Functional Characterization of MaSPL8 Reveals Its Different Roles in Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses in Mulberry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
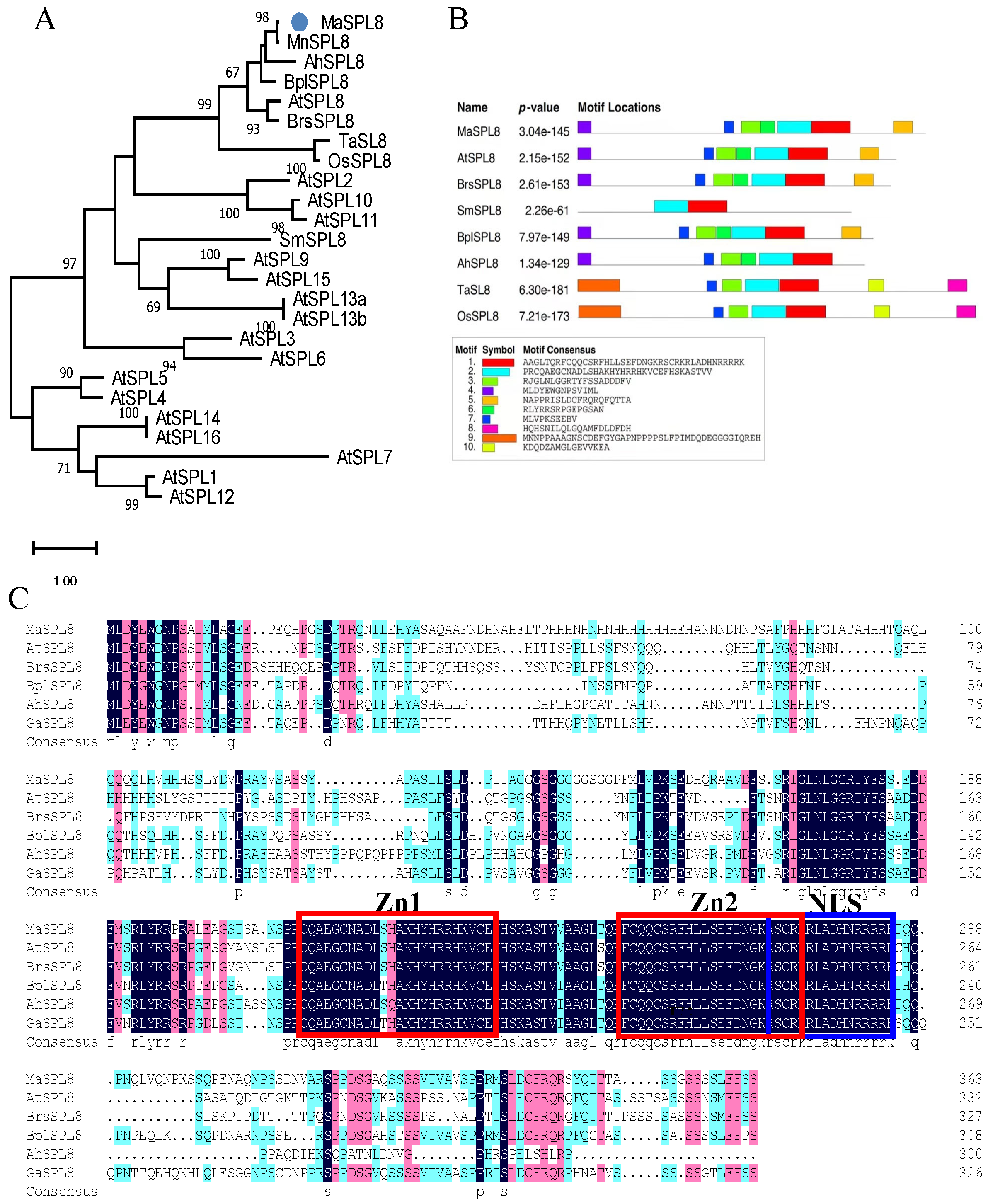
2.1. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of MaSPL8 in Mulberry
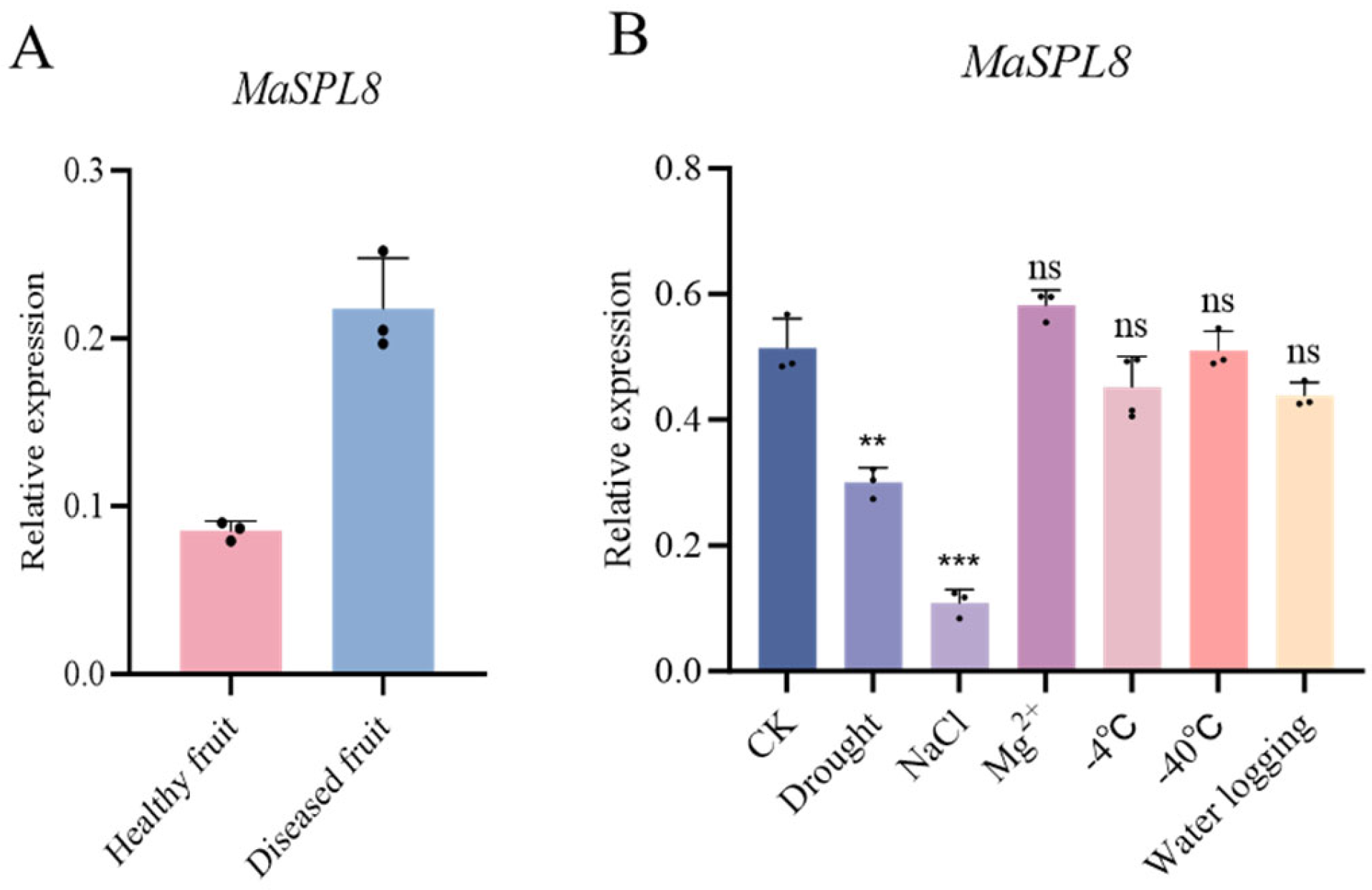
2.2. MaSPL8 Mediates Responses to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses
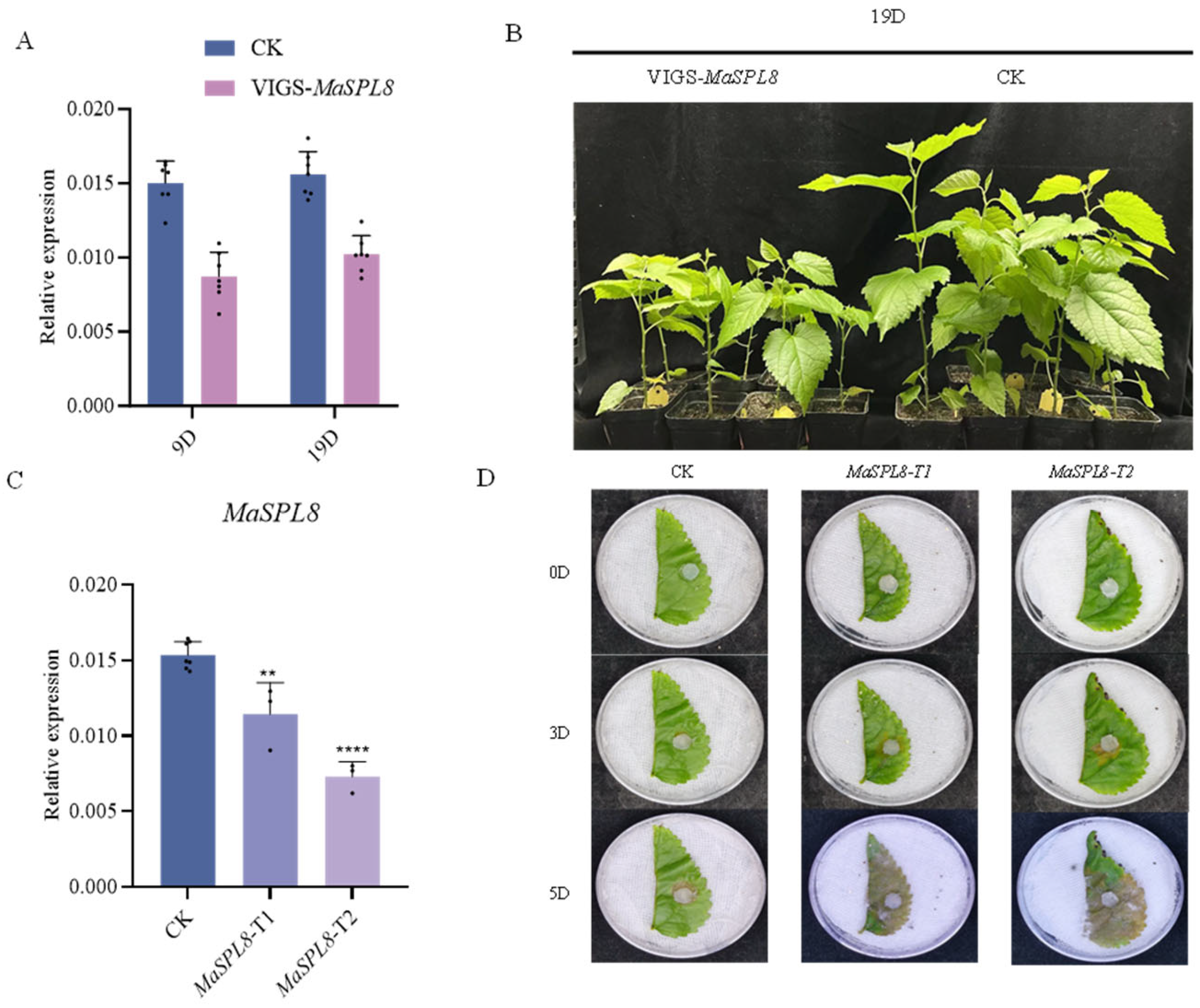
2.3. VIGS-Mediated MaSPL8 Silencing Impairs Growth and Enhances Pathogen Resistance
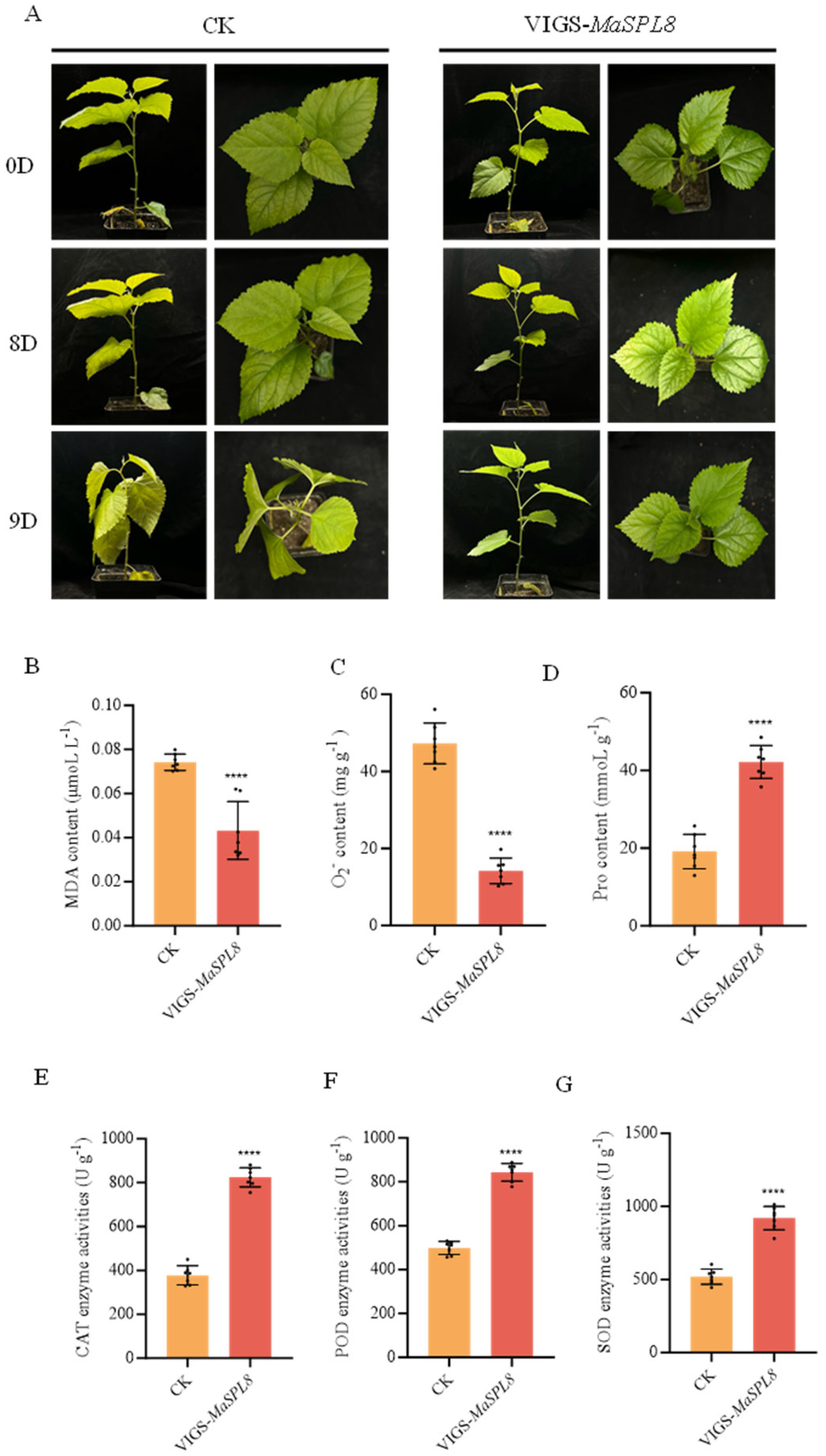
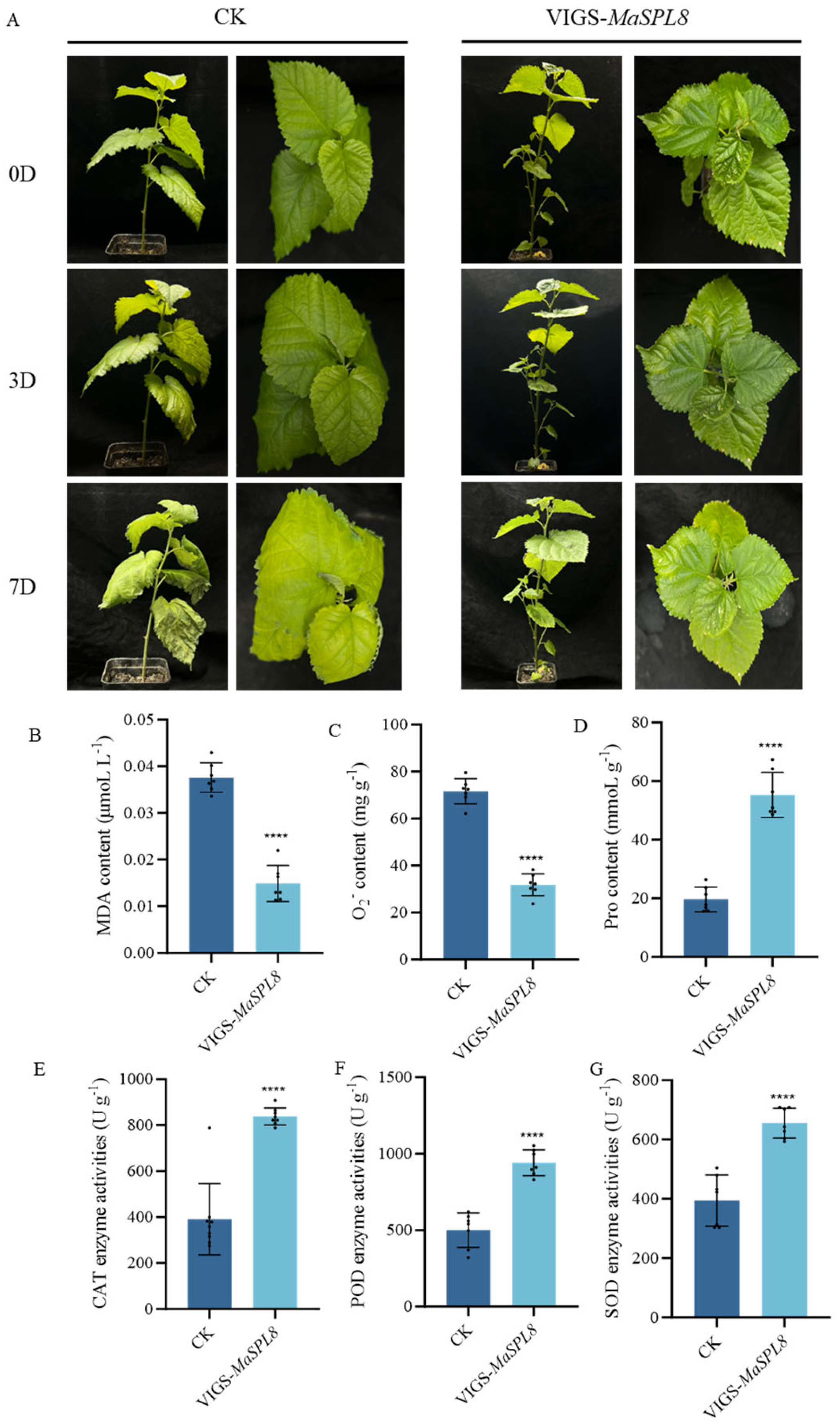
2.4. MaSPL8 Silencing Confers Drought and Salt Stress Tolerance
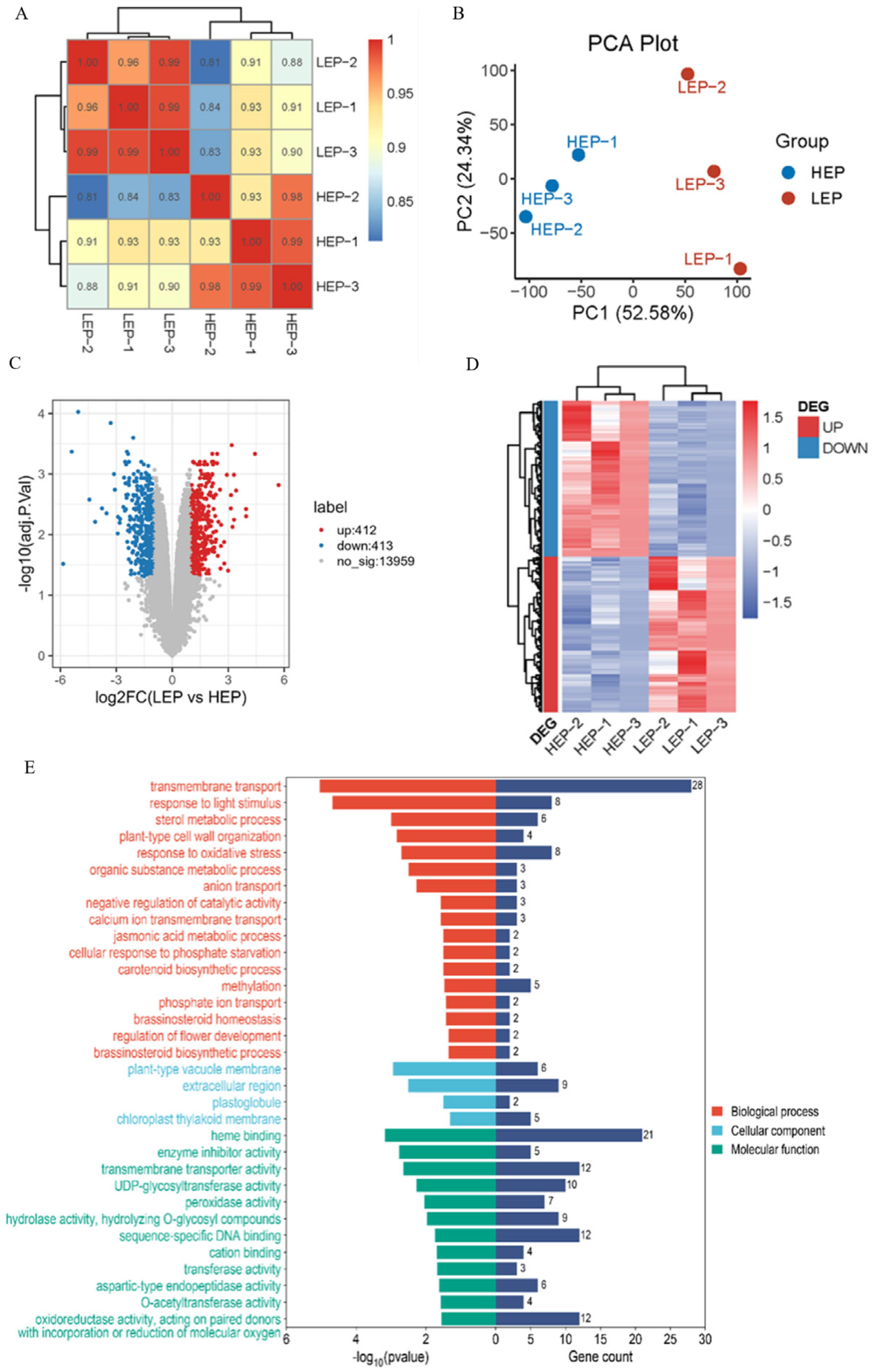
2.5. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the MaSPL8-Regulated Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Cloning and Characterization of MaSPL8 in Morus
4.3. Expression Profiles of MaSPL8
4.4. Obtaining Mulberry with DownRegulated MaSPL8 Using VIGS
4.5. Estimation of Plant Resistance to C. shiraiana Infection
4.6. Drought and Salt Stress Treatment and Physiology Indicator Determination
4.7. RNA-Seq and Comparative RNA-Seq Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, K.; Li, A.; Mao, L. SQUAMOSA Promoter-Binding Protein-like Transcription Factors: Star Players for Plant Growth and Development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2010, 52, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, J.C.; Hileman, L.C. Functional Evolution in the Plant SQUAMOSA-PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (SPL) Gene Family. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K.; Kigawa, T.; Inoue, M.; Tateno, M.; Yamasaki, T.; Yabuki, T.; Aoki, M.; Seki, E.; Matsuda, T.; Nunokawa, E.; et al. A Novel Zinc-binding Motif Revealed by Solution Structures of DNA-binding Domains of Arabidopsis SBP-family Transcription Factors. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 337, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkenbihl, R.P.; Jach, G.; Saedler, H.; Huijser, P. Functional Dissection of the Plant-specific SBP-Domain: Overlap of the DNA-binding and Nuclear Localization Domains. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 352, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riese, M.; Höhmann, S.; Saedler, H.; Münster, T.; Huijser, P. Comparative analysis of the SBP-box gene families in P. patens and seed plants. Gene 2007, 401, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Saddler, H.; Huijser, P. A new family of DNA binding proteins includes putative transcriptional regulators of the Antirrhinum majus floral meristem identity gene SQUAMOSA. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1996, 250, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, R.-F.; Zhou, J.-J.; Liu, S.-R.; Gan, Z.-M.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Hu, C.-G. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of SQUAMOSA—Promoter-Binding Protein (SBP) Genes Involved in the Flowering Development of Citrus Clementina. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Han, Y.; Ding, Q.; Ma, L. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of the SPL gene family in wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardon, G.; Höhmann, S.; Klein, J.; Nettesheim, K.; Saedler, H.; Huijser, P. Molecular characterisation of the Arabidopsis SBP-box genes. Gene 1999, 237, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Wu, C.; Xiong, L. Genomic organization, differential expression, and interaction of SQUAMOSA promoter-binding-like transcription factors and microRNA156 in rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Geng, S.; Wang, D.; Feng, N.; Zhang, D.; Wu, L.; Hao, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, A.; Mao, L. Characterization of Squamosa Promoter Binding Protein-LIKE genes in wheat. J. Plant Biol. 2015, 58, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.-D.; Yu, L.-J.; Li, Z.-J.; Yan, Y.; Han, R.; Liu, H.; Ma, M. Genome-wide analysis of the SPL family transcription factors and their responses to abiotic stresses in maize. Plant Gene 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, L.; Zhao, K.; Yao, W.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, T. Genome-Wide Analysis of Poplar SQUAMOSA-Promoter-Binding Protein (SBP) Family under Salt Stress. Forests 2021, 12, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.K.; Goel, R.; Kumari, S.; Dahuja, A. Genomic organization, phylogenetic comparison, and expression profiles of the SPL family genes and their regulation in soybean. Dev. Genes Evol. 2017, 227, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Salinas, M.; Höhmann, S.; Berndtgen, R.; Huijser, P. miR156-Targeted and Nontargeted SBP-Box Transcription Factors Act in Concert to Secure Male Fertility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3935–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, D.; Wang, J.; Yan, M.; Liu, G.; Dong, G.; Zeng, D.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, X. Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Niu, Q.W.; Ng, K.H.; Chua, N.H. The role of miR156/SPLs modules in Arabidopsis lateral root development. Plant J. 2015, 83, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuck, G.; Cigan, A.M.; Saeteurn, K.; Hake, S. The heterochronic maize mutant Corngrass1 results from overexpression of a tandem microRNA. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuck, G.; Whipple, C.; Jackson, D.; Hake, S. The maize SBP-box transcription factor encoded by tasselsheath4 regulates bract development and the establishment of meristem boundaries. Development 2010, 137, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Kong, D.; Duan, M.; Luo, L. Genome-wide identification and analysis of drought-responsive microRNAs in Oryza sativa. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 4157–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Liu, M.; Miao, J.; Ma, C.; Feng, Y.; Qian, J.; Li, H.; Bi, H.; Liu, W. The SPL transcription factor TaSPL6 negatively regulates drought stress response in wheat. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 206, 108264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.; Zheng, J.; Yan, M.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Yin, Y. A Comprehensive Analysis of the Peanut SQUAMOSA Promoter Binding Protein-like Gene Family and How AhSPL5 Enhances Salt Tolerance in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Plants 2024, 13, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, A.-Y.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Gu, X.; Ge, S.; Yang, J.; Luo, J. Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of the plant specific SBP-box transcription factor family. Gene 2008, 418, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, S.; Salinas, M.; Garcia-Molina, A.; Höhmann, S.; Berndtgen, R.; Huijser, P. SPL8 and miR156-targeted SPL genes redundantly regulate Arabidopsis gynoecium differential patterning. Plant J. 2013, 75, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unte, U.S.; Sorensen, A.-M.; Pesaresi, P.; Gandikota, M.; Leister, D.; Saedler, H.; Huijser, P. SPL8, an SBP-Box Gene That Affects Pollen Sac Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Schwarz, S.; Saedler, H.; Huijser, P. SPL8, a local regulator in a subset of gibberellin-mediated developmental processes in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 63, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Debnath, S.; Sun, L.; Flanagan, A.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wen, J.; Wang, Z.Y. From model to crop: Functional characterization of SPL8 in M. truncatula led to genetic improvement of biomass yield and abiotic stress tolerance in alfalfa. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 16, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, Q.; Dong, S.; Fu, F.; Xin, Y.; Kang, H.; Wu, Y.; Cao, X. Transcription factors CpSPL5 and CpSPL8 negatively regulate salt tolerance in Codonopsis pilosula by inhibiting SOS pathway. Plant J. 2024, 121, e17205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Quodt, V.; Chandler, J.; Höhmann, S.; Berndtgen, R.; Huijser, P. SPL8 Acts Together with the Brassinosteroid-Signaling Component BIM1 in Controlling Arabidopsis thaliana Male Fertility. Plants 2013, 2, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhinandan, K.; Skori, L.; Stanic, M.; Hickerson, N.M.N.; Jamshed, M.; Samuel, M.A. Abiotic Stress Signaling in Wheat–An Inclusive Overview of Hormonal Interactions During Abiotic Stress Responses in Wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, N.; Wang, R.F.; Hou, C.; Yu, T.; Miao, K.; Cao, F.Y.; Fang, R.J.; Liu, L. Functional characterization of two chalcone isomerase (CHI) revealing their responsibility for anthocyanins accumulation in mulberry. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Fan, W.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; Lv, J.; Xu, M.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Haplotype-resolved chromosomal-level genome assembly reveals regulatory variations in mulberry fruit anthocyanin content. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.J.; Zhang, L.D.; Li, J.; Zhu, C.Q.; Song, L.Y.; Huang, H.Z.; Xu, C.Q.; Li, Q.H.; Chen, L.; Jiang, C.K.; et al. Calcium regulates the physiological and molecular responses of Morus alba roots to cadmium stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Fan, W.; Zhu, P.; Xia, Z.; Hu, J.; Zhao, A. Mulberry RGS negatively regulates salt stress response and tolerance. Plant Signal. Behav. 2019, 14, 1672512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, B.; Luo, Y.; Wei, W.; Yuan, J.; Zhai, C.; He, N. The Mulberry SPL Gene Family and the Response of MnSPL7 to Silkworm Herbivory through Activating the Transcription of MnTT2L2 in the Catechin Biosynthesis Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, Z.; Kang, X.; Li, S.; Huang, S.; Zheng, L.; Fu, R.; Yidilisi, K.; Chao, N. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Different Mulberry Varieties to Reveal Candidate Genes and Small Secreted Peptides Involved in the Sclerotiniose Response. Forests 2024, 15, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, X.; Qu, S.; Shen, T.; Li, M.; Zhu, L. The roles of miR156 in abiotic and biotic stresses in plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 204, 108150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Liu, Y.; Azam, S.M.; Rahman, Z.U.; Priyadarshani, S.V.G.N.; Li, W.; Huang, X.; Hu, B.; Xiong, J.; Ali, U.; et al. Genomic Survey, Characterization, and Expression Profile Analysis of the SBP Genes in Pineapple (Ananas comosus L.). Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 1032846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unver, T.; Hou, H.; Li, J.; Gao, M.; Singer, S.D.; Wang, H.; Mao, L.; Fei, Z.; Wang, X. Genomic Organization, Phylogenetic Comparison and Differential Expression of the SBP-Box Family Genes in Grape. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ye, K.; Shi, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S. BZR1 Positively Regulates Freezing Tolerance via CBF-Dependent and CBF-Independent Pathways in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. The GSK3-like Kinase BIN2 Is a Molecular Switch between the Salt Stress Response and Growth Recovery in Arabidopsis thaliana. Dev. Cell 2020, 55, 367–380.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Hao, L.; Ma, B.; He, Z.; Luo, Y.; Xin, Y.; He, N. Ciboria carunculoides Suppresses Mulberry Immune Responses Through Regulation of Salicylic Acid Signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 658590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, G.; Mohapatra, S.K.; Rout, G.R. Plant membrane transporters function under abiotic stresses: A review. Planta 2024, 260, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Q.; Sun, J. Identification, expression and miRNA targeting of auxin response factor genes related to phyllody in the witches’ broom disease of jujube. Gene 2020, 746, 144656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.-F. Cold-responsive miRNAs and their target genes in the wild eggplant species Solanum aculeatissimum. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Chen, R.; Fan, Y.; Huang, X.; Luo, H.; Xiong, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Lei, J.; Zhou, H.; et al. Integrated mRNA and small RNA sequencing reveals microRNA regulatory network associated with internode elongation in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Luo, R.; Dai, X.; Liu, H.; Yu, G.; Han, S.; Lu, X.; Su, C.; Chen, Q.; Song, Q.; et al. Chromosome-level reference genome and population genomic analysis provide insights into the evolution and improvement of domesticated mulberry (Morus alba). Molecular plant 2020, 13, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, B.W. Performance of genetic programming optimised Bowtie2 on genome comparison and analytic testing (GCAT) benchmarks. BioData Min. 2015, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| miRNA | Target Gene | Expect | Alignment | Inhibition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR5658 | MaSPL8 | 2.5 | miRNA 21 AAAGUAGUAGUAGUAGUAGUA 1 | Cleavage |
| :: :::::::::: ::::: | ||||
| Target 154 ACUCCUCAUCAUCAUAAUCAU 174 | ||||
| miR4221 | MaSPL8 | 5 | miRNA 22 CGUUCUUAAGUUGUCUCCUUUU 1 | Cleavage |
| .::.: ::.:.::::...: | ||||
| Target 417 CGGAGGAGGCAGCGGAGGGGGA 438 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, L.; Zhang, W.; Wei, L.; Li, M.; Liu, L. Functional Characterization of MaSPL8 Reveals Its Different Roles in Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses in Mulberry. Plants 2025, 14, 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060950
Zheng L, Zhang W, Wei L, Li M, Liu L. Functional Characterization of MaSPL8 Reveals Its Different Roles in Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses in Mulberry. Plants. 2025; 14(6):950. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060950
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Longyan, Wenhao Zhang, Liuqing Wei, Mengqi Li, and Li Liu. 2025. "Functional Characterization of MaSPL8 Reveals Its Different Roles in Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses in Mulberry" Plants 14, no. 6: 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060950
APA StyleZheng, L., Zhang, W., Wei, L., Li, M., & Liu, L. (2025). Functional Characterization of MaSPL8 Reveals Its Different Roles in Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses in Mulberry. Plants, 14(6), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14060950






