Porous Materials and Nanozeolites
A topical collection in Materials (ISSN 1996-1944). This collection belongs to the section "Porous Materials".
Viewed by 65104
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. Svetlana Mintova
Prof. Dr. Svetlana Mintova
 Prof. Dr. Svetlana Mintova
Prof. Dr. Svetlana Mintova
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Laboratory of Catalysis and Spectrochemistry (LCS), CNRS-ENSICAEN, 14000 Caen, France
Interests: nanosized zeolites; zeotype materials; films; memranes; advanced applications
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Zeolites are fascinating materials with diverse capabilities which have gone beyond their traditional applications as catalysts, sorbents, and ion-exchangers. Novel synthesis methods are constantly being developed to enhance their performance and to make their synthesis industrially and envrinomentally friendly. Advanced characterization techniques are also continuously being explored to better understand the zeolite complex crystallization mechanism. These new developments have prompted zeolite researchers to collaborate with researchers from different areas, and excellent multidisciplinary studies have been published in recent years. Ever since the development of nanozeolites in the early 1990s, efforts have been devoted to expanding the number of zeolite structures available in nanozeolite form as well as modifying their properties for enhanced performance. Examples of recent developments include template-free synthesis of ultrasmall nanozeolites, synthesis of hierarchical nanozeolites, and synthesis of single crystal defect-free nanozeolites. In this Special Issue, we invite contributions from all areas of zeolites and related porous materials. Topics include but are not limited to green synthesis methods of zeolites and nanozeolites, post-synthetic modification of zeolites, development of advanced zeolite-based structured or multifunctional materials, characterization of zeolites, and interdisciplinary applications of nanozeolites and related porous materials.
Dr. Lubomira Tosheva
Prof. Svetlana Mintova
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Materials is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- synthesis of zeolites and related microporous materials
- post-synthetic modification
- advanced characterization
- applications
Published Papers (18 papers)
Open AccessReview
A Mini Review of Advances in Porous Materials Designing for Hydrogen Isotope Separation
by
Huafeng Zhu, Liangbo Xu, Jia Li, Duanwei He and Jingchuan Wang
Viewed by 997
Abstract
The separation of mixtures of hydrogen isotopes is one of the greatest challenges of modern separation technology. A newly proposed separation mechanism, the quantum sieving (QS) effect, is expected to achieve high separation factors, the main desired properties for hydrogen isotope separation (HIS).
[...] Read more.
The separation of mixtures of hydrogen isotopes is one of the greatest challenges of modern separation technology. A newly proposed separation mechanism, the quantum sieving (QS) effect, is expected to achieve high separation factors, the main desired properties for hydrogen isotope separation (HIS). Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) and zeolites are excellent candidates to study these quantum effects because of their well-defined and tunable pore structure and the potential to introduce strong adsorption sites directly into the framework structure. This paper briefly discusses the fundamentals of QS of hydrogen isotopes in nanoporous materials, mainly including kinetic quantum sieving (KQS) and chemical affinity quantum sieving (CAQS). Recent experimental advances in the separation of hydrogen isotopes from MOFs and zeolites are highlighted.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Mesoporous Materials for Metal-Laden Wastewater Treatment
by
Dmitrii Grozdov and Inga Zinicovscaia
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 1711
Abstract
Rapid technological, industrial and agricultural development has resulted in the release of large volumes of pollutants, including metal ions, into the environment. Heavy metals have become of great concern due to their toxicity, persistence, and adverse effects caused to the environment and population.
[...] Read more.
Rapid technological, industrial and agricultural development has resulted in the release of large volumes of pollutants, including metal ions, into the environment. Heavy metals have become of great concern due to their toxicity, persistence, and adverse effects caused to the environment and population. In this regard, municipal and industrial effluents should be thoroughly treated before being discharged into natural water or used for irrigation. The physical, chemical, and biological techniques applied for wastewater treatment adsorption have a special place in enabling effective pollutant removal. Currently, plenty of adsorbents of different origins are applied for the treatment of metal-containing aqueous solution and wastewater. The present review is focused on mesoporous materials. In particular, the recent achievements in mesoporous materials’ synthesis and application in wastewater treatment are discussed. The mechanisms of metal adsorption onto mesoporous materials are highlighted and examples of their multiple uses for metal removal are presented. The information contained in the review can be used by researchers and environmental engineers involved in the development of new adsorbents and the improvement of wastewater treatment technologies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
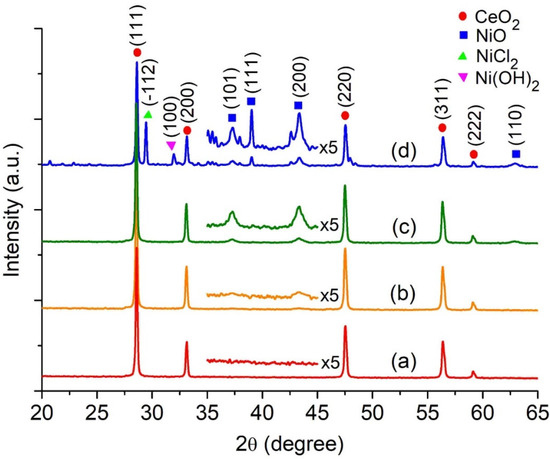
Highly Active Nickel (II) Oxide-Supported Cerium Oxide Catalysts for Valorization of Glycerol into Oxygenated Fuel Additives
by
Jimmy Nelson Appaturi, Pedro Maireles-Torres, Taghrid S. Alomar, Najla AlMasoud, Zeinhom M. El-Bahy, Tau Chuan Ling and Eng-Poh Ng
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1496
Abstract
Acetylation of glycerol to yield monoacetin (MAT), diacetin (DAT), and triacetin (TAT) over NiO-supported CeO
2 (
xNiO/CeO
2) catalysts is reported. The catalysts were synthesized utilizing a sol-gel technique, whereby different quantities of NiO (
x = 9, 27, and
[...] Read more.
Acetylation of glycerol to yield monoacetin (MAT), diacetin (DAT), and triacetin (TAT) over NiO-supported CeO
2 (
xNiO/CeO
2) catalysts is reported. The catalysts were synthesized utilizing a sol-gel technique, whereby different quantities of NiO (
x = 9, 27, and 45 wt%) were supported onto the CeO
2 substrate, and hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTABr) served as a porogen. The utilization of EDX elemental mapping analysis confirmed the existence of evenly distributed Ni
2+ ion and octahedral NiO nanoparticles on the CeO
2 surface through the DRS UV-Vis spectroscopy. The most active catalyst is 27NiO/CeO
2 based on TAT selectivity in the glycerol acetylation with ethanoic acid, attaining 97.6% glycerol conversion with 70.5% selectivity to TAT at 170 °C with a 1:10 glycerol/ethanoic acid molar ratio for 30 min using a non-microwave instant heating reactor. The 27NiO/CeO
2 is reusable without significant decline in catalytic performance after ten consecutive reaction cycles, indicating high structure stability with accessible active acidity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
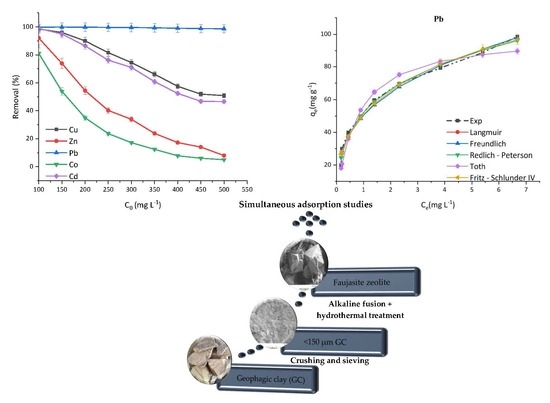
FAU-Type Zeolite Synthesis from Clays and Its Use for the Simultaneous Adsorption of Five Divalent Metals from Aqueous Solutions
by
Ifeoma V. Joseph, Lubomira Tosheva, Gary Miller and Aidan M. Doyle
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3900
Abstract
In this research, a vermiculite-kaolinite clay (VK) was used to prepare faujasite zeolites via alkaline fusion and hydrothermal crystallisation. The optimal synthesis conditions were 1 h fusion with NaOH at 800 °C, addition of deionised water to the fused sample at a sample
[...] Read more.
In this research, a vermiculite-kaolinite clay (VK) was used to prepare faujasite zeolites via alkaline fusion and hydrothermal crystallisation. The optimal synthesis conditions were 1 h fusion with NaOH at 800 °C, addition of deionised water to the fused sample at a sample to deionised water mass ratio of 1:5, 68 h of non-agitated ageing of the suspension, and 24 h of hydrothermal treatment at 90 °C. The efficacy of the prepared faujasite was compared to raw clay and a reference zeolite material through adsorption experiments of aqueous solutions containing five divalent cations—Cd, Co, Cu, Pb, and Zn. The results showed that in the presence of competing cations at concentrations of 300 mg L
−1 and adsorbent loading of 5 g L
−1, within the first 10 min, about 99% of Pb, 60% of Cu, 58% of Cd, 28% of Zn, and 19% of Co were removed by the faujasite prepared from clay. Two to four parameter nonlinear adsorption isotherms were used to fit the adsorption data and it was found that overall, three and four parameter isotherms had the best fit for the adsorption process.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
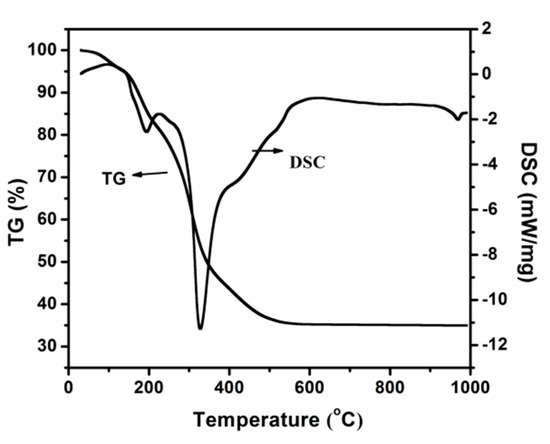
The Effect of the Activation Process and Metal Oxide Addition (CaO, MgO, SrO) on the Catalytic and Physicochemical Properties of Natural Zeolite in Transesterification Reaction
by
Pawel Mierczynski, Lukasz Szkudlarek, Karolina Chalupka, Waldemar Maniukiewicz, Satriyo K. Wahono, Krasimir Vasilev and Malgorzata I. Szynkowska-Jozwik
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 3028
Abstract
This work provides valuable information about unexplored catalytic systems tested in the transesterification reaction of vegetable oil with methanol. It was demonstrated that natural zeolite treatment leads to enhanced catalytic activity and yield of biodiesel production. The activation of the catalytic material in
[...] Read more.
This work provides valuable information about unexplored catalytic systems tested in the transesterification reaction of vegetable oil with methanol. It was demonstrated that natural zeolite treatment leads to enhanced catalytic activity and yield of biodiesel production. The activation of the catalytic material in a mixture of 5% H
2–95% Ar resulted in an improvement of the values of the TG conversion and fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) yield. In addition, it was proven that the incorporation of CaO, MgO and SrO oxides onto the natural zeolite surface improves the TG conversion and FAME yield values in the transesterification reaction.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
A Brief Review on Solvent-Free Synthesis of Zeolites
by
Jinlin Mei, Aijun Duan and Xilong Wang
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 4871
Abstract
The traditional hydrothermal method to prepare zeolite will inevitably use a large amount of water as a solvent, which will lead to higher autogenous pressure, low efficiency, and wastewater pollution. The solvent-free method can be used to synthesize various types of zeolites by
[...] Read more.
The traditional hydrothermal method to prepare zeolite will inevitably use a large amount of water as a solvent, which will lead to higher autogenous pressure, low efficiency, and wastewater pollution. The solvent-free method can be used to synthesize various types of zeolites by mechanical mixing, grinding, and heating of solid raw materials, which exhibits the apparent advantages of high yield, low pollution, and high efficiency. This review mainly introduces the development process of solvent-free synthesis, preparation of hierarchical zeolite, morphology control, synthesis mechanism and applications of solvent-free methods. It can be believed that solvent-free methods will become a research focus and have enormous industrial application potential.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
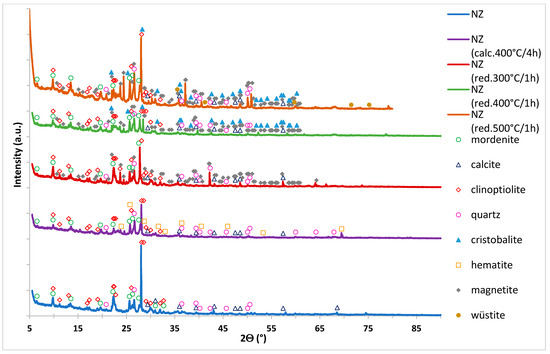
Biodiesel Production on Monometallic Pt, Pd, Ru, and Ag Catalysts Supported on Natural Zeolite
by
Pawel Mierczynski, Magdalena Mosińska, Lukasz Szkudlarek, Karolina Chalupka, Misa Tatsuzawa, Marwa Al Maskari, Waldemar Maniukiewicz, Satriyo K. Wahono, Krasimir Vasilev and Malgorzata I. Szynkowska-Jozwik
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2891
Abstract
Biodiesel production from rapeseed oil and methanol via transesterification reaction facilitated by various monometallic catalyst supported on natural zeolite (NZ) was investigated. The physicochemical characteristics of the synthesized catalysts were studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller method (BET), temperature-programmed-reduction in hydrogen (H
2
[...] Read more.
Biodiesel production from rapeseed oil and methanol via transesterification reaction facilitated by various monometallic catalyst supported on natural zeolite (NZ) was investigated. The physicochemical characteristics of the synthesized catalysts were studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller method (BET), temperature-programmed-reduction in hydrogen (H
2-TPR), temperature-programmed-desorption of ammonia (NH
3-TPD), Scanning Electron Microscope equipped with EDX detector (SEM-EDS), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) methods. The highest activity and methyl ester yields were obtained for the Pt/NZ catalyst. This catalyst showed the highest triglycerides conversion of 98.9% and fatty acids methyl esters yields of 94.6%. The activity results also confirmed the high activity of the carrier material (NZ) itself in the investigated reaction. Support material exhibited 90.5% of TG conversion and the Fatty Acid Methyl Esters yield (FAME) of 67.2%. Introduction of noble metals improves the TG conversion and FAME yield values. Increasing of the metal loading from 0.5 to 2 wt.% improves the reactivity properties of the investigated catalysts.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Zeolite Features on the Dehydration Reaction of Methanol to Dimethyl Ether: Catalytic Behaviour and Kinetics
by
Enrico Catizzone, Emanuele Giglio, Massimo Migliori, Paolo C. Cozzucoli and Girolamo Giordano
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 3351
Abstract
The synthesis of dimethyl ether (DME) is an important step in the production of chemical intermediate because it is possible to prepare it by direct hydrogenation of CO
2. This paper reports the effect of different zeolitic frameworks (such as: BEA, EUO,
[...] Read more.
The synthesis of dimethyl ether (DME) is an important step in the production of chemical intermediate because it is possible to prepare it by direct hydrogenation of CO
2. This paper reports the effect of different zeolitic frameworks (such as: BEA, EUO, FER, MFI, MOR, MTW, TON) on methanol conversion, DME selectivity and catalyst deactivation. The effect of crystal size, Si/Al ratio and acidity of the investigated catalysts have been also studied. Finally, the kinetic parameters (such as: ∆H, ∆S and ∆G) have been evaluated together with pre-exponential factor and activation energy for catalysts with FER and MFI structure topology.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Effect of H2O Activity on Zeolite Formation
by
Claudia Belviso and Francesco Cavalcante
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2242
Abstract
In an effort to understand the effects of H
2O activity on zeolite formation, we have synthesized LTA zeolite using a combination of freezing processes and varying drying temperatures. Sodium aluminate and sodium silicate were used to form LTA zeolite, according to
[...] Read more.
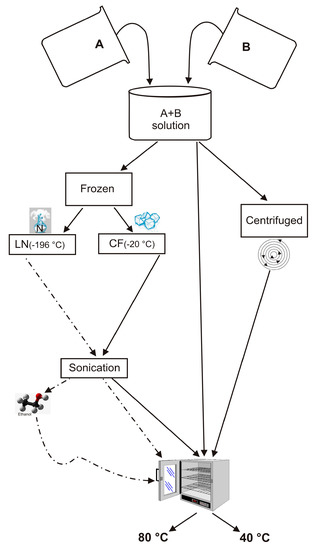
In an effort to understand the effects of H
2O activity on zeolite formation, we have synthesized LTA zeolite using a combination of freezing processes and varying drying temperatures. Sodium aluminate and sodium silicate were used to form LTA zeolite, according to the IZA (International Zeolite Association) protocol. The synthesis steps were modified by adding the precursor frozen process by a rapid liquid nitrogen (−196 °C) treatment or slow conventional freezer treatment (−20 °C). The samples were subsequently sonicated and then dried at 80 °C or 40 °C. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were performed on the samples immediately after the drying process as well as after 2 weeks and 1 month of aging the solid products. The results indicated that LTA zeolite does not form. The silica-alumina precursor after both freezing processes and after being dried at 80 °C showed the presence of sodalite displaying stable behavior over time. Both sets of samples dried at 40 °C and did not show the presence of zeolite immediately after the drying process. However, after 2 weeks, the liquid nitrogen–frozen precursor was characterized by the presence of EMT whereas zeolites never formed in the −20 °C samples. These results suggest that freezing processes differently control the H
2O activity during the drying and aging processes in the solid state. Thus, although the precursor chemical composition is the same, the type of zeolite formed is different.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
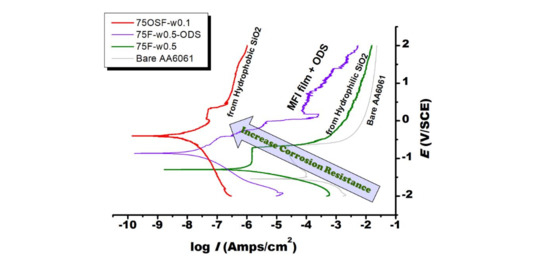
On the Anti-Corrosion Property of Dry-Gel-Conversion-Grown MFI Zeolite Coating on Aluminum Alloy
by
Shang-Tien Tsai, Wen-Chyuan ChangJean, Lin-Yi Huang and Tseng-Chang Tsai
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2288
Abstract
MFI zeolite film coated on AA6061 alloy was prepared from fumed silica modified with/without n-octyldecyltrimethoxysilane (ODS) by means of dry gel conversion (DGC) method. The DGC-grown MFI zeolite film could form a strong barrier to protect AA6061 surface against the corrosion from NaCl
[...] Read more.
MFI zeolite film coated on AA6061 alloy was prepared from fumed silica modified with/without n-octyldecyltrimethoxysilane (ODS) by means of dry gel conversion (DGC) method. The DGC-grown MFI zeolite film could form a strong barrier to protect AA6061 surface against the corrosion from NaCl solution. By using fumed silica as a starting material, the hydrophilicity and anti-corrosion capability of the MFI zeolite film declined with increasing humidity in the DGC synthesis. By silanization with ODS, the surface hydrophobicity of the MFI zeolite film increased, leading to substantial enhancement in anti-corrosion capability. On the other hand, MFI film grown from ODS-modified fumed silica exhibited low hydrophilicity and a much improved anti-corrosion protection property by four orders of magnitude, even stronger than the ODS post-treated MFI film. The strong anti-corrosion capability is attributed to the “thick layer” surface hydrophobicity of zeolite crystal.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
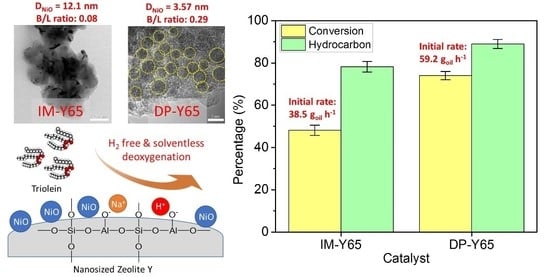
Deposition of NiO Nanoparticles on Nanosized Zeolite NaY for Production of Biofuel via Hydrogen-Free Deoxygenation
by
Min-Yee Choo, Lee Eng Oi, T. Jean Daou, Tau Chuan Ling, Yu-Chuan Lin, Gabriele Centi, Eng-Poh Ng and Joon Ching Juan
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 3271
Abstract
Nickel-based catalysts play an important role in the hydrogen-free deoxygenation for the production of biofuel. The yield and quality of the biofuel are critically affected by the physicochemical properties of NiO supported on nanosized zeolite Y (Y65, crystal size of 65 nm). Therefore,
[...] Read more.
Nickel-based catalysts play an important role in the hydrogen-free deoxygenation for the production of biofuel. The yield and quality of the biofuel are critically affected by the physicochemical properties of NiO supported on nanosized zeolite Y (Y65, crystal size of 65 nm). Therefore, 10 wt% NiO supported on Y65 synthesized by using impregnation (IM) and deposition–precipitation (DP) methods were investigated. It was found that preparation methods have a significant effect on the deoxygenation of triolein. The initial rate of the DP method (14.8 g
oil·h
−1) was 1.5 times higher than that of the IM method (9.6 g
oil·h
−1). The DP-Y65 showed the best deoxygenation performance with a 80.0% conversion and a diesel selectivity of 93.7% at 380 °C within 1 h. The outstanding performance from the DP method was due to the smaller NiO particle size (3.57 ± 0.40 nm), high accessibility (H.F value of 0.084), and a higher Brönsted to Lewis acidity (B/L) ratio (0.29), which has improved the accessibility and deoxygenation ability of the catalyst. The NH
4+ released from the decomposition of the urea during the DP process increased the B/L ratio of zeolite NaY. As a result, the pretreatment to convert Na-zeolite to H-zeolite in a conventional zeolite synthesis can be avoided. In this regard, the DP method offers a one-pot synthesis to produce smaller NiO-supported nanosized zeolite NaY with a high B/L ratio, and it managed to produce a higher yield with selectivity towards green diesel
via deoxygenation under a hydrogen-free condition.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
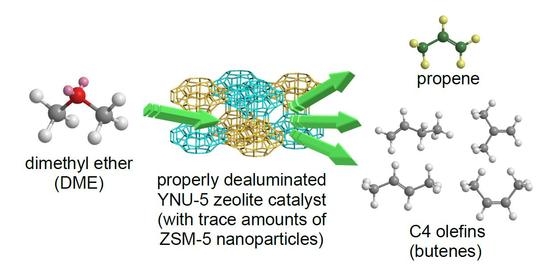
The Synthesis of YNU-5 Zeolite and Its Application to the Catalysis in the Dimethyl Ether-to-Olefin Reaction
by
Qing Liu, Yuka Yoshida, Naoto Nakazawa, Satoshi Inagaki and Yoshihiro Kubota
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3478
Abstract
During prior investigations of the synthesis of the novel zeolite YNU-5 (
YFI), it was found that a very slight amount of an impurity phase contaminated the desired zeolitic phase. This impurity was very often ZSM-5 (
MFI). The phase composition
[...] Read more.
During prior investigations of the synthesis of the novel zeolite YNU-5 (
YFI), it was found that a very slight amount of an impurity phase contaminated the desired zeolitic phase. This impurity was very often ZSM-5 (
MFI). The phase composition was determined to be sensitive to the water in the synthesis mixture, and it was possible to obtain a pure phase and also to intentionally generate a specific impurity phase. In the present work, trials based on the dimethyl ether-to-olefin (DTO) reaction using a fixed-bed downflow reactor were performed to assess the effect of the purity of YNU-5 on its catalytic performance. Dealuminated pure YNU-5 exhibited rapid deactivation due to coking at time on stream (TOS) values exceeding 5 min. Surprisingly, this deactivation was greatly suppressed when the material contained a trace amount of ZSM-5 consisting of nano-sized particles. The formation of ZSM-5 nanoparticles evidently improved the performance of the catalytic system during the DTO reaction. The product distributions obtained from this reaction using highly dealuminated and very pure YNU-5 resembled those generated by 12-ring rather than 8-ring zeolite catalysts. The high selectivity for desirable C3 and C4 olefins during the DTO reaction over YNU-5 is beneficial.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Progress in the Utilization of Coal Fly Ash by Conversion to Zeolites with Green Energy Applications
by
Silviya Boycheva, Denitza Zgureva, Katerina Lazarova, Tsvetanka Babeva, Cyril Popov, Hristina Lazarova and Margarita Popova
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 4367
Abstract
Fly ash (FA) from lignite coal combusted in different Thermal Power Plants (TPPs) was used for the synthesis of zeolites (FAZs) of the Na-X type by alkaline activation via three laboratory procedures. FAZs were characterized with respect to their morphology, phase composition and
[...] Read more.
Fly ash (FA) from lignite coal combusted in different Thermal Power Plants (TPPs) was used for the synthesis of zeolites (FAZs) of the Na-X type by alkaline activation via three laboratory procedures. FAZs were characterized with respect to their morphology, phase composition and surface properties, which predetermine their suitability for applications as catalysts and adsorbents. FAZs were subsequently modified with metal oxides (CuO) to improve their catalytic properties. The catalytic activity of non-modified and CuO-modified FAZs in the total oxidation of volatile organic compounds was investigated. FAZs were studied for their potential to retain CO
2, as their favorable surface characteristics and the presence of iron oxides make them suitable for carbon capture technologies. Thin films of FAZs were deposited by in situ crystallization, and investigated for their morphology and optical sensitivity when exposed to pollutants in the gas phase, e.g., acetone. This study contributes to the development of novel technological solutions for the smart and valuable utilization of FA in the context of the circular economy and green energy production.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
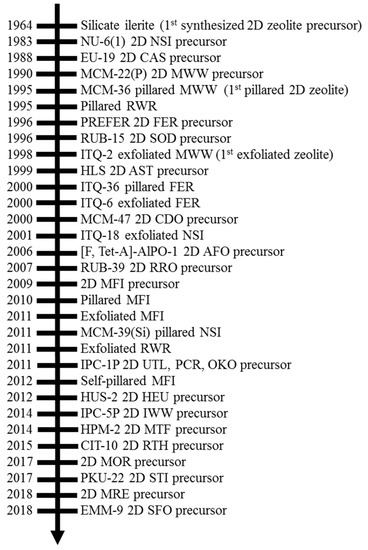
Two-Dimensional Zeolite Materials: Structural and Acidity Properties
by
Emily Schulman, Wei Wu and Dongxia Liu
Cited by 60 | Viewed by 10579
Abstract
Zeolites are generally defined as three-dimensional (3D) crystalline microporous aluminosilicates in which silicon (Si
4+) and aluminum (Al
3+) are coordinated tetrahedrally with oxygen to form large negative lattices and consequent Brønsted acidity. Two-dimensional (2D) zeolite nanosheets with single-unit-cell or near
[...] Read more.
Zeolites are generally defined as three-dimensional (3D) crystalline microporous aluminosilicates in which silicon (Si
4+) and aluminum (Al
3+) are coordinated tetrahedrally with oxygen to form large negative lattices and consequent Brønsted acidity. Two-dimensional (2D) zeolite nanosheets with single-unit-cell or near single-unit-cell thickness (~2–3 nm) represent an emerging type of zeolite material. The extremely thin slices of crystals in 2D zeolites produce high external surface areas (up to 50% of total surface area compared to ~2% in micron-sized 3D zeolite) and expose most of their active sites on external surfaces, enabling beneficial effects for the adsorption and reaction performance for processing bulky molecules. This review summarizes the structural properties of 2D layered precursors and 2D zeolite derivatives, as well as the acidity properties of 2D zeolite derivative structures, especially in connection to their 3D conventional zeolite analogues’ structural and compositional properties. The timeline of the synthesis and recognition of 2D zeolites, as well as the structure and composition properties of each 2D zeolite, are discussed initially. The qualitative and quantitative measurements on the acid site type, strength, and accessibility of 2D zeolites are then presented. Future research and development directions to advance understanding of 2D zeolite materials are also discussed.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Facile Synthesis of Super-Microporous Titania–Alumina with Tailored Framework Properties
by
Yongfeng Li, Jiaojiao Su, Guiping Li and Xiufeng Meng
Viewed by 2451
Abstract
Super-microporous material (pore size 1–2 nm) can bridge the pore size gap between the zeolites (<1 nm) and the mesoporous oxides (>2 nm). A series of super-microporous titania–alumina materials has been successfully prepared via a facile one-pot evaporation-induced self-assembly (EISA) strategy by different
[...] Read more.
Super-microporous material (pore size 1–2 nm) can bridge the pore size gap between the zeolites (<1 nm) and the mesoporous oxides (>2 nm). A series of super-microporous titania–alumina materials has been successfully prepared via a facile one-pot evaporation-induced self-assembly (EISA) strategy by different solvents using fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether (AEO-7) as the template. Moreover, no extra acid or base is added in our synthesis process. When titanium isopropylate is used as the titanium source, these materials exhibit high BET surface areas (from 275 to 396 m
2/g) and pore volumes (from 0.14 to 0.18 cm
3/g). The sample prepared using methanol as the solvent shows the largest Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area of 396 m
2/g. When tetrabutyl titanate is used as the titanium source, these materials exhibit high BET surface areas (from 282 to 396 m
2/g) and pore volumes (from 0.13 to 0.18 cm
3/g). The sample prepared using ethanol as the solvent shows the largest BET surface area of 396 m
2/g.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Zeolite Nanocrystals Protect the Performance of Organic Additives and Adsorb Acid Compounds during Lubricants Oxidation
by
Moussa Zaarour, Hussein El Siblani, Nicolas Arnault, Philippe Boullay and Svetlana Mintova
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3162
Abstract
Zeolite nanocrystals were used as proactive agents to extend the lifetime of commercial lubricants by protecting the performance additives from depletion and adsorbing the acid formed during oxidation. The nanosized zeolites were introduced into four lubricants and subjected to oxidation (90 °C and
[...] Read more.
Zeolite nanocrystals were used as proactive agents to extend the lifetime of commercial lubricants by protecting the performance additives from depletion and adsorbing the acid formed during oxidation. The nanosized zeolites were introduced into four lubricants and subjected to oxidation (90 °C and 150 °C). A strong affinity towards protection of zinc dialkyldithiophosphate (ZDDP) additive was demonstrated by
31P NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) and FTIR (fourier-transform infrared) spectroscopy even after heating at 150 °C for 24 h. FTIR profiles of lubricants aged in the presence of LTL (Linde Type L zeolite) showed lower oxidation degree while the formed oxidation products (aldehydes, ketones, and acids) were adsorbed on the zeolite crystals acting as scavengers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
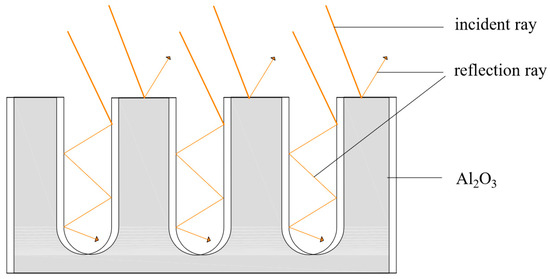
Investigation on the Solar Absorption Property of the Nanoporous Alumina Sheet for Solar Application
by
Song He, Yanmei Zhang, Wansheng Yang, Zhangyuan Wang, Xudong Zhao and Pingnuo Wang
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3699
Abstract
In order to improve the absorption performance of the aluminum sheet for solar application, the nanoporous alumina sheets with the pore diameters of 30 nm and 400 nm were prepared by the anodic oxidation method. The absorption properties of the nanoporous alumina sheets
[...] Read more.
In order to improve the absorption performance of the aluminum sheet for solar application, the nanoporous alumina sheets with the pore diameters of 30 nm and 400 nm were prepared by the anodic oxidation method. The absorption properties of the nanoporous alumina sheets under different solar radiation intensity were studied and compared with the conventional polished aluminum sheet. The results showed that the average absorptivity of the aluminum sheets decreased with the increase of the radiation intensity. When the radiation intensity was 100 W/m
2, the nanoporous alumina sheet with the 30 nm pore diameter had the highest average solar absorptivity of 0.39, which was 18% higher than that of the nanoporous alumina sheet with 400 nm pore diameter, and 50% higher than that of the polished aluminum sheet. The maximum instantaneous absorption efficiency of the nanoporous alumina sheet with 30 nm pore diameter was found at 0.92 when the radiation intensity was 100 W/m
2. The testing results indicated that the nanoporous alumina sheet with the 30 nm pore diameter performed the best compared with the other two aluminum sheets. By error propagation analysis, the relative error of the average amount of heat absorption and the average absorptivity were acceptable.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
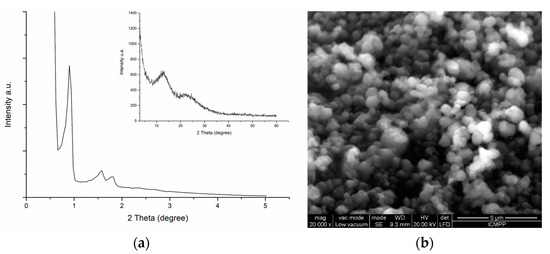
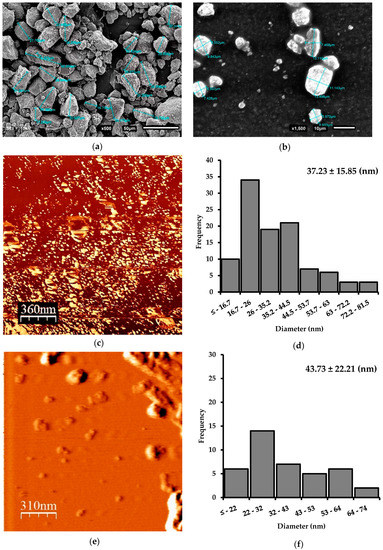
Obtaining Nanoparticles of Chilean Natural Zeolite and its Ion Exchange with Copper Salt (Cu2+) for Antibacterial Applications
by
Judith Vergara-Figueroa, Serguei Alejandro-Martín, Héctor Pesenti, Fabiola Cerda, Arturo Fernández-Pérez and William Gacitúa
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 4996
Abstract
This article describes the production of nanoparticles of Chilean natural zeolite, using three size reduction methods: Ball mill, microgrinding, and microfluidization. Morphological characterization of samples indicated an average diameter of 37.2 ± 15.8 nm of the zeolite particles. The size reduction and chemical
[...] Read more.
This article describes the production of nanoparticles of Chilean natural zeolite, using three size reduction methods: Ball mill, microgrinding, and microfluidization. Morphological characterization of samples indicated an average diameter of 37.2 ± 15.8 nm of the zeolite particles. The size reduction and chemical treatments did not affect the morphology or integrity of the zeolite. An increase of the zeolite samples’ Si/Al ratio was observed after the acid treatment and was confirmed by SEM-EDX analysis. Moreover, the effectiveness of the copper salt ion exchange (Cu
2+) to the zeolite nanoparticles was analyzed by SEM-EDX. XRD analysis indicated that clinoptilolite and mordenite are the main phases of Chilean natural zeolite, and the crystalline structure was not affected by the modification processes. The FTIR characterization showed the presence of chemical bonds of copper with the zeolite nanoparticle framework. The ion-exchanged zeolite nanoparticles were evaluated for antibacterial behavior by the disc diffusion method. Additionally, the minimum inhibitory concentration and minimum bactericidal concentration were obtained. Microbiological assays with copper-exchanged nanozeolites showed an antimicrobial activity with a bactericidal effect against
Escherichia coli and
Staphylococcus aureus, which are the primary pathogens of food and are also resistant to multiple drugs. In this study, a new application for natural nanozeolites is demonstrated, as the incorporated copper ions (Cu
2+) in nanozeolites registered a productive antibacterial activity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures