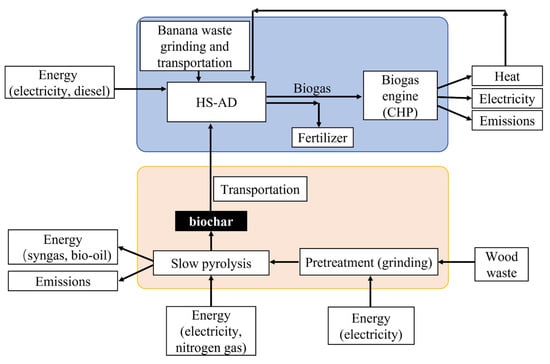
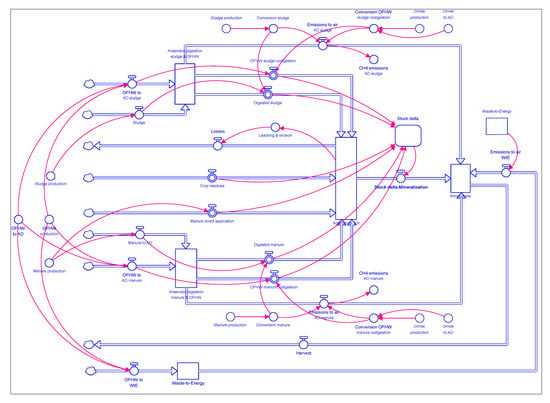
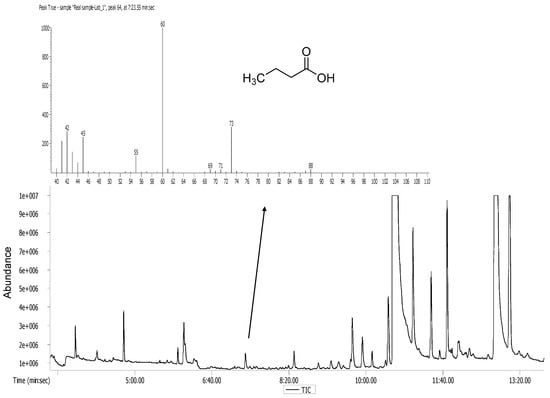
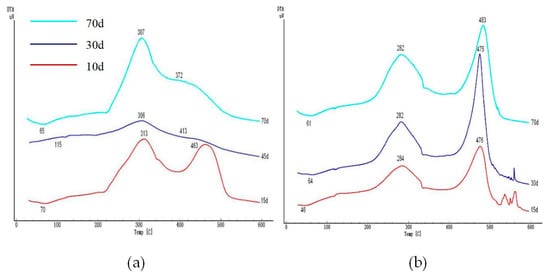
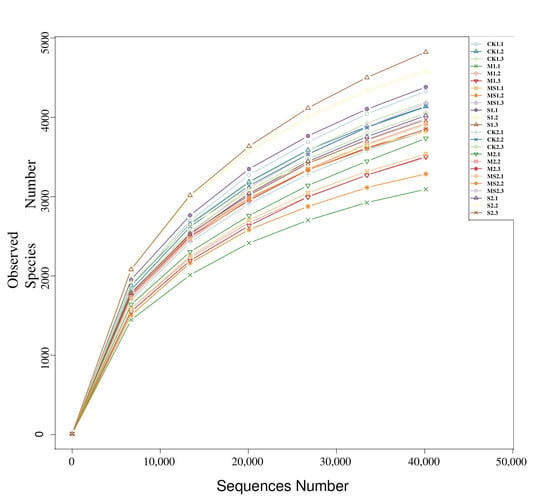
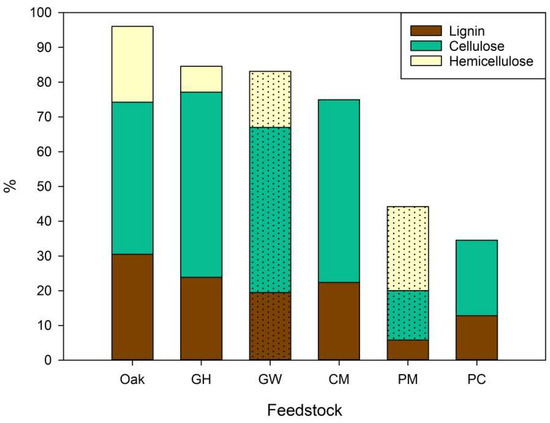
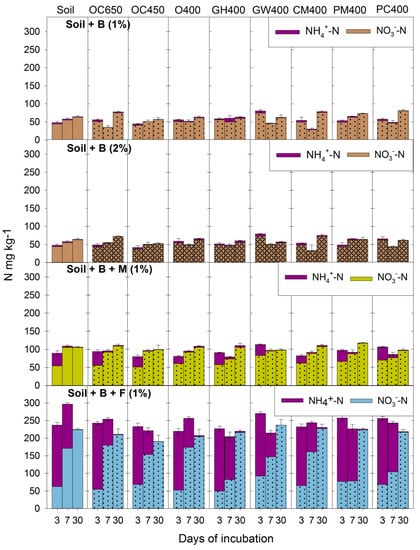
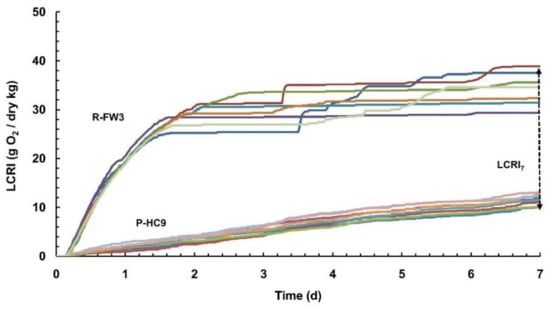
Organic Waste Management
A topical collection in Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This collection belongs to the section "Environmental Sustainability and Applications".
Viewed by 132349Editor
Interests: municipal solid waste management; composting; biorefining of solid waste; life cycle analysis
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
During the past two decades, under the frameworks of sustainability and circular economy, there has been a high legislative focus on the management of organic waste and biowaste to prevent it from landfilling and to promote its valorization. According to two key European directives (1999/31/EC and 2008/98/EC), organic waste needs to be diverted from landfilling at rates higher than 65% and biowaste needs to be separated at the source at levels higher than 10% to up to 50%. The typical hierarchy pyramid on solid waste actions places biological organic waste management techniques on top of the thermal treatment based energy recovery techniques rendering the former (i.e., composting, anaerobic digestion) more attractive to implement. Low technology composting of organic waste at the community or household level (which is highly promoted lately by municipalities) could be considered as a re-use and even a prevention technique, instead of a recycling technique, which would automatically promote it to the highest position of the waste hierarchy. In addition to typical end-of-the pipe treatment methods, much focus has been recently given on valorization techniques that aim to recover useful products during organic waste biological processes (e.g., recovery of enzymes during solid state fermentation, hydrogen production during anaerobiosis, biomass derived bioethanol) in addition to the typical compost and methane recovery. It is, thus, evident that the term “waste” will soon be fully abandoned and be, likely, soon replaced by the term “by-product”.
This Special Issue will focus on biological organic (solid) waste management techniques, as viewed through the prism of circular economy, and will cover the following state-of-the-art topics:
- Industrial and medium scale MBT facilities
- MBT technology: Aerobic versus anaerobic processes
- Compost, CLO, digestate and other MBT outputs: Quality aspects and indices
- Valorization of organic waste and recovery of useful compounds
- Organic waste source separation schemes: decentralized vs. centralized schemes
- Home and community composting
- Biochar as a soil amendment
- Waste-based bioethanol generation
- Hydrogen production via anaerobic digestion
- Life cycle analysis in organic waste management
Dr. Dimitrios Komilis
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- anaerobic processes
- biochar
- bioethanol
- compost quality indices
- home composting
- hydrogen production
- life cycle analysis
- MBT technology
- organic waste collection
- organic waste valorization