Journal Description
Photonics
Photonics
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the science and technology of optics and photonics, published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Inspec, Ei Compendex, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Optics)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 14.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 1.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journal: Lights.
Impact Factor:
2.1 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.1 (2023)
Latest Articles
Circuit-QED for Multi-Loop Fluxonium-Type Qubits
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 417; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050417 - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
Fluxonium qubits, designed to mitigate charge noise and enhance anharmonicity, are among the most promising superconducting platforms for quantum computing. To understand and exploit their quantum properties and design novel fluxonium-based architectures with improved functionalities, these systems require an accurate Hamiltonian formulation to
[...] Read more.
Fluxonium qubits, designed to mitigate charge noise and enhance anharmonicity, are among the most promising superconducting platforms for quantum computing. To understand and exploit their quantum properties and design novel fluxonium-based architectures with improved functionalities, these systems require an accurate Hamiltonian formulation to capture their energy level structure and quantum dynamics. This work presents a systematic method for constructing the Hamiltonian for multi-loop circuits that partitions the system into a set of uncoupled harmonic oscillators and a coupled anharmonic part originating from the Josephson circuit elements, allowing clear identification of independent modes and isolating the nonlinearity in the Josephson terms. While demonstrated for fluxonium-type multi-loop circuits, this method can be generalized to other superconducting qubit architectures within the broader context of circuit QED, making it a versatile tool for exploring different circuit configurations. Our systematic and flexible modeling approach forms the theoretical basis for the qubit measurement and control experiments validating multi-loop fluxonium architectures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes: Innovations and Applications)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Improved Optical Signal Processing with On-Chip Programmable Filter
by
Tiantian Li, Yumeng Liu, Luwen Xing, Shuo Lang, Zhangfeng Ge, Dongdong Han, Zhanqiang Hui, Huimin Du and Haowen Shu
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 416; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050416 - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
Bandwidth-limited transmitters have become a severe issue with the rapid growth of bandwidth-hungry services. We investigate the impact of an on-chip optical pre-emphasizer on a bandwidth-limited transmitter and quantitatively analyze the results of bandwidth extension. Improvements in eye diagram performance are discussed. The
[...] Read more.
Bandwidth-limited transmitters have become a severe issue with the rapid growth of bandwidth-hungry services. We investigate the impact of an on-chip optical pre-emphasizer on a bandwidth-limited transmitter and quantitatively analyze the results of bandwidth extension. Improvements in eye diagram performance are discussed. The 3 dB electro-optical bandwidth of the transmission system is effectively extended from 18 GHz to 40 GHz. The extinction ratio of the on–off keying (OOK) signal at data rates of 20 to 50 Gbps is improved by 0.64–3.2 dB. Additionally, the Q factor of the eye diagram increases by 0.78–4.36 at data rates ranging from 20 to 50 Gbps.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Fiber Laser Technology and Its Application)
►▼
Show Figures
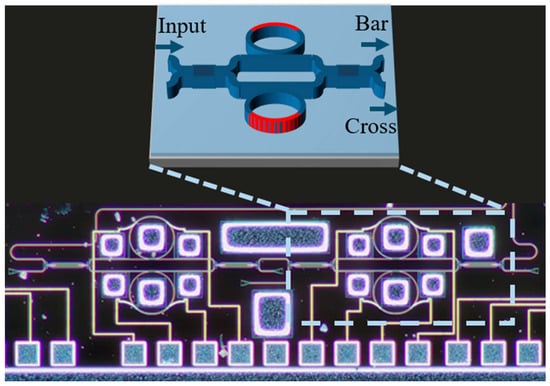
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Measurement of Coherence Time in Cold Atom-Generated Tunable Photon Wave Packets Using an Unbalanced Fiber Interferometer
by
Ya Li, Wanru Wang, Qizhou Wu, Youxing Chen, Can Sun, Hai Wang and Weizhe Qiao
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 415; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050415 - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the realm of quantum communication and photonic technologies, the extension of coherence time for photon wave packets is essential for improving system efficacy. This research introduces a methodology for measuring coherence time utilizing an unbalanced fiber interferometer, specifically designed for tunable pulse-width
[...] Read more.
In the realm of quantum communication and photonic technologies, the extension of coherence time for photon wave packets is essential for improving system efficacy. This research introduces a methodology for measuring coherence time utilizing an unbalanced fiber interferometer, specifically designed for tunable pulse-width photon wave packets produced by cold atoms. By synchronously generating write pulses, signal light, and frequency-locking light from a single laser source, the study effectively mitigated frequency discrepancies that typically arise from the use of multiple light sources. The implementation of frequency-resolved photon counting under phase-locked conditions was accomplished through the application of polarization filtering and cascaded filtering techniques. The experimental results indicated that the periodicity of frequency shifts in interference fringe patterns diminishes as the differences in delay arm lengths increase, while fluctuations in fiber length and high-frequency laser jitter adversely affect interference visibility. Through an analysis of the correlation between delay and photon counts, the coherence time of the write laser was determined to be 2.56 µs, whereas the Stokes photons produced through interactions with cold atoms exhibited a reduced coherence time of 1.23 µs. The findings suggest that enhancements in laser bandwidth compression and fiber phase stability could further prolong the coherence time of photon wave packets generated by cold atoms, thereby providing valuable technical support for high-fidelity quantum information processing.
Full article
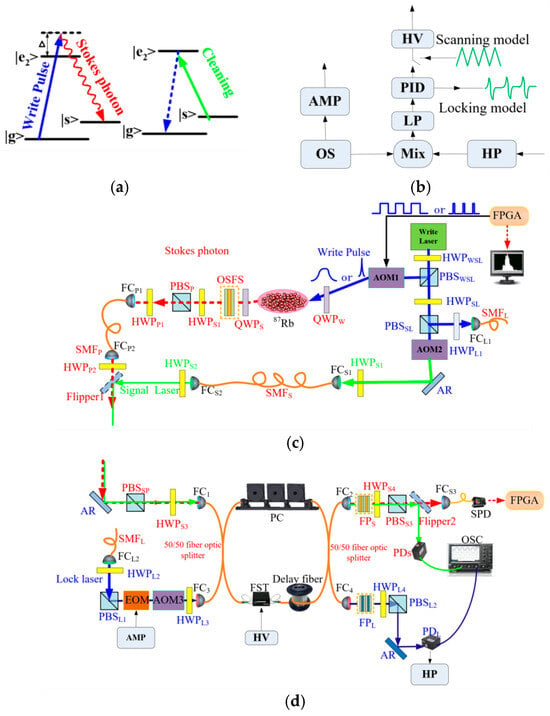
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Design and Analysis of High-Precision Workbench with Large Stroke and Heavy Load for Fabricating Large-Area Grating
by
Guangdong Yu, Heshig Bayan, Qi Chen, Hao Chen, Xin He and Xuefeng Yao
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 414; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050414 - 24 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
When scanning beam interference lithography (SBIL) technology is used for grating fabrication, the stroke, bearing capacity, and accuracy of the workbench determine the size and accuracy of the grating. For large-area gratings with dimensions exceeding the meter level, the existing workbench cannot fully
[...] Read more.
When scanning beam interference lithography (SBIL) technology is used for grating fabrication, the stroke, bearing capacity, and accuracy of the workbench determine the size and accuracy of the grating. For large-area gratings with dimensions exceeding the meter level, the existing workbench cannot fully meet the requirements. Therefore, the structure design, drive type, and assembly technology of the workbench were studied in this research, and a two-dimensional workbench with a large stroke, heavy load, and high precision was developed. The performance of this workbench was tested. The stroke of the workbench can reach 1800 mm × 700 mm; the straightness is better than 1.5 μm for the whole stroke range. The load can be up to 2.5 t and the positioning accuracy can achieve the nanometer level. A scanning exposure experiment was carried out with this workbench and a grating of 1400 mm × 420 mm was made. The performance index of the grating was outstanding, achieving the intended goals of the experiment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Multimodal Imaging in Stem Cell Therapy for Retinal Disease
by
Mi Zheng and Yannis M. Paulus
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 413; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050413 - 24 Apr 2025
Abstract
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising approach for treating various retinal diseases, particularly degenerative retinal diseases such as geographic atrophy in age-related macular degeneration (AMD), retinitis pigmentosa (RP), and Stargardt disease. A wide variety of imaging techniques have been employed in
[...] Read more.
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising approach for treating various retinal diseases, particularly degenerative retinal diseases such as geographic atrophy in age-related macular degeneration (AMD), retinitis pigmentosa (RP), and Stargardt disease. A wide variety of imaging techniques have been employed in both preclinical and clinical settings to assess the efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy for retinal diseases. These techniques can be classified into two categories: methods for imaging stem cells and those for the overall morphology and function of the retina. The techniques employed for stem cell imaging include optical imaging, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and radionuclide imaging. Additional imaging techniques include fundus photography, fluorescein angiography, and fundus autofluorescence. Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and thus, the use of multimodal imaging can help to overcome the shortcomings and achieve a more comprehensive evaluation of stem cell therapy in retinal disease. This review discusses the characteristics of the main techniques and cell-labeling techniques applied in stem cell therapy, with a particular focus on the applications of multimodal imaging. Furthermore, this review discusses the challenges and prospects of multimodal imaging in stem cell therapy for retinal disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Exploring Cutting-Edge Technologies and Applications of Optics and Photonics)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessCommunication
Asymmetry Analysis of the Autler–Townes Doublet in the Trap-Loss Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Cesium MOT with Single-Step Rydberg Excitation
by
Xiaokai Hou, Yuewei Wang, Jun He and Junmin Wang
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 412; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050412 - 24 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The Autler–Townes (AT) doublet, a fundamental manifestation of quantum interference effects, serves as a critical tool for studying the dynamic behavior of Rydberg atoms. Here, we investigate the asymmetry of the Autler–Townes (AT) doublet in the trap-loss fluorescence spectroscopy (TLFS) of cesium (Cs)
[...] Read more.
The Autler–Townes (AT) doublet, a fundamental manifestation of quantum interference effects, serves as a critical tool for studying the dynamic behavior of Rydberg atoms. Here, we investigate the asymmetry of the Autler–Townes (AT) doublet in the trap-loss fluorescence spectroscopy (TLFS) of cesium (Cs) atoms confined in a magneto-optical trap (MOT) with single-step Rydberg excitation using a 319-nm ultraviolet (UV) laser. A V-type three-level system involving the ground state

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dynamic Measurement of Flowing Microparticles in Microfluidics Using Pulsed Modulated Digital Holographic Microscopy
by
Yunze Lei, Yuge Li, Xiaofang Wang, Kequn Zhuo, Ying Ma, Sha An, Juanjuan Zheng, Kai Wen, Lihe Yan and Peng Gao
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 411; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050411 - 24 Apr 2025
Abstract
We propose a pulsed modulated digital holographic microscopy (PM-DHM) technique for the dynamic measurement of flowing microparticles in microfluidic systems. By digitally tuning the pulse width and the repetition rate of a laser source within a single-frame exposure, this method enables the recording
[...] Read more.
We propose a pulsed modulated digital holographic microscopy (PM-DHM) technique for the dynamic measurement of flowing microparticles in microfluidic systems. By digitally tuning the pulse width and the repetition rate of a laser source within a single-frame exposure, this method enables the recording of multiple images of flowing microparticles at different time points within a single hologram, allowing the quantification of velocity and acceleration. We demonstrate the feasibility of PM-DHM by measuring the velocity, acceleration, and forces exerted on PMMA microspheres and red blood cells flowing in microfluidic chips. Compared to traditional frame-sampling-based imaging methods, this technique has a much higher time resolution (in a range of microseconds) that is limited only by the pulse duration. This method demonstrates significant potential for high-throughput label-free flow cytometry detection and offers promising applications in drug development and cell analysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Quantitative Phase Microscopy: Techniques and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Impact of Non-Vertical Sidewalls on Bandgap Properties of Lithium Niobate Photonic Crystals
by
Peyman Bagheri, Xiaoyan Zhou and Lin Zhang
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 410; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050410 - 24 Apr 2025
Abstract
We investigate the influence of non-vertical sidewall angles on the band structure characteristics of thin-film lithium niobate (LN) photonic crystals (PhCs), considering both suspended LN membranes and LN on insulator (LNOI) configurations. Utilizing the gap-to-midgap ratio as a figure-of-merit, we observe a 34%
[...] Read more.
We investigate the influence of non-vertical sidewall angles on the band structure characteristics of thin-film lithium niobate (LN) photonic crystals (PhCs), considering both suspended LN membranes and LN on insulator (LNOI) configurations. Utilizing the gap-to-midgap ratio as a figure-of-merit, we observe a 34% reduction for a suspended LN PhC with 60° sidewall angles compared to the one with vertical sidewalls and a more substantial 73% reduction for LNOI PhCs with 70° sidewall angles. We address this challenge through the optimization of geometrical parameters of PhC unit cells with non-vertical sidewalls, taking fabrication feasibility into account. Our work provides a design guideline for the development of realistic LN PhC devices for future large-scale LN photonic circuits.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Progress in Integrated Photonics)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Hybrid Method for Solving the Radiative Transport Equation
by
André Liemert, Dominik Reitzle and Alwin Kienle
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 409; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050409 - 24 Apr 2025
Abstract
The spherical harmonics method (
The spherical harmonics method (
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biomedical Photonics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Lower-Level Relaxation on the Pulse Generation Performance of Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser
by
Fuqiang Ma, Shiyu Wang, Bingbin Li, Peijin Shang, Jinyou Li and Zheyuan Li
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 408; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050408 - 24 Apr 2025
Abstract
When analyzing and designing Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers, the impact of lower-energy-level relaxation on the pulse waveform is often ignored. This approximation typically does not result in significant deviations when the laser pulse duration is much longer than the relaxation time of the lower
[...] Read more.
When analyzing and designing Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers, the impact of lower-energy-level relaxation on the pulse waveform is often ignored. This approximation typically does not result in significant deviations when the laser pulse duration is much longer than the relaxation time of the lower energy level. However, when the pulse duration approaches the nanosecond range, the spontaneous emission time of lower energy level in the Nd:YAG crystal, which is approximately 30 ns, can severely affect the pulse waveform. In this study, a theoretical model is proposed to investigate the influence of lower-energy-level relaxation on the output pulse waveform of an Nd:YAG laser. Specifically, the output waveform of a narrow-pulse-width Q-switched Nd:YAG laser is simulated. The results indicate that for narrow-pulse-width laser output, lower-energy-level relaxation causes a secondary peak to appear after the main peak of the Q-switched pulse. The energy of this secondary peak is more than two times higher than that of the main peak. An experimental system for acousto-optic Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers has also been established, and the Q-switched pulse waveforms are measured under conditions similar to those in the simulations. The tail peak phenomenon observed in the experiments is consistent with the simulation results, verifying the accuracy of the theoretical model. These findings provide a crucial theoretical foundation for understanding and optimizing Nd:YAG lasers and have significant implications for the development of similar technologies. In laser technology, particularly for applications requiring high precision and performance, considering such factors is essential for optimizing the design and functionality of laser systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Photodetectors for Next-Generation Imaging and Sensing Systems)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Far-Field Topological Structure of the Second Harmonic from Higher-Order Poincaré Sphere Beam
by
Yangyang Li, Ziping Zhu, Yuanxiang Wang, Jiantai Dou, Li Fan, Bo Li and Youyou Hu
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 407; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050407 - 24 Apr 2025
Abstract
In this paper, the far-field topological structures (FFTSs) of the second harmonic (SH) from higher-order Poincaré sphere (HOPS) beams, including circularly polarized vortex beams (VBs), cylindrically vector beams (CVBs) and elliptically polarized CVBs (EPCVBs), were demonstrated and reported. To begin with, the hidden
[...] Read more.
In this paper, the far-field topological structures (FFTSs) of the second harmonic (SH) from higher-order Poincaré sphere (HOPS) beams, including circularly polarized vortex beams (VBs), cylindrically vector beams (CVBs) and elliptically polarized CVBs (EPCVBs), were demonstrated and reported. To begin with, the hidden FFTSs of the SH after propagating the twice Rayleigh range were simulated based on the vectorial coupled wave equations and the Collins formula. Then, the experimental setup was established to achieve the SH from the HOPS by applying two orthogonal 5% MgO: PPLN crystals, the FFTSs of which were demonstrated. The theoretical and experimental results indicate that for the circularly polarized VBs, the FFTSs of the SH still exhibit the 135°-linearly polarized VBs, which is similar to that of the SH in-source plane, because the SH is the eigen-mode of free space, while for the CVBs, the FFTSs of the SH generally show the disappearance of the central dark core, replaced by the maximum light intensity at the center due to the topological phase transition during propagation. Especially of note, for the EPCVBs, the FFTSs of the SH display the maximum light intensity at the center, but the FFTSs in the horizontal and vertical directions reveal rotational symmetry related to the chirality of the EPCVBs. The results reveal the evolution mechanisms of the SH from the HOPS in the far field, which may facilitate the applications of the SH from HOPS beam.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fundamentals and Applications of Vortex Beams)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
55% Efficient High-Power Multijunction Photovoltaic Laser Power Converters for 1070 nm
by
Simon Fafard and Denis Masson
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 406; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050406 - 23 Apr 2025
Abstract
High-efficiency multijunction laser power converters are demonstrated for the first time at high power for optical inputs around 1070 nm. The InP-based photovoltaic power-converting III–V heterostructures are designed with eight lattice-matched InGaAsP subcells (PT8-1070 nm). Conversion efficiencies of 55% were obtained at 18
[...] Read more.
High-efficiency multijunction laser power converters are demonstrated for the first time at high power for optical inputs around 1070 nm. The InP-based photovoltaic power-converting III–V heterostructures are designed with eight lattice-matched InGaAsP subcells (PT8-1070 nm). Conversion efficiencies of 55% were obtained at 18 W of output power. Endurance testing was performed for over 1000 h of continuous operation with an average output power of 13.2 W at an input wavelength of 1064 nm. An average steady-state efficiency of 54.4% at an ambient temperature of ~20 °C was obtained for that duration. The results demonstrate that 1 cm2 optical power converter devices can produce electrical outputs of 20 W at maximum power voltages around Vmpp ~6 V, thus retaining an optimal load near Rmpp at ~2 ohms. Efficiencies between 57.9% and 59.0% were also obtained for smaller 0.029 cm2 chips for input intensities between 35 and 69 W/cm2. This is an important development for power beaming applications: the unprecedented combination of power and conversion efficiency capabilities is expected to enable deployments for key wavelengths between 1040 and 1080 nm.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue High-Performance Semiconductor Optoelectronic Devices)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Adaptive Generation Method for Small Volume Easy Fabrication Freeform Unobscured Three-Mirror Systems Based on Machine Learning
by
Yiwei Sun, Yangjie Wei and Ji Zhao
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 405; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050405 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Freeform unobscured multiple-mirror systems have been widely applied in high-precision optical fields due to their high imaging quality and no chromatic aberration and central obstruction. However, how to design a freeform unobscured multiple-mirror system with small system volume, imaging quality, and low manufacturing
[...] Read more.
Freeform unobscured multiple-mirror systems have been widely applied in high-precision optical fields due to their high imaging quality and no chromatic aberration and central obstruction. However, how to design a freeform unobscured multiple-mirror system with small system volume, imaging quality, and low manufacturing difficulty is challenging. This study proposes an adaptive generation method for freeform unobscured three-mirror systems with small volume and ease of fabrication based on machine learning, considering the fabrication constraints, volume limitations, imaging quality, and design efficiency. First, an error function based on volume, fabrication, and imaging quality functions is constructed, and a dataset is generated using this error function. Then, a machine learning model is trained using this dataset, enabling efficient prediction of the parameters for small-volume, easy-to-fabricate freeform unobscured three-mirror systems. Finally, the parameters of the freeform unobscured three-mirror system are predicted using the trained model, and combined with the freeform surface generation method, a freeform unobscured three-mirror imaging system is automatically obtained. Experimental results demonstrate that our method can effectively generate freeform unobscured three-mirror systems that meet the requirements for small volume and easy fabrication, providing a new approach for optical design.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Topics in Freeform Optics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing for Visible Light Communication Based on Minimum Shift Keying Modulation
by
Ying Zhang, Kexin Li and Yufeng Yang
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 404; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050404 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
With the rapid development of visible light communication (VLC) technology, traditional modulation schemes can no longer meet the high demands for bandwidth efficiency and signal stability in complex application scenarios. In particular, in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems, issues such as the
[...] Read more.
With the rapid development of visible light communication (VLC) technology, traditional modulation schemes can no longer meet the high demands for bandwidth efficiency and signal stability in complex application scenarios. In particular, in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems, issues such as the nonlinearity of Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) and carrier frequency offset have worsened system performance. To address these challenges, this paper proposes an N-order Minimum Shift Keying (NMSK) OFDM system with Fast Hartley Transform (FHT) for signal mapping. Monte Carlo simulations systematically compare the performance of low-order and high-order NMSK modulations under various conditions. The results indicate that low-order NMSK exhibits superior robustness against bit errors and interference, while high-order NMSK can maintain a stable PAPR and provide higher spectral efficiency in high-bandwidth demand scenarios. Further experiments validate the stability of high-order NMSK in high-density multi-user and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) environments, proving its adaptability and effectiveness in such scenarios. The high-order NMSK modulation scheme provides strong support for the reliability and bandwidth efficiency of future 6G VLC networks, offering significant application prospects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Photonics: 10th Anniversary)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dynamically Tunable Singular States Through Air-Slit Control in Asymmetric Resonant Metamaterials
by
Yeong Hwan Ko and Robert Magnusson
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 403; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050403 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
This study presents a novel method for dynamically tuning singular states in one-dimensional (1D) photonic lattices (PLs) using air-slit-based structural modifications. Singular states, arising from symmetry-breaking-induced resonance radiation, generate diverse spectral features through interactions between resonance modes and background radiation. By strategically incorporating
[...] Read more.
This study presents a novel method for dynamically tuning singular states in one-dimensional (1D) photonic lattices (PLs) using air-slit-based structural modifications. Singular states, arising from symmetry-breaking-induced resonance radiation, generate diverse spectral features through interactions between resonance modes and background radiation. By strategically incorporating air slits to break symmetry in 1D PLs, we demonstrated effective control of resonance positions, enabling dual functionalities including narrowband band pass and notch filtering. These singular states originate from asymmetric guided-mode resonances (aGMRs), which can be interpreted by analytical modeling of the equivalent slab waveguide. Moreover, the introduction of multiple air slits significantly enhances spectral tunability by inducing multiple folding behaviors in the resonance bands. This approach allows for effective manipulation of optical properties through simple adjustments of air-slit displacements. This work provides great potential for designing multifunctional photonic devices with advanced metamaterial technologies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optical Metasurfaces: Applications and Trends)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Series/Parallel Boost/Buck DC/DC Converter as a Visible Light Communication HB-LED Driver Based on Split Power
by
Daniel G. Aller, Diego G. Lamar, Juan R. Garcia-Mere, Marta M. Hernando, Juan Rodriguez and Javier Sebastian
Photonics 2025, 12(5), 402; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050402 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
This paper presents a high-brightness LED (HB-LED) driver for visible light communication (VLC) based on two converters. The first is a high-frequency buck DC/DC converter and the second is a low-frequency boost DC/DC converter, connected in series with respect to the LED load
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a high-brightness LED (HB-LED) driver for visible light communication (VLC) based on two converters. The first is a high-frequency buck DC/DC converter and the second is a low-frequency boost DC/DC converter, connected in series with respect to the LED load and connected in parallel at the input, forming a series/parallel boost/buck DC/DC converter. It is well known that a VLC system needs to perform two different tasks: biasing the HB-LED load and transmitting the communication signal. These typically have different power requirements; the bias power is 75%, while the communication power is 25% of the total power. The requirements of each converter are also different; the communication signal requires a fast output response and, therefore, a high switching frequency, while the biasing control does not require a converter with a high output voltage response. The proposed architecture in this paper takes advantage of the differences between the two tasks and achieves high efficiency and high communication performance by means of splitting power between the two DC/DC converters. The high-frequency buck DC/DC converter tracks the communication signal, while the low-frequency boost DC/DC converter is responsible for lighting tasks. This technique enables high efficiency because most of the power is processed by the low-frequency converter, while a minor part of the power is processed by the high-frequency converter, achieving high communication performance. To provide experimental results, the proposed VLC HB-LED driver was built and validated by reproducing a 64-QAM with a bit rate up to 1.5 Mbps, reaching 91.5% overall efficiency.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Technologies in Optical Wireless Communications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Metasurface-Refractive Hybrid Lens Modeling with Vector Field Physical Optics
by
Ko-Han Shih and C. Kyle Renshaw
Photonics 2025, 12(4), 401; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040401 - 21 Apr 2025
Abstract
Metasurfaces (MSs) have emerged as a promising technology for optical system design. When combined with traditional refractive optics, MS-refractive hybrid lenses can enhance imaging performance, reduce optical aberrations, and introduce new functionalities such as polarization control. However, modeling these hybrid lenses requires advanced
[...] Read more.
Metasurfaces (MSs) have emerged as a promising technology for optical system design. When combined with traditional refractive optics, MS-refractive hybrid lenses can enhance imaging performance, reduce optical aberrations, and introduce new functionalities such as polarization control. However, modeling these hybrid lenses requires advanced simulation techniques that usually go beyond conventional raytracing tools. This work presents a physical optics framework for modeling MS-refractive hybrid lenses. We introduce a ray-wave hybrid method that integrates multiple propagation techniques to account for vector wave propagation through various optical elements. At the center of the proposed framework is the Gaussian decomposition method for modeling beam propagation through refractive optics. Ray-path diffraction is automatically considered in this method, and complex input wavefront can be modeled as well. Several techniques are integrated to ensure accuracy in decomposing an incoming vector wave into Gaussian beamlets, such as adaptive consideration of local wavefront principal curvatures and best-fit beam width estimation from the local covariance matrix. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, we apply it to several hybrid lens designs, including polarization-sensitive MSs and aberration-correcting MSs integrated into complex optical systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancements in Optical Metamaterials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exact Solutions to Cancer Laser Ablation Modeling
by
Luisa Consiglieri
Photonics 2025, 12(4), 400; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040400 - 21 Apr 2025
Abstract
The present paper deals with the study of the fluence rate over both healthy and tumor tissues in the presence of focal laser ablation (FLA). We propose new analytical solutions for a coupled partial differential equation (PDE) system, which includes the transport equation
[...] Read more.
The present paper deals with the study of the fluence rate over both healthy and tumor tissues in the presence of focal laser ablation (FLA). We propose new analytical solutions for a coupled partial differential equation (PDE) system, which includes the transport equation modeling of light penetration into biological tissue, the bioheat equation modeling the heat transfer, and its respective damage. The present work could be the first step toward knowledge of the mathematical framework for biothermophysical problems, as well as the main key to simplify the numerical calculations due to its zero cost. We derive exact solutions and simulate results from them. We discuss the potential physical contributions and present respective conclusions about the following: (1) the validity of the diffusion approximation of the radiative transfer equation; (2) the local behavior of the source of scattered photons; (3) the unsteady state of the fluence rate; and (4) the boundedness of the critical time of the thermal damage to the cancerous tissue. We also discuss some controversial and diverging hypotheses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Lasers, Light Sources and Sensors)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Microstructured Waveguide Sensors for Point-of-Care Health Screening
by
Svetlana S. Konnova, Pavel A. Lepilin, Anastasia A. Zanishevskaya, Alexey Y. Gryaznov, Natalia A. Kosheleva, Victoria P. Ilinskaya, Julia S. Skibina and Valery V. Tuchin
Photonics 2025, 12(4), 399; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040399 - 20 Apr 2025
Abstract
Biosensor technologies in medicine, as in many other areas, are replacing labor-intensive methods of monitoring human health. This paper presents the results of experimental studies on label-free sensors based on a hollow core microstructured optical waveguide (HC-MOW) for human blood serum analysis. The
[...] Read more.
Biosensor technologies in medicine, as in many other areas, are replacing labor-intensive methods of monitoring human health. This paper presents the results of experimental studies on label-free sensors based on a hollow core microstructured optical waveguide (HC-MOW) for human blood serum analysis. The MOWs with a hollow core of 247.5 µm in diameter were manufactured and used in our work. These parameters allow the hollow core to be filled with high-viscosity solutions due to the capillary properties of the fiber. Calculations of the spectral properties of the HC-MOW fiber were carried out and experimentally confirmed. Twenty-one blood serum samples from volunteers were analyzed using standard photometry (commercial kits) and an experimental biosensor. The obtained transmission spectra were processed by the principal component analysis method and conclusions were drawn about the possibility of using this biosensor in point-of-care medicine. A significant difference was shown between the blood serum of healthy patients and patients with confirmed diagnoses and a long history of cardiovascular system abnormalities. Algorithms for spectra processing using the Origin program are presented.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optical Sensors for Advanced Biomedical Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Noise Reduction in LED-Based Photoacoustic Imaging
by
Takahiro Kono, Kazuma Hashimoto, Keisuke Fukuda, Uma Maheswari Rajagopalan, Kae Nakamura and Jun Yamada
Photonics 2025, 12(4), 398; https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040398 - 18 Apr 2025
Abstract
Photoacoustic tomography (PAT), also known as optoacoustic tomography, has been emerging as a biomedical imaging modality that can provide cross-sectional or three-dimensional (3D) visualization of biological tissues such as blood vessels and lymphatic vessels in vivo at high resolution. The principle behind the
[...] Read more.
Photoacoustic tomography (PAT), also known as optoacoustic tomography, has been emerging as a biomedical imaging modality that can provide cross-sectional or three-dimensional (3D) visualization of biological tissues such as blood vessels and lymphatic vessels in vivo at high resolution. The principle behind the visualization involves the light being absorbed by the tissues which results in the generation of ultrasound. Depending on the strength of ultrasound and its decay rate, it could be used to visualize the absorber location. In general, pulsed lasers such as the Q-switched Nd-YAG and OPO lasers that provide high-energy widths in the range of a few nanoseconds operating at low repetition rates are commonly used as a light source in photoacoustic imaging. However, such lasers are expensive and occupy ample space. Therefore, PAT systems that use LED as the source instead of lasers, which have the advantage of being obtainable at low cost and portable, are gaining attention. However, LED light sources have significantly low energy, and the photoacoustic signals generated have a low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Therefore, in LED-based systems, one way to strengthen the signal and improve the SNR is to significantly increase the repetition rate of LED pulses and use signal processing, which can be achieved using a high-power LED along M-sequence signal decoding. M-sequence signal decoding is effective, especially under high repetition rates, thus improving the SNR. However, power supplies for high-power LEDs have a circuit jitter, resulting in random temporal fluctuations in the emitted light. Such jitters, in turn, would affect the M-sequence-based signal decoding. Therefore, we propose a new decoding algorithm which compensates for LED jitter in the M-sequence signal processing. We show that the proposed new signal processing method can significantly improve the SNR of the photoacoustic signals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Trends in Biomedical Optical Imaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Photonics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Optics, Sensors, Materials, Fibers, Photonics, Micromachines
Distributed Optical Fiber Sensors
Topic Editors: Jian Li, Hao Wu, Giancarlo C. Righini, Zhe Ma, Yahui WangDeadline: 15 June 2025
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, JSAN, Photonics, Sensors, Telecom
Machine Learning in Communication Systems and Networks, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Yichuang Sun, Haeyoung Lee, Oluyomi SimpsonDeadline: 20 July 2025
Topic in
Energies, Photonics, Sustainability, Solar, Nanomaterials
Photovoltaic Materials and Devices—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Bin Yang, Yongbo YuanDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Energies, Entropy, Photonics, Technologies
Advances in Solar Technologies, Second Edition
Topic Editors: Jayanta Deb Mondol, Annamaria Buonomano, Biplab DasDeadline: 31 March 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Photonics
Advances in Nonlinear Optics: From Fundamentals to Applications
Guest Editors: Wenjie Wan, Yuanlin ZhengDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Photonics
Advances in Nonlinear Fiber Optics: Science and Applications
Guest Editors: Jingwei Wu, Fabio ManginiDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Photonics
Advanced Methods in Exploring Light–Matter Interactions and Nonlinear Effects Optics Applications
Guest Editors: Zhaohong Liu, Yuanqin Xia, Xiao Fang, Jiawei Sun, Zeyu Gao, Jiarui LiDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
Photonics
Advanced Laser Beam Control Technology and Applications
Guest Editors: Lizhi Dong, Xin Yu, Qing YeDeadline: 30 April 2025












