Multi-Population Analysis for Leaf and Neck Blast Reveals Novel Source of Neck Blast Resistance in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
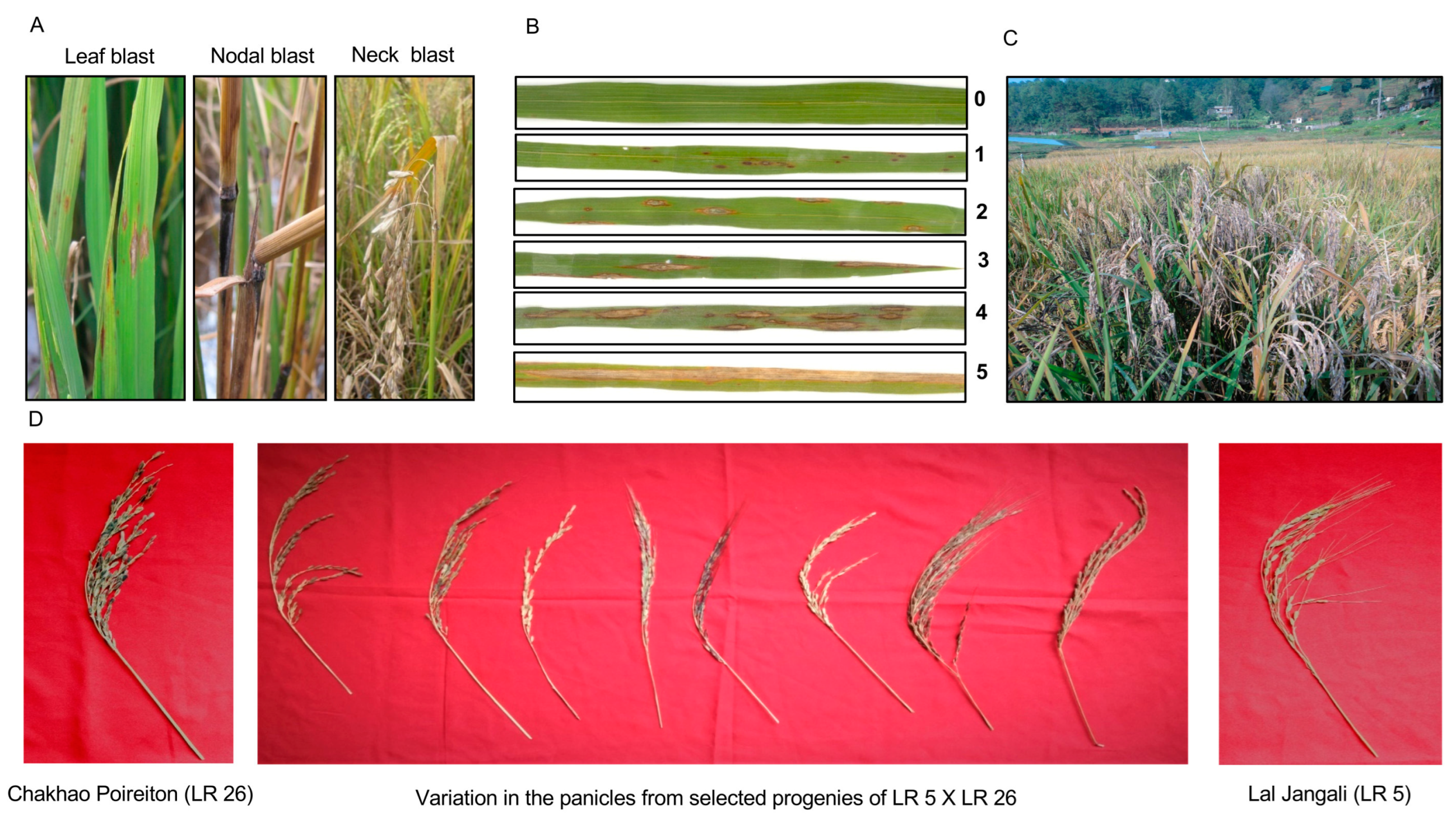
2.1. Phenotypic Variation in Response to Local Blast Pathotypes
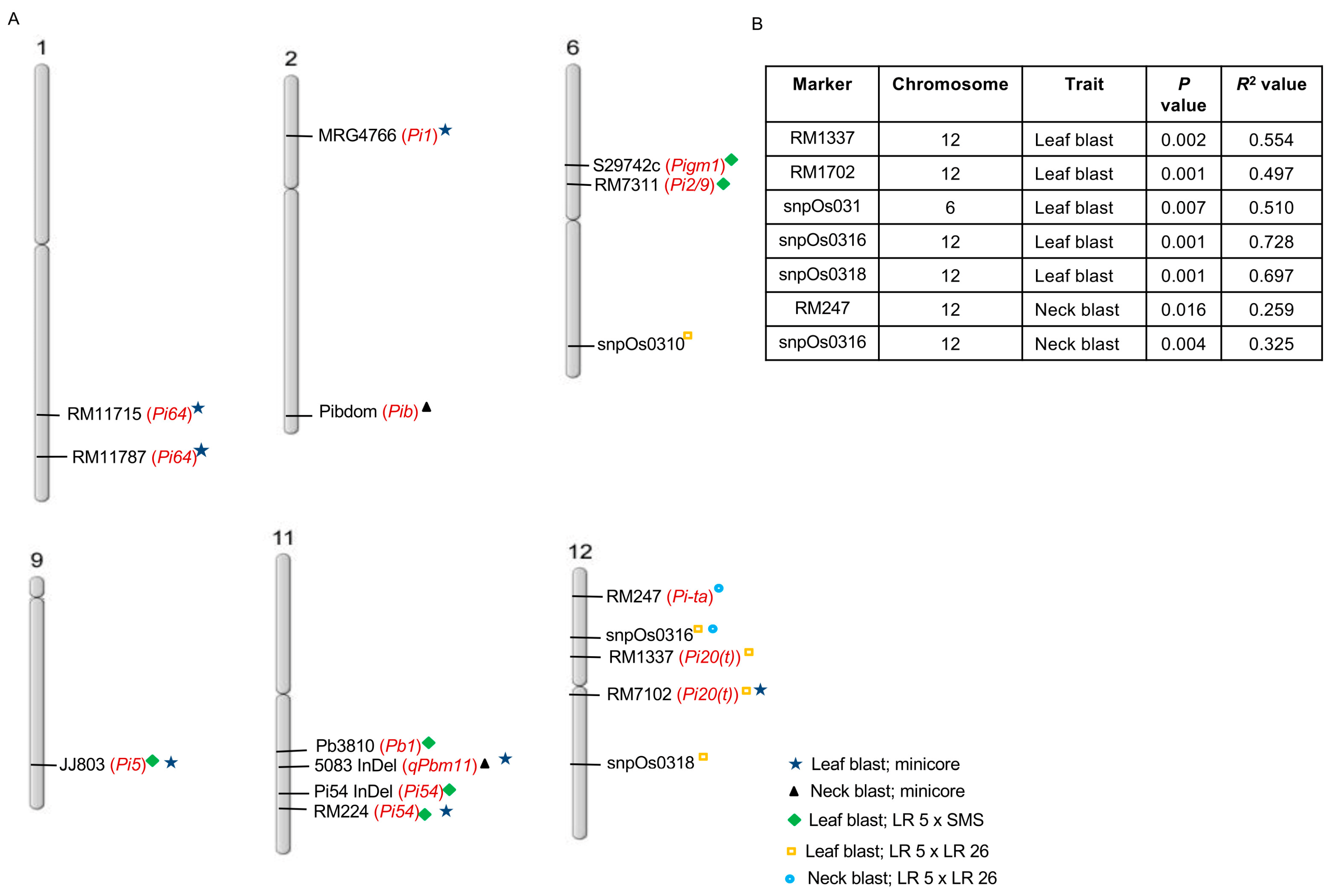
2.2. Genotyping for Reported Genes Conferring Resistance to Blast Disease
2.3. Marker–Trait Association
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Disease Scoring and Genotyping
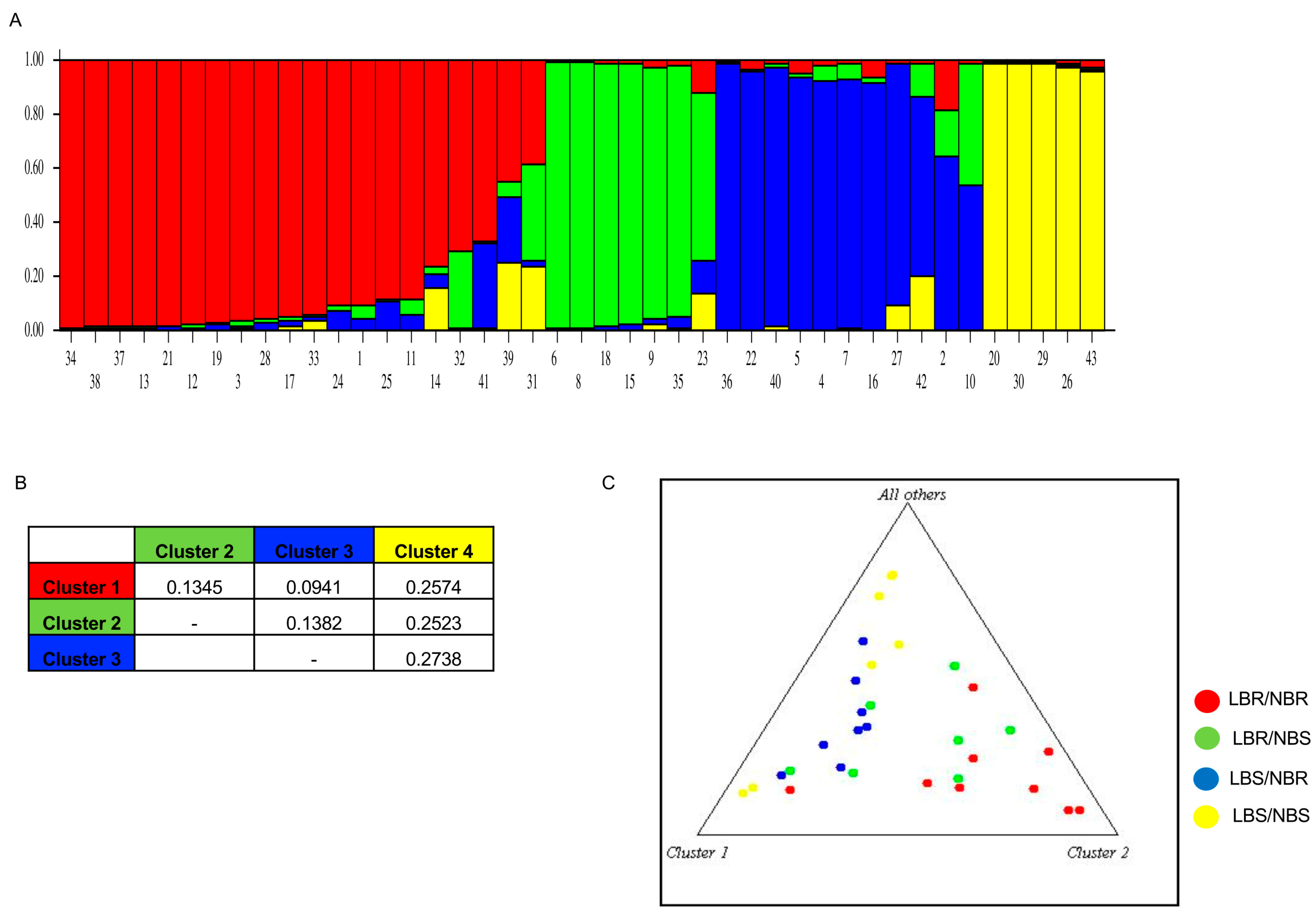
4.3. Allelic Score and STRUCTURE Analysis
4.4. Marker–Trait Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verma, D.K.; Srivastav, P.P. Bioactive compounds of rice (Oryza sativa L.): Review on paradigm and its potential benefit in human health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konjengbam, N.S.; Mahanta, M.; Lyngdoh, A.A. Rice cultivation-A way of life for the people of North Eastern Hill region of India. In Integrative Advances in Rice Research; Intechopen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 131–144. [Google Scholar]
- Government of India. Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare. Agricultural Statistics at a Glance. 2022. Available online: https://desagri.gov.in/document-report-category/agriculture-statistics-at-a-glance/ (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Neupane, N.; Bhusal, K. A review of blast disease of rice in Nepal. J. Plant Pathol. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 528. [Google Scholar]
- Asibi, A.E.; Chai, Q.; Coulter, J.A. Rice blast: A disease with implications for global food security. Agronomy 2019, 9, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, S.A.; Imtiaz, A.A.; Hossain, M.B.; Husna, A.; Eaty, M.; Khatun, N. Rice blast disease. Annu. Rev. Biol. 2020, 35, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.I.; Sen, P.P.; Bhuiyan, R.; Kabir, E.; Chowdhury, A.K.; Fukuta, Y.; Ali, A.; Latif, M.A. Phenotypic screening and molecular analysis of blast resistance in fragrant rice for marker assisted selection. C. R. Biol. 2014, 337, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, M.U.; Wang, G.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ahmad, I.; Rajput, N.; Li, M.; Feng, Z.; Hu, K.; Khan, N.U.; et al. Approaches to reduce rice blast disease using knowledge from host resistance and pathogen pathogenicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Inoue, H.; Kato, T.; Funao, T.; Shirota, M.; Shimizu, T.; Kanamori, H.; Yamane, H.; Hayano-Saito, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; et al. Durable panicle blast-resistance gene Pb1 encodes an atypical CC-NBS-LRR protein and was generated by acquiring a promoter through local genome duplication. Plant J. 2010, 64, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, T.; Rai, A.; Gupta, S.; Vijayan, J.; Devanna, B.; Ray, S. Rice blast management through host-plant resistance: Retrospect and prospects. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lei, C.; Xu, X.; Hao, K.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, X.; Ma, J.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, X.; et al. Pi64, encoding a novel CC-NBS-LRR protein, confers resistance to leaf and neck blast in rice. Mol. Plant Microbe Interac. 2015, 28, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglawe, S.B.; Bangale, U.; Devi, S.J.S.; Balija, V.; Bhadana, V.P.; Sharma, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Prasad, M.S.; Madhav, M.S. Characterization of Akhanaphou, an unique landrace from North-East India and its RIL population for rice leaf and neck blast resistance. Curr. Trends Biotechnol. Pharm. 2018, 12, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Debnath, A.; Bhutia, K.L.; Sumpi, H. Mapping and deployment of blast resistance gene in rice—A work in progress. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 2073–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, I.; Sasahara, H.; Tabuchi, H.; Shigemune, A.; Matsushita, K.; Maeda, H.; Goto, A.; Fukuoka, S.; Ando, T.; Miura, K. Quantitative trait loci analysis of blast resistance in Oryza sativa L. ‘Hokuriku 193’. Breed. Sci. 2017, 67, 16099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.K.; Aravindan, S.; Ngangkham, U.; Raghu, S.; Prabhukarthikeyan, S.R.; Keerthana, U.; Marndi, B.C.; Adak, T.; Munda, S.; Deshmukh, R.; et al. Blast resistance in Indian rice landraces: Genetic dissection by gene specific markers. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, J.; Alam, S.; Mandal, N.P.; Variar, M.; Shukla, P. Molecular screening for identification of blast resistance genes in Northeast and Eastern Indian rice germplasm (Oryza sativa L.) with PCR based makers. Euphytica 2014, 196, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Kumar, A.; Touthang, L.; Das, S.P.; Rai, M.; Verma, V.K.; Mishra, V.K. Revealing the novel genetic resources for blast resistance in diverse rice landraces of North-Eastern hills of Himalayas. In Plant Molecular Biology Reporter; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lap, B.; Magudeeswari, P.; Tyagi, W.; Rai, M. Genetic analysis of purple pigmentation in rice seed and vegetative parts—Implications on developing high-yielding purple rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Appl. Genet. 2014, 65, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumnam, J.S.; Rai, M.; Tyagi, W. Allele mining across two low-P tolerant genes PSTOL1 and PupK20-2 reveals novel haplotypes in rice genotypes adapted to acidic soils. Plant Genet. Resour. 2017, 15, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dkhar, F.; Rai, M.; Tyagi, W. Looking beyond PsTOL1: Marker development for two novel rice genes showing differential expression in P deficient conditions. J Genet. 2014, 93, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.R.; Shanker, P.; Singh, B.K.; Jana, T.K.; Madhav, M.S.; Gaikwad, K.; Singh, N.K.; Plaha, P.; Rathour, R. Molecular mapping of rice blast resistance gene Pi-k h in the rice variety Tetep. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2005, 14, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosahatti, R.; Koti, P.S.; Devappa, V.H.; Ngangkham, U.; Devanna, P.; Yadav, M.K.; Mishra, K.K.; Aditya, J.P.; Boraiah, P.K.; Gaber, A.; et al. Phenotypic and genotypic screening of fifty-two rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes for desirable cultivars against blast disease. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280762. [Google Scholar]
- Mahender, A.; Swain, D.M.; Gitishree, D.; Subudhi, H.N.; Rao, G.J.N. Molecular analysis of native Manipur rice accessions for resistance against blast. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.; Liu, K.; Jiang, T.; Xiong, Z.; Song, Q.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a rice panicle blast resistance gene, Pb2, encoding NLR protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, T.; Hayano-Saito, Y.; Oide, S.; Ebana, K.; La, N.T.; Hayashi, K.; Ashizawa, T.; Suzuki, F.; Koizumi, S. Quantitative trait locus analysis of resistance to panicle blast in the rice cultivar Miyazakimochi. Rice 2014, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, N.; Wei, X.; Shen, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, M.; Yin, C.; He, W.; Guan, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Fine mapping of a panicle blast resistance gene Pb-bd1 in Japonica landrace Bodao and its application in rice breeding. Rice 2019, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lei, C.; Cheng, Z.; Jia, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Su, N.; Guo, X.; et al. Identification of SSR markers for a broad-spectrum blast resistance gene Pi20(t) for marker-assisted breeding. Mol. Breed. 2008, 22, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Tyagi, W. Haplotype breeding for unlocking and utilizing plant genomics data. Front Genet. 2022, 13, 1006288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.K.; Singh, A.; Pattnaik, S.; Sandhu, M.; Kaur, S.; Jain, S.; Tiwari, S.; Mehrotra, S.; Anumalla, M.; Samal, R.; et al. Identification of a diverse mini-core panel of Indian rice germplasm based on genotyping using microsatellite markers. Plant Breed. 2015, 134, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutia, K.L.; Nongbri, E.L.; Sharma, T.O.; Rai, M.; Tyagi, W. A 1.84-Mb region on rice chromosome 2 carrying SPL4, SPL5 and MLO8 genes is associated with higher yield under phosphorus-deficient acidic soil. J. Appl. Genet. 2021, 62, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challam, C.; Kharshing, G.; Yumnam, J.S.; Rai, M.; Tyagi, W. Association of qLTG3-1 with germination stage cold tolerance in diverse rice germplasm from the Indian subcontinent. Plant Genet. Resour-C. 2013, 11, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunematsu, H.; Yanoria, M.J.T.; Ebron, L.A.; Hayashi, N.; Ando, I.; Kato, H.; Imbe, T.; Khush, G.S. Development of monogenic lines for rice blast resistance. Breed. Sci. 2000, 50, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Yanoria, M.J.T.; Tsunematsu, H.; Kato, H.; Imbe, T.; Fukuta, Y. Development of new sets of international standard differential varieties for blast resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). JARQ 2007, 41, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, Y.; Xalaxo, S.; Verulkar, S.; Yadav, N.; Singh, S.; Singh, N.; Prasad, K.S.; Kondayya, K.; Rao, P.R.; et al. From QTL to variety-harnessing the benefits of QTLs for drought, flood and salt tolerance in mega rice varieties of India through a multi-institutional network. Plant Sci. 2016, 242, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackill, D.J.; Bonman, J.M. Inheritance of blast resistance in near-isogenic lines of rice. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.G.; Thompson, W. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8, 4321–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Singh, H.; Deshmukh, R.K.; Singh, A.; Singh, A.K.; Gaikwad, K.; Sharma, T.R.; Mohapatra, T.; Singh, N.K. Highly variable SSR markers suitable for rice genotyping using agarose gels. Mol. Breed. 2010, 25, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Stephens, M.; Donnelly, P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genet. 2000, 155, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earl, D.A. Structure Harvester: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Sun, Y.; Xu, M. Rice blast resistance gene Pi1 Identified by MRG4766 marker in 173 Yunnan rice landraces. Rice Genom. Genet. 2012, 3, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Yano, M.; Yamanouchi, U.; Iwamoto, M.; Monna, L.; Hayasaka, H.; Sasaki, T. The Pib gene for rice blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Plant J. 1999, 19, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inukai, T.; Nelson, R. Mapping for blast resistance gene H-3 derived from rice cuhivar Pai-Kan-Tao. Rep. Hokkaido Br. Crop. Sol. See Jap. Soc. Breed. 1994, 35, 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shen, Y.; He, Z. Genetic characterization and fine mapping of the blast resistance locus Pigm (t) tightly linked to Pi2 and Pi9 in a broad-spectrum resistant Chinese variety. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Deng, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, P.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Jiang, N.; Kang, H.; Ning, Y.; et al. Molecular mapping of the blast resistance genes Pi2-1 and Pi51 (t) in the durably resistant rice ‘Tianjingyeshengdao’. Phytopathology 2012, 102, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Qu, S.; Liu, G.; Zhou, B.; Bellizzi, M.; Zeng, L.; Dai, L.; Wang, G.L. The broad- spectrum blast resistance gene Pi9 encodes a nucleotide binding site– leucine-rich repeat protein and is a member of a multigene family in rice. Genetics 2006, 172, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.W.; Cho, Y.C.; Kim, Y.G.; Suh, J.P.; Jeung, J.U.; Roh, J.H.; Lee, Y.T. Development of near isogenic japonica rice lines with enhanced resistance to Magnaporthe grisea. Mol. Cells 2008, 25, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, J.L.; Correa-Victoria, F.J.; Escobar, F.; Prado, G.; Aricapa, G.; Duque, M.C.; Tohme, J. Identification of microsatellite markers linked to the blast resistance gene Pi-1 (t) in rice. Euphytica 2008, 160, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.Y.; Saito, K.; Sugiura, N.; Hayashi, N.; Tsuji, T.; Izawa, T.I.M. Identification of a RFLP marker tightly linked to the panicle blast resistance gene, Pb1, in rice. Breed. Sci. 2000, 50, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bao, Y.; Xie, L.; Su, Y.; Chu, R.; He, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Fine mapping and identification of blast resistance gene Pi-hk1 in a broad-spectrum resistant japonica rice landrace. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sun, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, S.; Dai, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, Z.; Pan, S.; Wang, D.; et al. Molecular mapping of the blast resistance gene Pi49 in the durably resistant rice cultivar Mowanggu. Euphytica 2013, 192, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, R.; Ogawa, T. RFLP mapping of blast resistance gene Pi-km in rice. Int. Rice. Res. Notes 1996, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Rutger, J.; Xia, Y. Rapid survey for presence of a blast resistance gene Pi-ta in rice cultivars using the dominant DNA mar-kers derived from portions of the Pi-ta gene. Plant Breed. 2007, 126, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, M.; Roy-Barman, S.; Chattoo, B. Molecular mapping of a novel blast resistance gene Pi38 in rice using SSLP and AFLP markers. Plant Breed. 2006, 125, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inukai, T.; Nelson, R.; Zeigler, R.; Sarkarung, S.; Mackill, D.; Bonman, J.; Kinoshita, T. Genetic analysis of blast resistance in tropical rice cultivars using near isogenic lines. In Rice Genetics III; Khush, G.S., Ed.; World Scientific: Singapore, 1996; pp. 447–450. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Lin, F.; Wang, L.; Pan, Q. The in-silico map-based cloning of Pi36, a rice coiled-coil-nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat gene that confers race-specific resistance to the blast fungus. Genetics 2007, 176, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.G.; Jin, S.J.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wang, F.; Li, J.H.; Liu, Z.R.; Liu, Y.B. Improving blast resistance of a thermo-sensitive genic male sterile rice line GD- 8S by molecular marker- assisted selection. Rice Sci. 2008, 15, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Yoshida, H.; Ashikawa, I. Development of PCR-based allelespecific and InDel marker sets for nine rice blast resistance genes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Population | Crosses | No. of Plants/Genotypes/Lines | Markers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural population | - | 43 genotypes | 25 |
| Biparental population | LR 5 × SMS | 42 plants | 25 |
| LR 5 × LR 26 | 29 plants | 184 |
| Markers | Leaf Blast (χ2 Value) | Neck Blast (χ2 Value) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance | Susceptible | Resistance | Susceptible | |
| JJ803 | 0.001 * | 0.000 * | 0.763 | 0.525 |
| Ckm2 | 0.315 | 0.077 | 0.735 | 0.482 |
| AP5659 | 0.461 | 0.174 | 0.866 | 0.704 |
| RM224 | 0.175 | 0.023 * | 0.959 | 0.899 |
| S29742 | 0.55 | 0.255 | 0.990 | 0.974 |
| RM1337 | 0.341 | 0.091 | 0.761 | 0.522 |
| Ckm-1 | 0.975 | 0.936 | 0.786 | 0.562 |
| RM7102 | 0.227 | 0.039 * | 0.889 | 0.988 |
| MRG4766 | 0.109 | 0.009 * | 0.927 | 0.826 |
| RM247 | 0.826 | 0.631 | 0.997 | 0.992 |
| 5083InDel | 0.152 | 0.017 * | 0.297 | 0.068 |
| MiY11269 | 0.625 | 0.336 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| MiY11276 | 0.273 | 0.057 | 0.527 | 0.231 |
| RM136 | 0.728 | 0.472 | 0.997 | 0.992 |
| RM512 | 0.995 | 0.988 | 0.933 | 0.841 |
| Pb3810 | 0.937 | 0.848 | 0.821 | 0.622 |
| RM206 | 0.562 | 0.266 | 0.998 | 0.995 |
| RM527 | 0.332 | 0.086 | 0.738 | 0.487 |
| RM7311 | 0.997 | 0.991 | 0.933 | 0.840 |
| RM11715 | 0.571 | 0.276 | 0.643 | 0.357 |
| RM11787 | 0.740 | 0.491 | 0.770 | 0.536 |
| Pi54 InDel | 0.982 | 0.953 | 0.500 | 0.207 |
| Marker | Mean (AA) | Mean (AB) | Mean (BB) | t (Additive) | t (Dominance) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf Blast Score | |||||
| JJ803 | 2.846 | 2.533 | 2.636 | 0.410 | 3.588 ** |
| S29742 | 2.947 | 2.083 | 2.571 | 0.807 | 4.052 ** |
| MRG4766 | 3.333 | 2.450 | 1.500 | 2.277 | 2.236 * |
| RM7311 | 3.111 | 2.250 | 2.400 | 1.553 | 3.325 ** |
| PB3810 | 3.375 | 2.769 | 1.167 | 3.973 ** | 2.446 * |
| RM224 | 3.571 | 2.500 | 1.429 | 3.790 ** | 3.371 ** |
| Pi54 | 3.600 | 2.643 | 1.250 | 3.287 ** | 2.777 ** |
| RM527 | 2.700 | 2.500 | 0.448 | ||
| Marker | Neck Blast Score | ||||
| Mean (AA) | Mean (AB) | Mean (BB) | t (Additive) | t (Dominance) | |
| JJ803 | 12.978 | 19.247 | 23.279 | 1.273 | 1.429 |
| S29742 | 12.407 | 21.885 | 21.885 | 1.517 | 1.179 |
| MRG4766 | 14.250 | 23.067 | 27.020 | 1.049 | 1.032 |
| RM7311 | 15.344 | 21.675 | 34.846 | 1.703 | 1.908 |
| PB3810 | 12.349 | 23.736 | 28.287 | 1.879 | 1.168 |
| RM224 | 18.866 | 22.687 | 27.024 | 0.830 | 1.537 |
| Pi54 | 10.222 | 26.948 | 27.260 | 1.649 | 0.679 |
| RM527 | 15.376 | 26.134 | 1.717 | ||
| Markers | Leaf Blast (χ2 Value) | Neck Blast (χ2 Value) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance | Susceptible | Resistance | Susceptible | |
| HvSSR02-14 | 0.206 | 0.145 | 0.140 | 0.126 |
| HvSSR02-82 | 0.421 | 0.372 | 0.184 | 0.169 |
| HvSSR03-71 | 0.722 | 0.691 | 0.722 | 0.691 |
| HvSSR05-59 | 0.128 | 0.091 | 0.371 | 0.354 |
| S29742 indel | 0.440 | 0.423 | 0.352 | 0.315 |
| HvSSR07-38 | 0.128 | 0.091 | 0.371 | 0.354 |
| JJ803 | 0.510 | 0.447 | 0.480 | 0.448 |
| HvSSR10-30 | 0.478 | 0.431 | 0.934 | 0.931 |
| HvSSR11-13 | 0.196 | 0.165 | 0.593 | 0.565 |
| HvSSR11-23 | 0.359 | 0.269 | 0.845 | 0.839 |
| RM224 | 0.699 | 0.665 | 0.245 | 0.194 |
| MiY11276 | 0.465 | 0.433 | 0.257 | 0.257 |
| RM1337 | 0.003 * | 0.002 * | 0.309 | 0.309 |
| RM247 | 0.194 | 0.134 | 0.025 * | 0.016 * |
| RM7102 | 0.002 * | 0.001 * | 0.487 | 0.480 |
| snpOS0296 | 0.765 | 0.726 | 0.372 | 0.227 |
| snpOS0298 | 0.394 | 0.317 | 0.315 | 0.174 |
| snpOS0307 | 0.890 | 0.872 | 0.900 | 0.864 |
| snpOS0309 | 0.890 | 0.872 | 0.960 | 0.945 |
| snpOS0312 | 0.754 | 0.729 | 0.864 | 0.801 |
| snpOS0299 | 0.612 | 0.583 | 0.884 | 0.831 |
| snpOS0301 | 0.966 | 0.962 | 0.225 | 0.074 |
| snpOS0302 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.117 | 0.021 * |
| snpOS0305 | 0.776 | 0.745 | 0.400 | 0.255 |
| snpOS0308 | 0.910 | 0.894 | 0.464 | 0.321 |
| snpOS0310 | 0.020 * | 0.007 * | 0.098 | 0.019 * |
| snpOS0311 | 0.068 | 0.068 | 0.064 | 0.009 * |
| snpOS0315 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.737 | 0.628 |
| snpOS0316 | 0.001 * | 0.000 * | 0.050 | 0.004 * |
| snpOS0318 | 0.002 * | 0.001 * | 0.267 | 0.182 |
| snpOS0022 (BADH2) | 0.328 | 0.279 | 0.844 | 0.801 |
| snpOS0024 (CHALK5) | 0.591 | 0.562 | 0.524 | 0.404 |
| snpOS0068 (BPH17) | 0.441 | 0.394 | 0.505 | 0.382 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Debnath, A.; Sumpi, H.; Lap, B.; Bhutia, K.L.; Behera, A.; Tyagi, W.; Rai, M. Multi-Population Analysis for Leaf and Neck Blast Reveals Novel Source of Neck Blast Resistance in Rice. Plants 2024, 13, 2475. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172475
Debnath A, Sumpi H, Lap B, Bhutia KL, Behera A, Tyagi W, Rai M. Multi-Population Analysis for Leaf and Neck Blast Reveals Novel Source of Neck Blast Resistance in Rice. Plants. 2024; 13(17):2475. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172475
Chicago/Turabian StyleDebnath, Ashim, Hage Sumpi, Bharati Lap, Karma L. Bhutia, Abhilash Behera, Wricha Tyagi, and Mayank Rai. 2024. "Multi-Population Analysis for Leaf and Neck Blast Reveals Novel Source of Neck Blast Resistance in Rice" Plants 13, no. 17: 2475. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172475
APA StyleDebnath, A., Sumpi, H., Lap, B., Bhutia, K. L., Behera, A., Tyagi, W., & Rai, M. (2024). Multi-Population Analysis for Leaf and Neck Blast Reveals Novel Source of Neck Blast Resistance in Rice. Plants, 13(17), 2475. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13172475






