.27 b | 26.25 ab | 25.14 ab | ||
| D5 | 8.25 d | 40.15 b | 26.68 a | 24.93 b | ||
| Ningza1838 | D1 | 9.17 a | 40.16 a | 25.59 b | 25.08 bc | |
| D2 | 8.77 b | 40.00 a | 25.24 b | 25.99 a | ||
| D3 | 8.67 b | 39.81 a | 25.93 b | 25.59 ab | ||
| D4 | 8.39 c | 39.52 a | 27.04 a | 25.05 c | ||
| D5 | 8.26 c | 39.68 a | 27.15 a | 24.91 c | ||
| 2022–2023 | Qinyou10 | D1 | 9.12 a | 41.33 a | 24.73 c | 24.82 b |
| D2 | 8.77 b | 40.68 ab | 24.74 c | 25.81 a | ||
| D3 | 8.57 bc | 40.24 b | 25.70 b | 25.49 ab | ||
| D4 | 8.32 c | 40.29 b | 26.35 ab | 25.03 b | ||
| D5 | 8.28 c | 40.05 b | 26.68 a | 24.99 b | ||
| Ningza1838 | D1 | 9.20 a | 40.18 a | 25.48 c | 25.15 c | |
| D2 | 8.70 b | 40.08 a | 25.37 c | 25.85 a | ||
| D3 | 8.74 b | 39.74 a | 25.75 bc | 25.76 ab | ||
| D4 | 8.28 c | 39.82 a | 27.03 a | 24.87 c | ||
| D5 | 8.32 c | 39.93 a | 26.53 ab | 25.22 bc |
| Items | Variety | Planting Density | Main Stem | Branch Racemes from Top to Bottom | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||||
| Pod number in population (×106 ha−1) | Qinyou 10 | D1 | 16.48 | 5.46 | 6.27 | 7.32 | 7.49 | 7.42 | 7.14 | 6.84 | 5.92 | 4.70 | 3.15 |
| D2 | 21.74 | 5.97 | 7.73 | 8.40 | 8.51 | 8.98 | 7.78 | 6.56 | 5.84 | 3.66 | |||
| D3 | 25.93 | 7.43 | 7.66 | 8.52 | 9.59 | 10.19 | 8.94 | 8.40 | 7.63 | ||||
| D4 | 28.79 | 9.02 | 8.76 | 10.78 | 11.43 | 11.12 | 9.56 | 6.64 | |||||
| D5 | 33.27 | 6.30 | 8.02 | 11.89 | 12.66 | 8.69 | 10.62 | ||||||
| Ningza 1838 | D1 | 16.59 | 4.88 | 6.09 | 7.40 | 7.28 | 7.39 | 6.73 | 6.86 | 4.87 | 4.54 | 5.31 | |
| D2 | 21.37 | 5.83 | 7.84 | 7.89 | 8.44 | 8.59 | 7.64 | 6.27 | 5.27 | 3.56 | |||
| D3 | 25.64 | 7.24 | 7.26 | 8.18 | 9.03 | 9.77 | 7.89 | 8.04 | 7.22 | ||||
| D4 | 28.79 | 8.78 | 8.39 | 10.36 | 11.52 | 9.98 | 8.93 | 8.26 | |||||
| D5 | 32.37 | 6.33 | 8.00 | 10.67 | 12.62 | 12.03 | 11.18 | ||||||
| Seed number per pod | Qinyou 10 | D1 | 18.0 | 15.8 | 17.1 | 16.7 | 18.1 | 18.2 | 18.6 | 18.5 | 16.6 | 17.1 | 14.8 |
| D2 | 18.7 | 16.4 | 17.6 | 17.3 | 18.7 | 17.7 | 19.2 | 18.3 | 16.2 | 13.0 | |||
| D3 | 16.9 | 17.2 | 16.4 | 16.1 | 15.2 | 15.4 | 16.9 | 14.9 | 16.4 | ||||
| D4 | 18.3 | 10.3 | 15.4 | 16.4 | 13.5 | 17.5 | 17.0 | 8.6 | |||||
| D5 | 15.9 | 14.2 | 10.9 | 14.3 | 16.1 | 16.1 | 14.8 | ||||||
| Ningza 1838 | D1 | 18.2 | 14.9 | 16.1 | 16.7 | 18.2 | 18.6 | 16.7 | 20.9 | 17.6 | 17.3 | 15.4 | |
| D2 | 18.9 | 17.1 | 16.9 | 17.6 | 18.0 | 18.5 | 18.6 | 16.9 | 15.5 | 14.3 | |||
| D3 | 17.0 | 17.8 | 14.3 | 15.4 | 15.3 | 17.4 | 15.5 | 14.4 | 16.0 | ||||
| D4 | 16.6 | 14.3 | 14.6 | 15.6 | 15.8 | 15.2 | 15.6 | 9.2 | |||||
| D5 | 15.8 | 12.5 | 14.0 | 14.6 | 15.7 | 14.7 | 13.8 | ||||||
| 1000-seed weight (g) | Qinyou 10 | D1 | 4.012 | 3.595 | 3.599 | 3.369 | 3.536 | 3.285 | 3.376 | 3.222 | 3.161 | 3.275 | 2.994 |
| D2 | 3.833 | 3.576 | 3.617 | 3.825 | 3.441 | 3.585 | 3.524 | 3.309 | 3.468 | 3.578 | |||
| D3 | 3.893 | 3.626 | 3.745 | 3.741 | 3.671 | 3.593 | 3.378 | 3.517 | 3.304 | ||||
| D4 | 3.548 | 3.145 | 3.247 | 2.927 | 2.968 | 2.988 | 2.796 | 2.852 | |||||
| D5 | 3.360 | 3.059 | 2.997 | 2.991 | 2.951 | 2.803 | 2.887 | ||||||
| Ningza 1838 | D1 | 4.089 | 3.909 | 3.780 | 3.594 | 3.630 | 3.597 | 3.571 | 3.478 | 3.343 | 3.487 | 3.136 | |
| D2 | 4.084 | 3.835 | 3.661 | 3.875 | 3.484 | 3.643 | 3.549 | 3.471 | 3.568 | 3.346 | |||
| D3 | 4.155 | 3.662 | 3.835 | 3.662 | 3.599 | 3.637 | 3.447 | 3.567 | 3.397 | ||||
| D4 | 3.529 | 3.384 | 3.412 | 3.226 | 3.247 | 3.183 | 3.007 | 2.871 | |||||
| D5 | 3.284 | 3.221 | 2.947 | 3.064 | 2.994 | 2.947 | 3.010 | ||||||
| Items | Variety | Planting Density | Main Stem | Branch Racemes from Top to Bottom | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||||
| Pod number in population (×106 ha−1) | Qinyou 10 | D1 | 15.98 | 5.51 | 6.24 | 7.41 | 7.41 | 7.52 | 7.15 | 6.84 | 6.05 | 4.71 | 3.15 |
| D2 | 21.27 | 6.02 | 7.98 | 8.36 | 8.67 | 8.97 | 7.85 | 6.57 | 5.91 | 3.70 | |||
| D3 | 25.09 | 7.42 | 7.44 | 8.65 | 9.44 | 10.07 | 8.91 | 8.35 | 7.59 | ||||
| D4 | 27.40 | 8.91 | 8.46 | 10.66 | 11.52 | 11.11 | 9.39 | 6.68 | |||||
| D5 | 31.14 | 6.22 | 7.65 | 11.53 | 12.48 | 8.64 | 10.53 | ||||||
| Ningza 1838 | D1 | 16.15 | 4.88 | 6.10 | 7.27 | 7.27 | 7.39 | 6.62 | 6.72 | 4.87 | 4.58 | 5.27 | |
| D2 | 21.04 | 5.83 | 7.80 | 8.16 | 8.47 | 8.78 | 7.67 | 6.39 | 5.36 | 3.52 | |||
| D3 | 24.81 | 7.19 | 7.23 | 8.20 | 9.21 | 9.84 | 7.99 | 8.12 | 7.37 | ||||
| D4 | 27.60 | 8.64 | 8.18 | 10.37 | 11.24 | 9.69 | 8.82 | 8.09 | |||||
| D5 | 29.79 | 6.16 | 7.70 | 10.26 | 12.11 | 11.70 | 10.77 | ||||||
| Seed number per pod | Qinyou 10 | D1 | 17.9 | 15.9 | 17.4 | 16.9 | 18.3 | 18.6 | 18.8 | 18.6 | 16.8 | 17.0 | 15.0 |
| D2 | 18.5 | 16.1 | 17.3 | 17.1 | 18.5 | 17.6 | 18.8 | 17.9 | 16.0 | 12.5 | |||
| D3 | 17.1 | 16.8 | 16.3 | 16.1 | 15.3 | 15.4 | 16.9 | 14.9 | 15.9 | ||||
| D4 | 18.1 | 10.5 | 15.3 | 16.5 | 13.4 | 17.5 | 16.7 | 8.5 | |||||
| D5 | 16.1 | 13.7 | 10.6 | 14.2 | 15.8 | 15.9 | 14.5 | ||||||
| Ningza 1838 | D1 | 17.8 | 14.8 | 16.1 | 16.6 | 18.0 | 18.7 | 16.6 | 20.7 | 17.1 | 17.4 | 15.0 | |
| D2 | 18.9 | 16.6 | 16.8 | 17.2 | 18.5 | 18.1 | 18.7 | 16.7 | 15.8 | 14.0 | |||
| D3 | 16.8 | 17.7 | 14.6 | 15.1 | 15.3 | 17.3 | 15.7 | 14.5 | 16.2 | ||||
| D4 | 16.5 | 14.1 | 15.0 | 15.4 | 15.7 | 15.4 | 16.1 | 9.4 | |||||
| D5 | 15.9 | 12.8 | 14.0 | 14.5 | 15.9 | 14.6 | 13.9 | ||||||
| 1000-seed weight (g) | Qinyou 10 | D1 | 3.945 | 3.578 | 3.518 | 3.382 | 3.501 | 3.265 | 3.303 | 3.261 | 3.166 | 3.252 | 2.999 |
| D2 | 3.854 | 3.543 | 3.619 | 3.782 | 3.360 | 3.523 | 3.512 | 3.319 | 3.378 | 3.479 | |||
| D3 | 3.861 | 3.576 | 3.634 | 3.654 | 3.589 | 3.515 | 3.367 | 3.422 | 3.384 | ||||
| D4 | 3.478 | 3.139 | 3.238 | 2.927 | 2.912 | 2.918 | 2.724 | 2.839 | |||||
| D5 | 3.346 | 3.101 | 2.977 | 2.972 | 2.964 | 2.839 | 2.887 | ||||||
| Ningza 1838 | D1 | 4.085 | 3.807 | 3.708 | 3.507 | 3.549 | 3.572 | 3.531 | 3.430 | 3.310 | 3.379 | 3.054 | |
| D2 | 4.106 | 3.803 | 3.742 | 3.935 | 3.582 | 3.624 | 3.521 | 3.540 | 3.612 | 3.362 | |||
| D3 | 4.190 | 3.666 | 3.791 | 3.620 | 3.688 | 3.670 | 3.464 | 3.514 | 3.442 | ||||
| D4 | 3.526 | 3.399 | 3.396 | 3.177 | 3.202 | 3.133 | 3.015 | 2.863 | |||||
| D5 | 3.368 | 3.315 | 3.048 | 3.083 | 3.033 | 2.981 | 3.050 | ||||||
| Year | Variety | Planting Density | Main Raceme | Branch Raceme from Top to Bottom | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||||
| 2021– 2022 | Qinyou10 | D1 | 24.83 | 6.46 | 8.01 | 8.61 | 10.01 | 9.26 | 9.38 | 8.54 | 6.50 | 5.48 | 2.92 |
| D2 | 28.41 | 6.37 | 8.94 | 10.08 | 9.94 | 10.39 | 9.57 | 7.24 | 5.97 | 3.08 | |||
| D3 | 30.46 | 8.24 | 8.26 | 9.15 | 9.54 | 10.06 | 9.09 | 7.85 | 7.35 | ||||
| D4 | 39.25 | 6.13 | 8.96 | 10.87 | 9.63 | 12.23 | 9.51 | 3.42 | |||||
| D5 | 41.69 | 6.39 | 6.01 | 11.94 | 14.10 | 12.23 | 10.67 | ||||||
| Ningza1838 | D1 | 24.64 | 5.65 | 7.32 | 8.81 | 9.55 | 9.87 | 7.99 | 9.93 | 5.7 | 5.45 | 5.09 | |
| D2 | 30.01 | 6.97 | 8.81 | 9.81 | 9.64 | 10.53 | 9.18 | 6.67 | 5.30 | 3.09 | |||
| D3 | 33.03 | 8.60 | 7.15 | 8.42 | 9.07 | 11.32 | 7.70 | 7.54 | 7.18 | ||||
| D4 | 35.40 | 8.98 | 8.65 | 10.97 | 12.44 | 10.16 | 8.81 | 4.60 | |||||
| D5 | 38.92 | 5.92 | 7.46 | 11.04 | 13.79 | 12.07 | 10.80 | ||||||
| 2022– 2023 | Qinyou10 | D1 | 23.71 | 6.60 | 8.00 | 8.92 | 9.96 | 9.56 | 9.32 | 8.71 | 6.75 | 5.46 | 3.00 |
| D2 | 28.13 | 6.38 | 9.28 | 10.05 | 9.99 | 10.32 | 9.66 | 7.26 | 5.94 | 2.98 | |||
| D3 | 30.40 | 8.17 | 8.08 | 9.33 | 9.49 | 9.96 | 9.31 | 7.78 | 7.48 | ||||
| D4 | 37.84 | 6.42 | 9.21 | 11.32 | 9.87 | 12.44 | 9.36 | 3.54 | |||||
| D5 | 41.02 | 6.47 | 5.92 | 11.91 | 14.34 | 9.52 | 10.82 | ||||||
| Ningza1838 | D1 | 24.25 | 5.66 | 7.52 | 8.69 | 9.58 | 10.18 | 8.01 | 9.85 | 5.70 | 5.56 | 4.99 | |
| D2 | 29.47 | 6.64 | 8.84 | 10.01 | 10.16 | 10.43 | 9.10 | 6.81 | 5.54 | 3.00 | |||
| D3 | 32.00 | 8.54 | 7.33 | 8.20 | 9.49 | 11.42 | 7.93 | 7.54 | 7.54 | ||||
| D4 | 34.69 | 8.96 | 9.04 | 10.93 | 12.29 | 10.10 | 9.29 | 4.70 | |||||
| D5 | 37.99 | 6.24 | 7.83 | 10.98 | 13.94 | 12.11 | 10.91 | ||||||
| Year | Items | October | November | December | January | February | March | April | May |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021–2022 | Rainfall (mm) | 98.0 | 36.6 | 5.4 | 77.1 | 25.3 | 166.1 | 86.2 | 15.5 |
| Mean temperature (°C) | 18.8 | 11.6 | 5.0 | 3.9 | 4.0 | 12.6 | 17.3 | 21.3 | |
| 2022–2023 | Rainfall (mm) | 131.6 | 74.0 | 8.9 | 40.9 | 69.0 | 35.5 | 43.1 | 72.5 |
| Mean temperature (°C) | 16.7 | 13.7 | 2.8 | 3.7 | 5.5 | 12.8 | 17.0 | 21.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, G.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Qian, C.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, Q. Optimal Planting Density Increases the Seed Yield by Improving Biomass Accumulation and Regulating the Canopy Structure in Rapeseed. Plants 2024, 13, 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141986
Lin G, Wang L, Li Y, Li J, Qian C, Zhang X, Zuo Q. Optimal Planting Density Increases the Seed Yield by Improving Biomass Accumulation and Regulating the Canopy Structure in Rapeseed. Plants. 2024; 13(14):1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141986
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Guobing, Long Wang, Yiyang Li, Jing Li, Chen Qian, Xia Zhang, and Qingsong Zuo. 2024. "Optimal Planting Density Increases the Seed Yield by Improving Biomass Accumulation and Regulating the Canopy Structure in Rapeseed" Plants 13, no. 14: 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141986
APA StyleLin, G., Wang, L., Li, Y., Li, J., Qian, C., Zhang, X., & Zuo, Q. (2024). Optimal Planting Density Increases the Seed Yield by Improving Biomass Accumulation and Regulating the Canopy Structure in Rapeseed. Plants, 13(14), 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13141986






