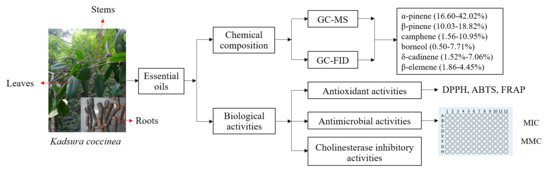
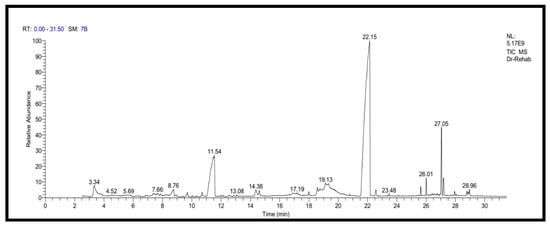
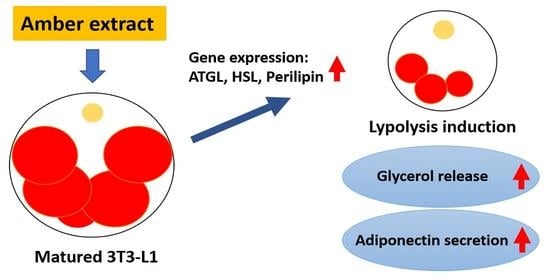
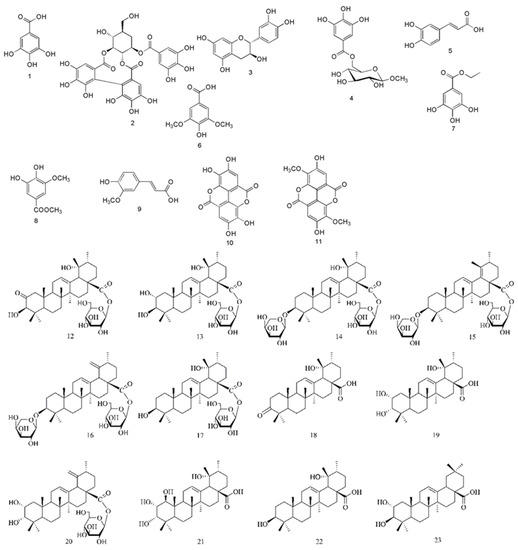
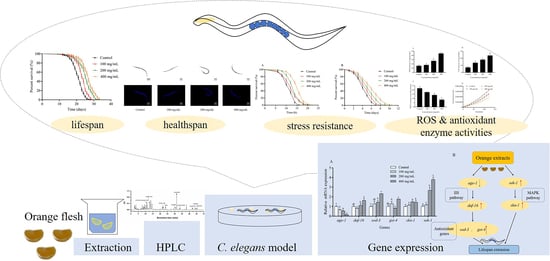
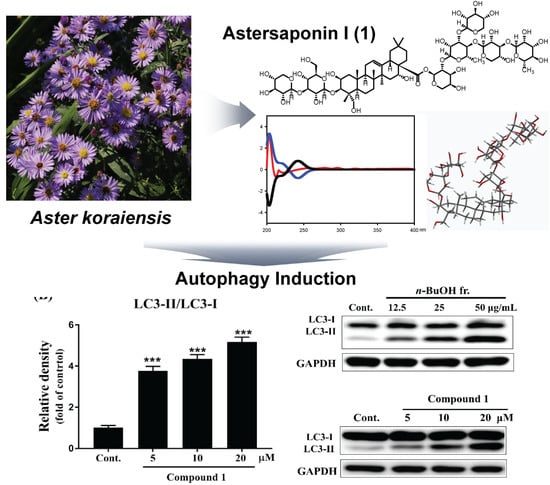
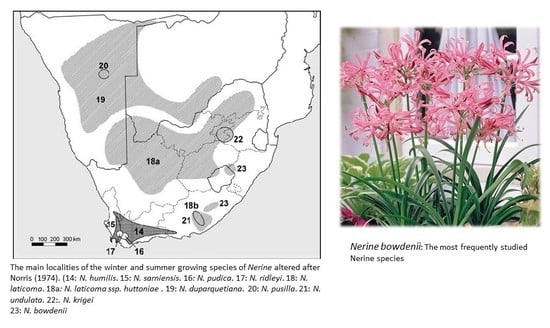
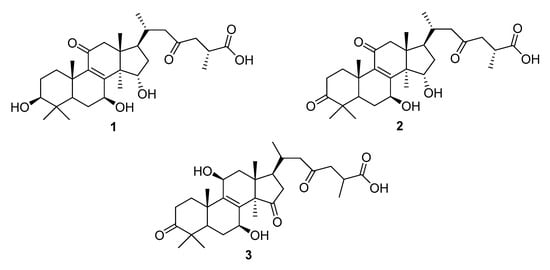
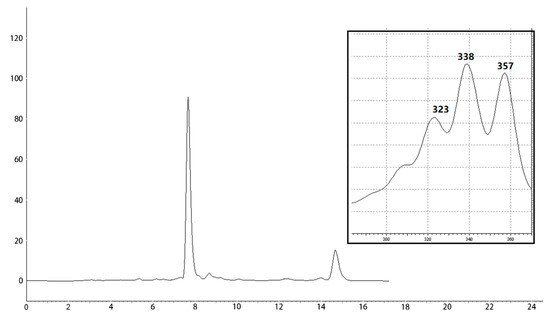
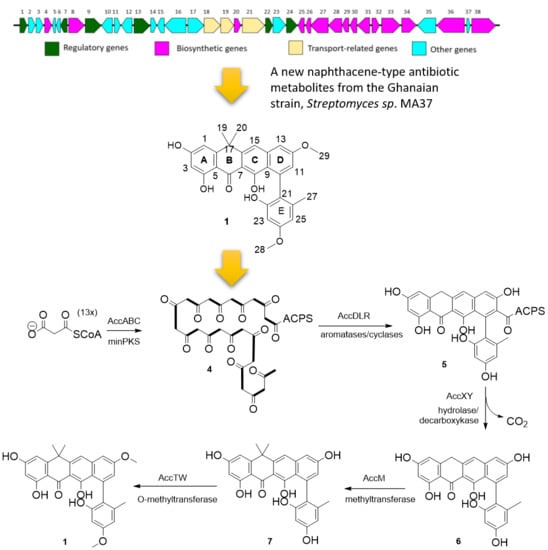
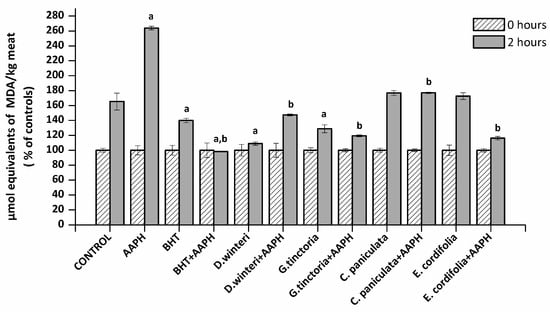
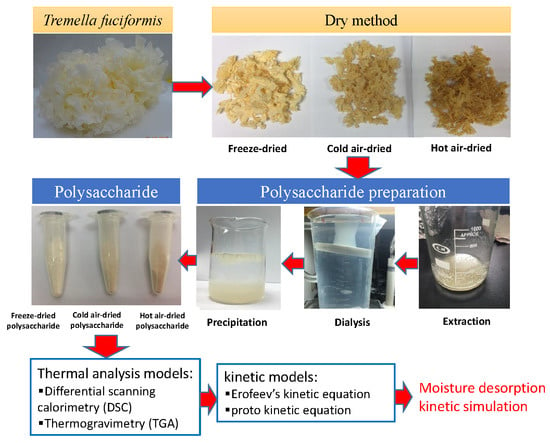
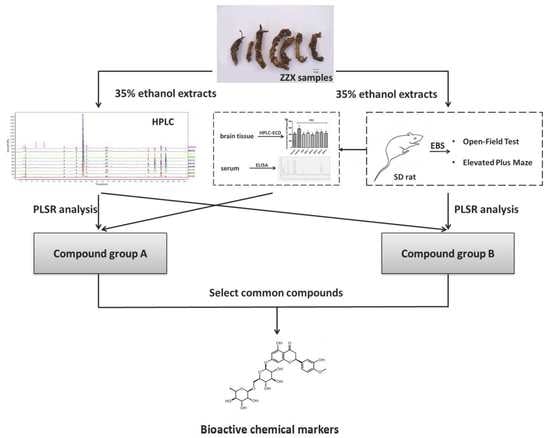
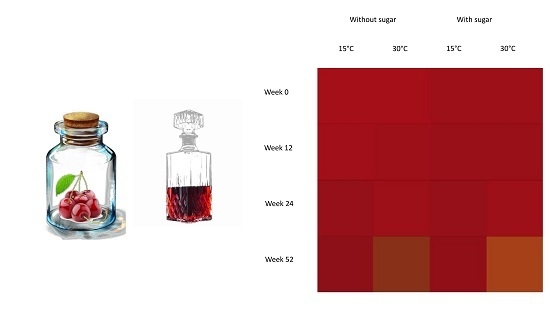
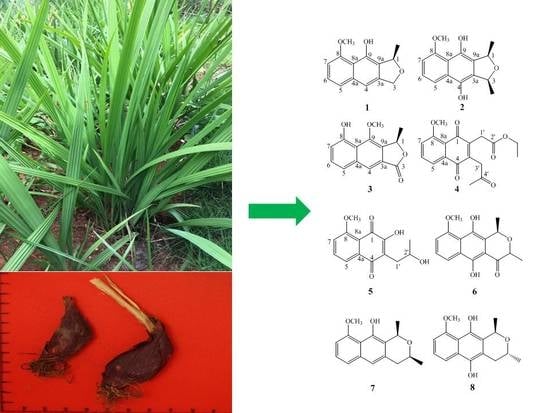
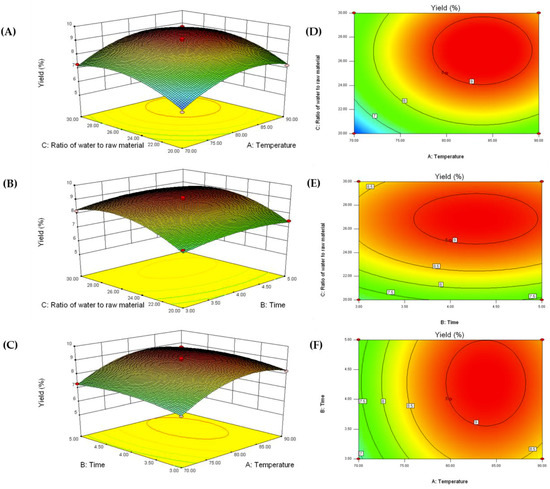
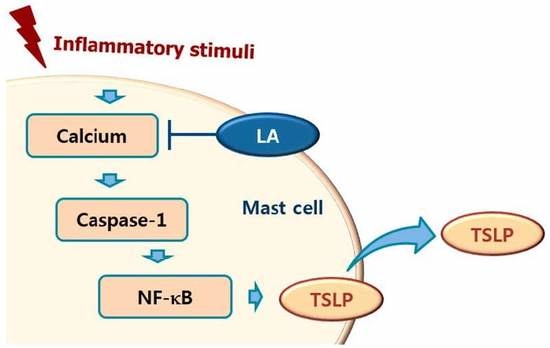
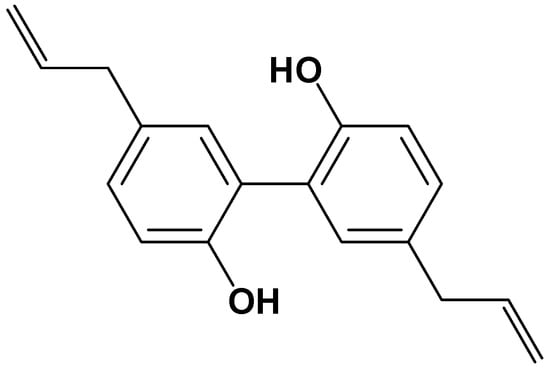
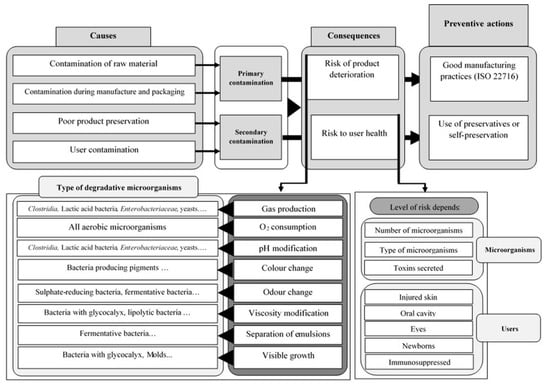
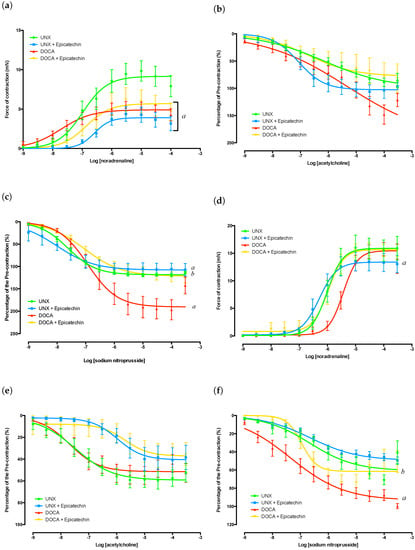
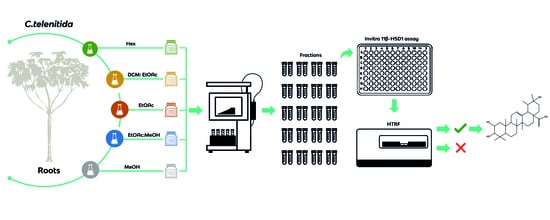
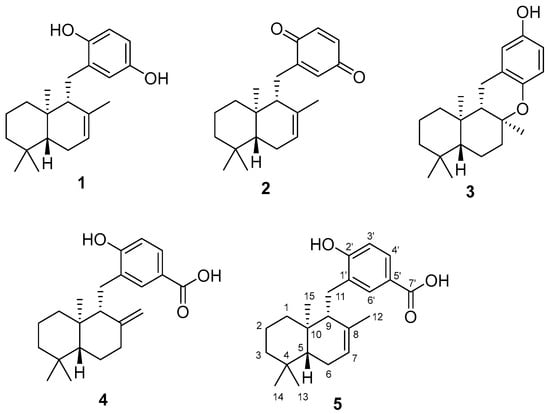
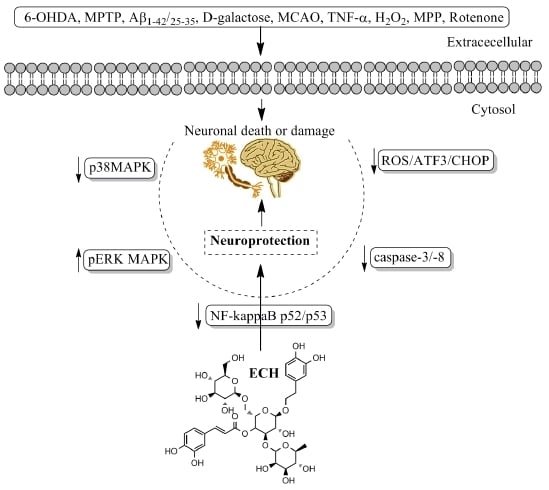
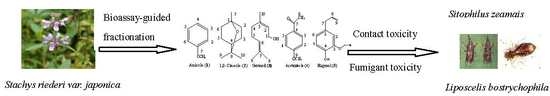
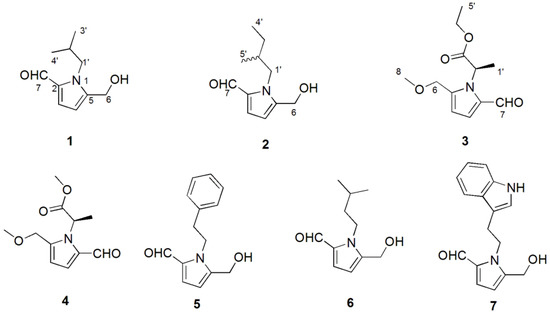
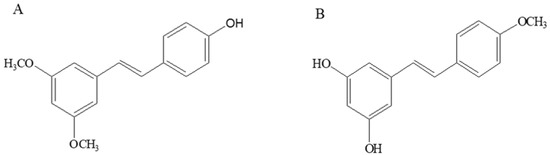
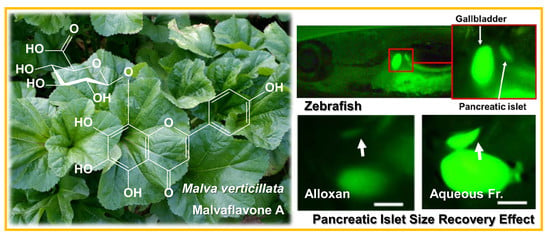
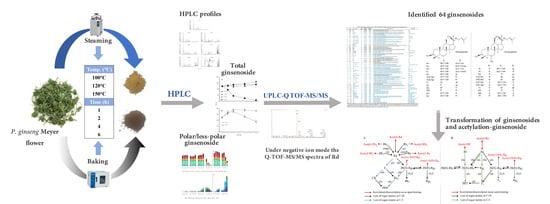
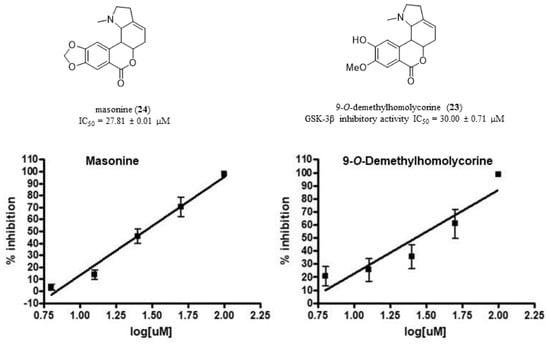
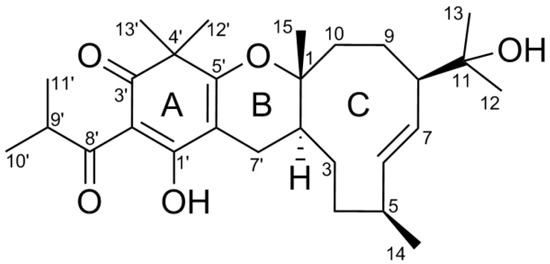
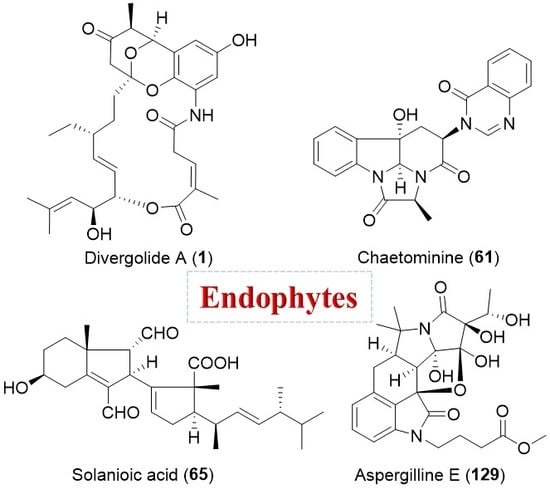
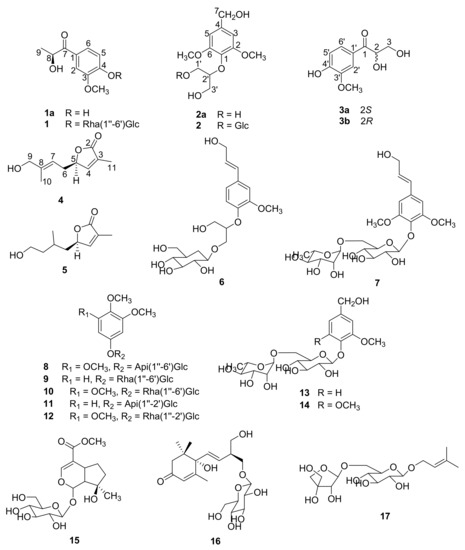
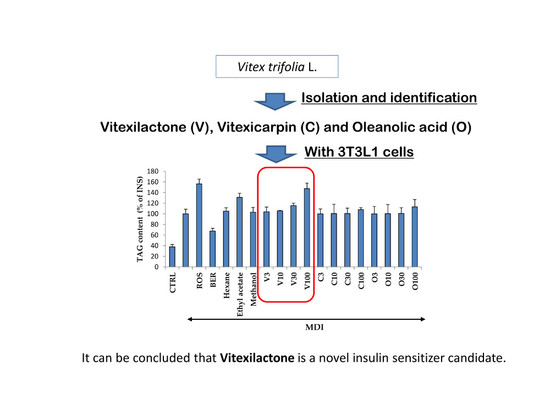
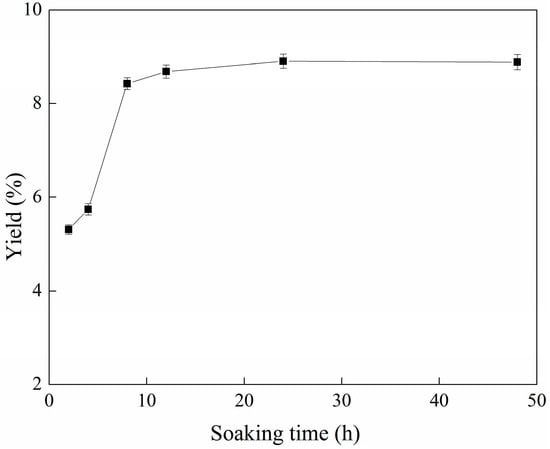
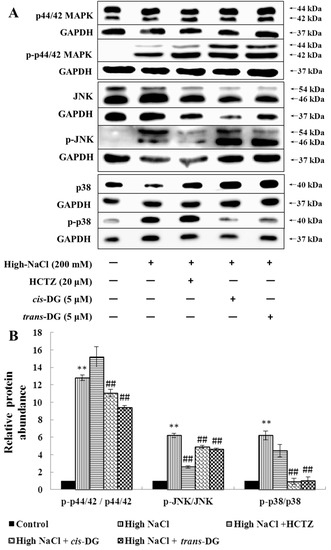
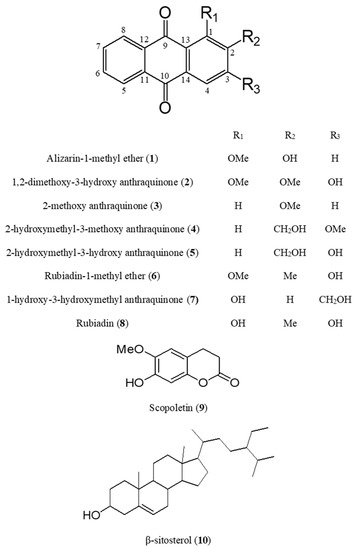
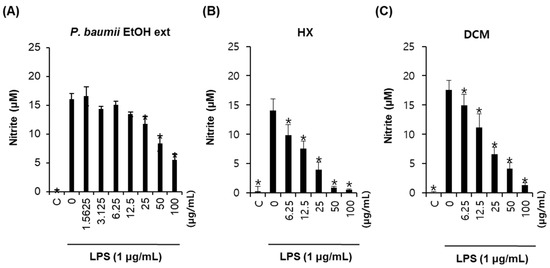
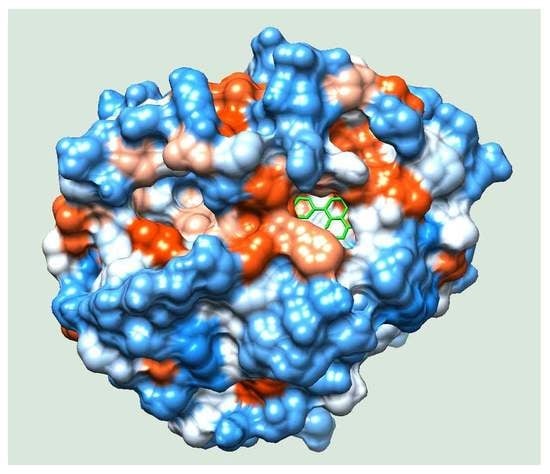
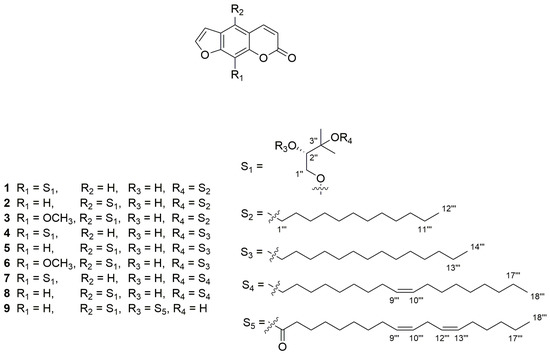
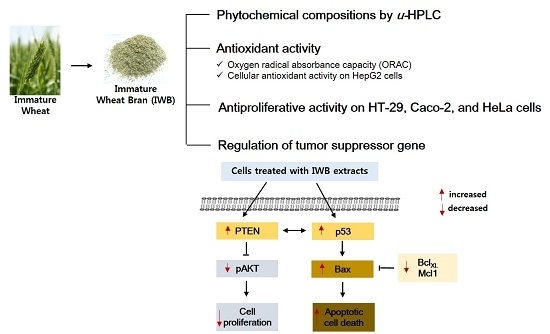
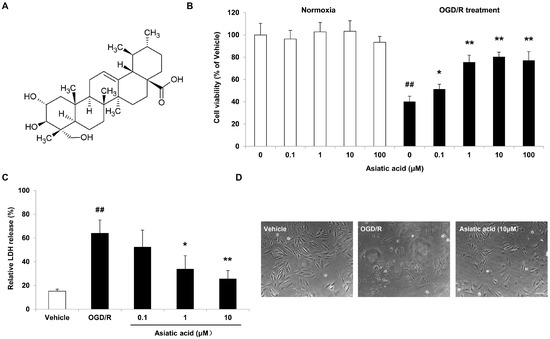
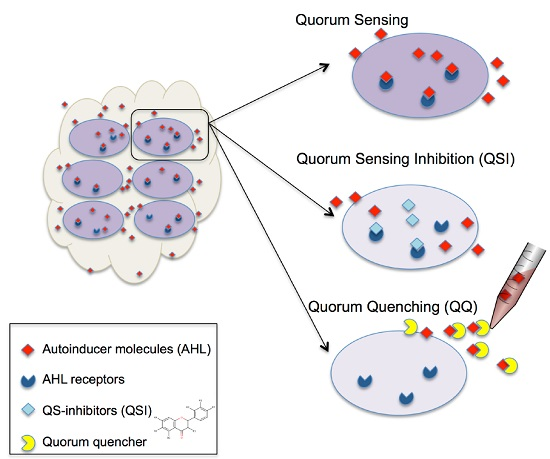
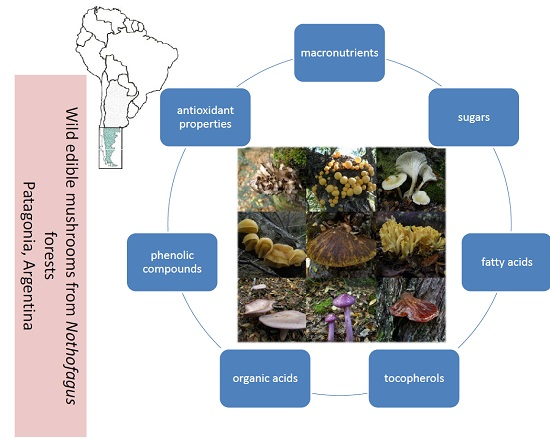
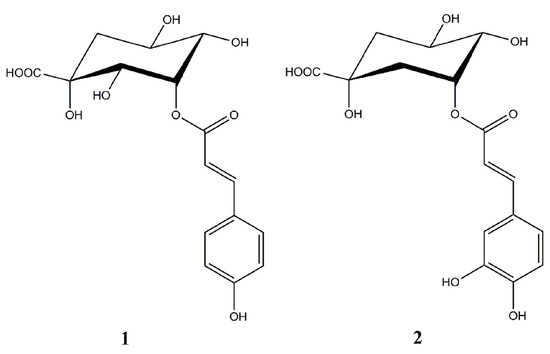
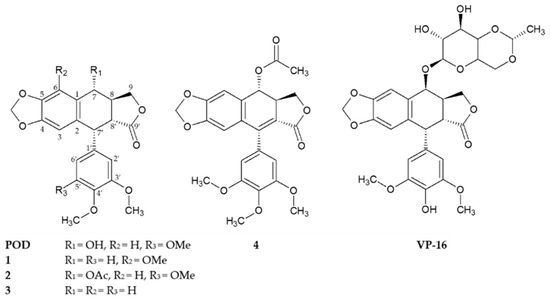
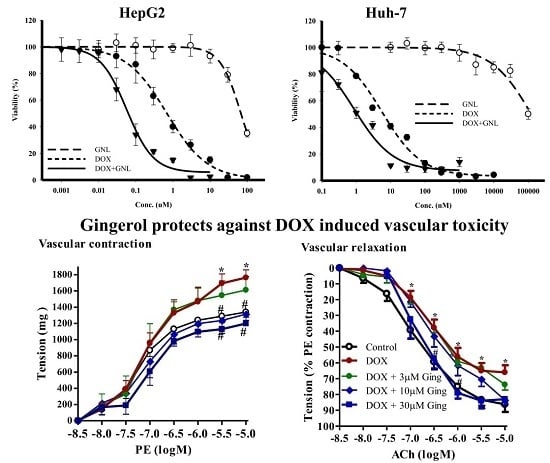
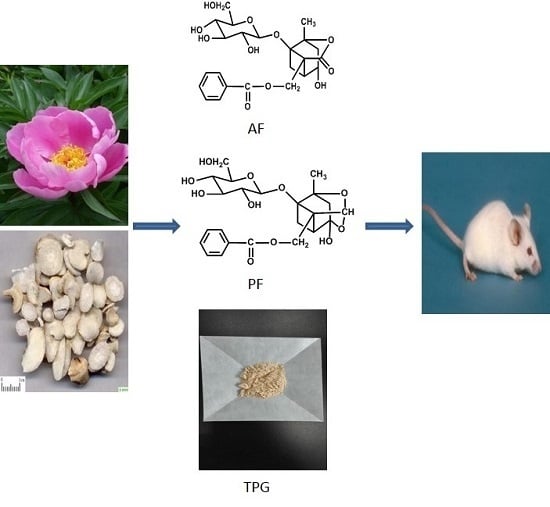
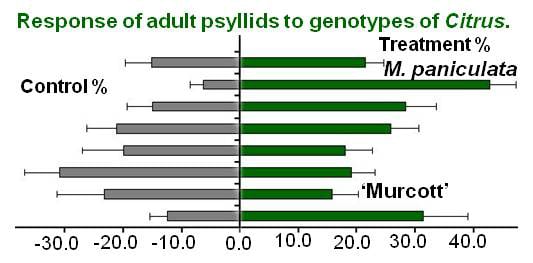
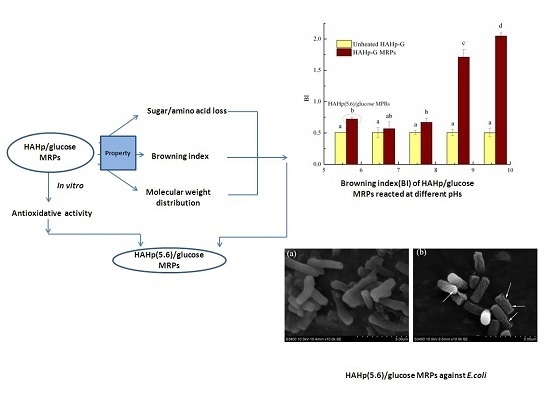
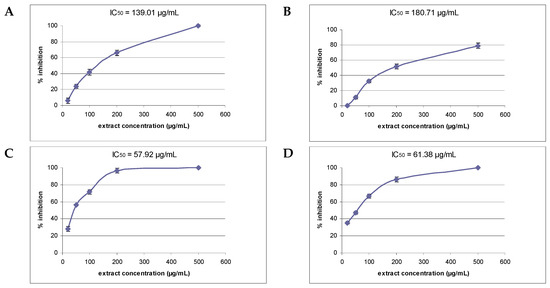
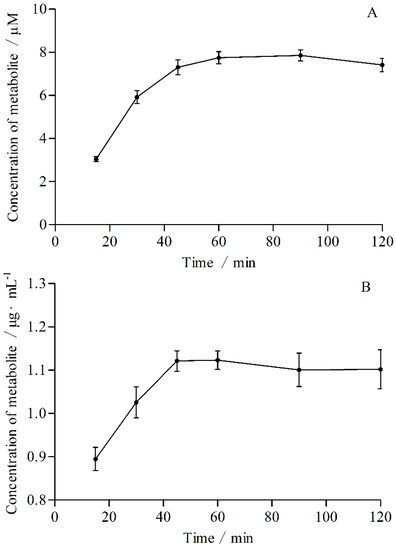
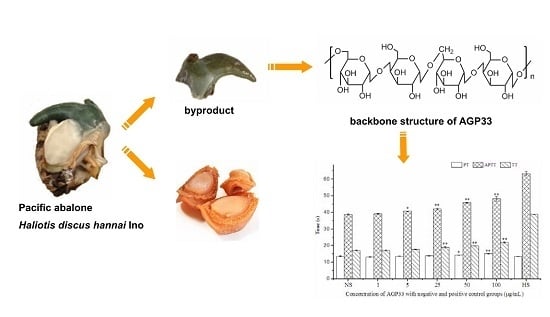
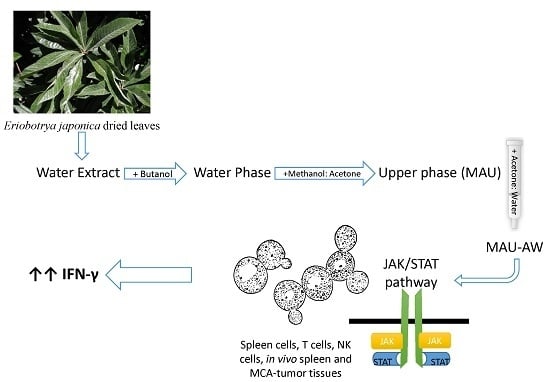
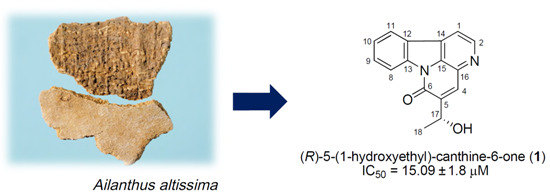
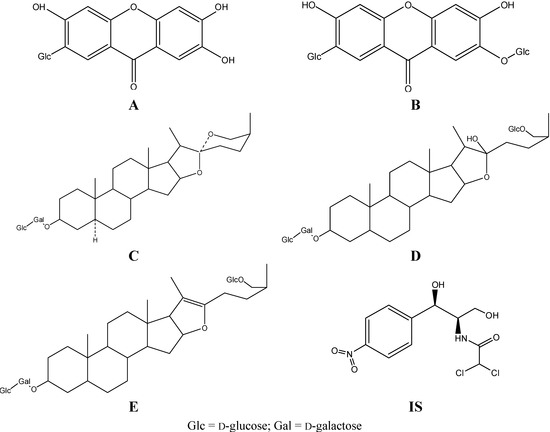
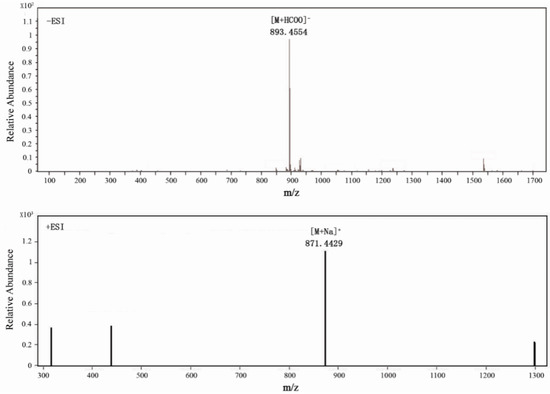
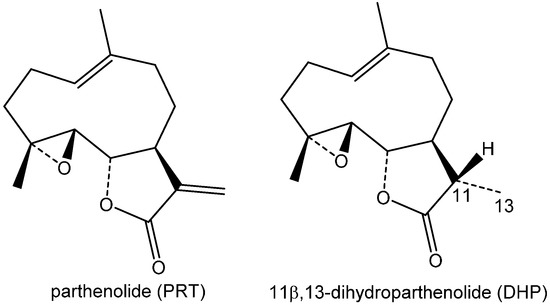
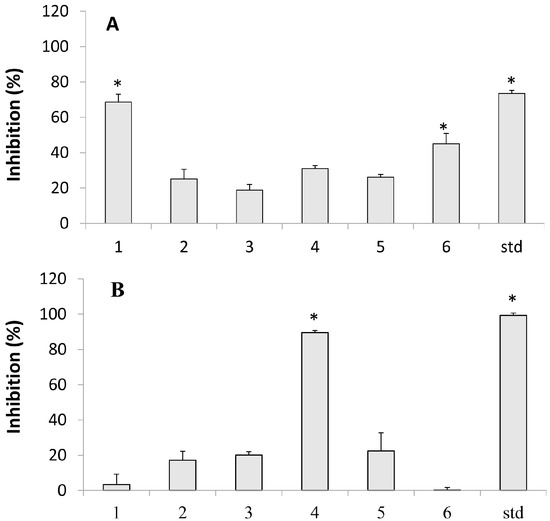
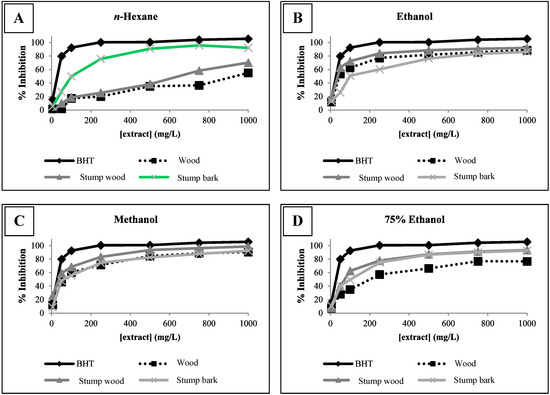
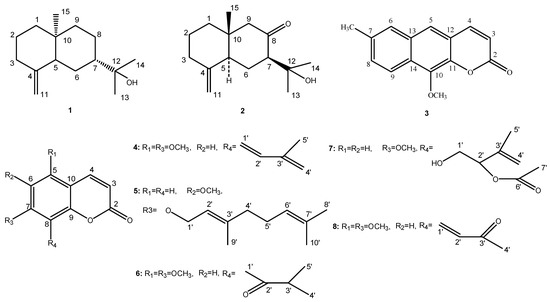
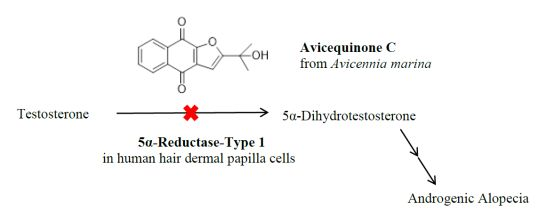
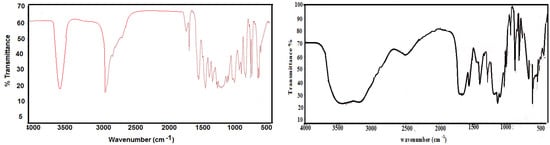
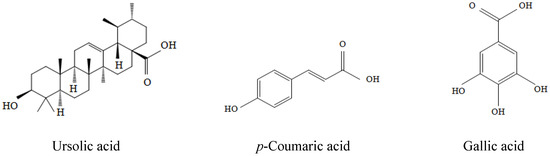
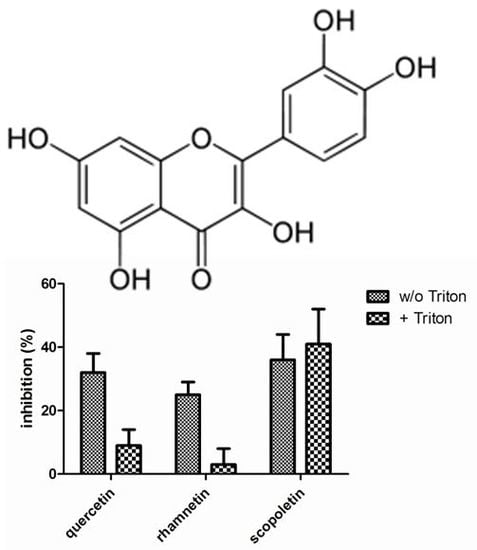
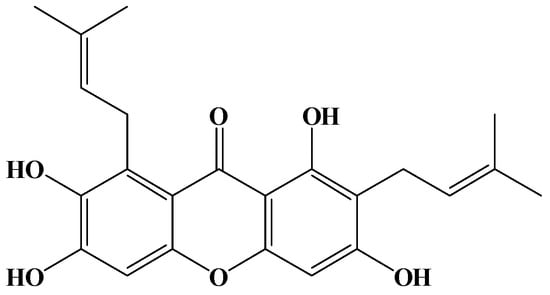
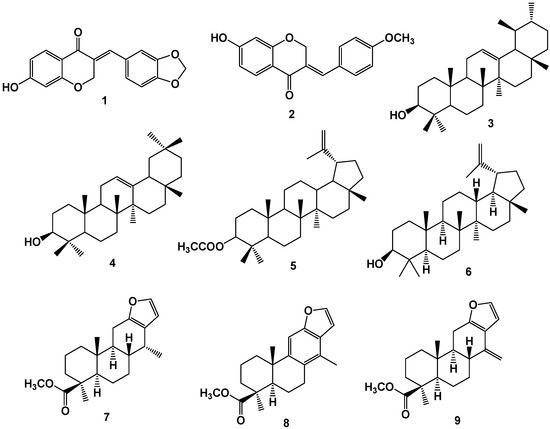
Bioactive Compounds
A topical collection in Molecules (ISSN 1420-3049). This collection belongs to the section "Natural Products Chemistry".
Viewed by 3172135Editors
Interests: cancer chemoprevention; nutrition; olive oil; polyphenols; natural bioactive compounds; antioxidants; oxidative stress; genotoxicity; mutagenicity; apoptosis; cell cycle regulation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
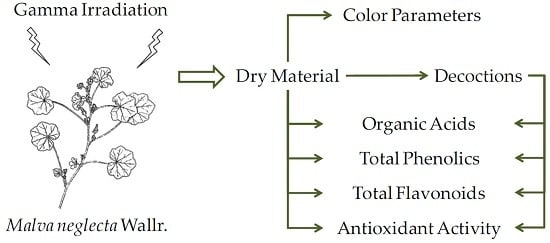
Interests: chemistry of natural products; emerging conservation technologies; gamma and electron beam irradiation; development of functional food; recovery of biological waste; bio-based ingredients
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
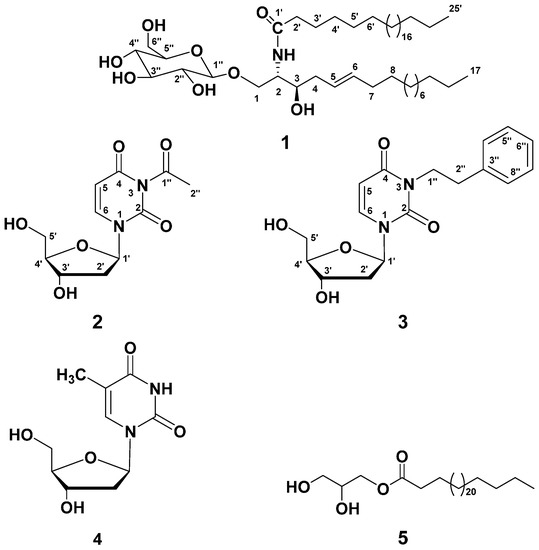
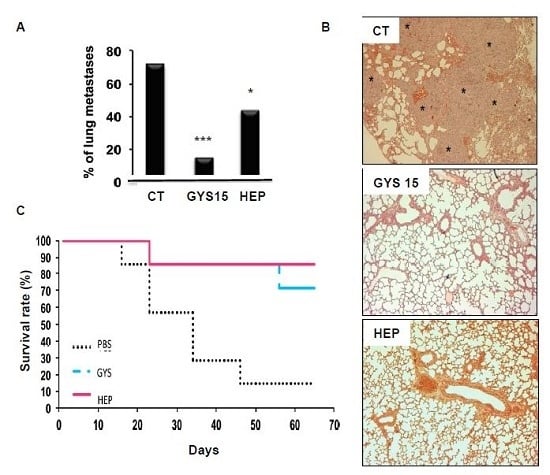
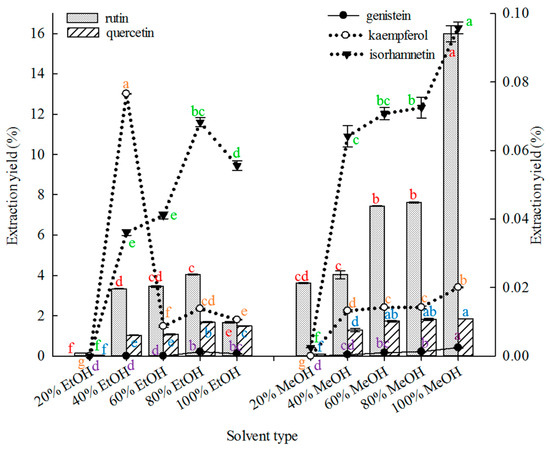
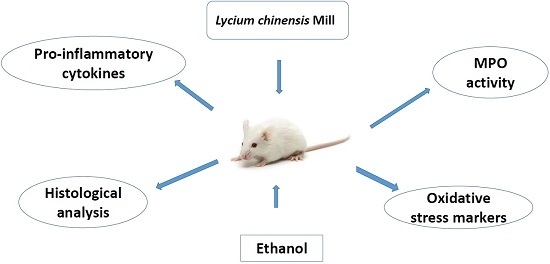
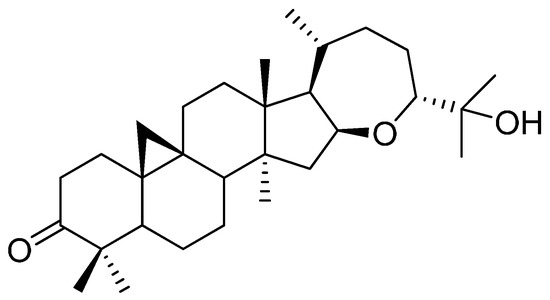
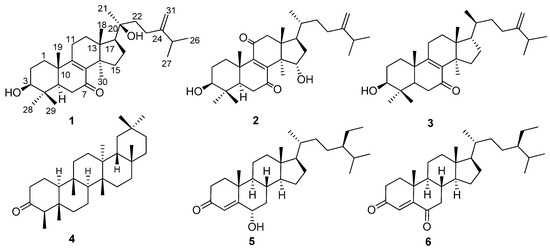
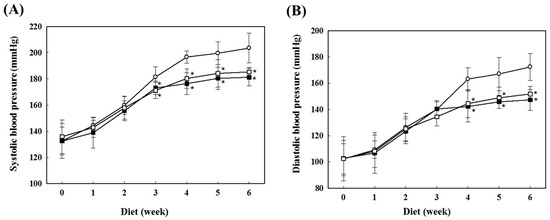
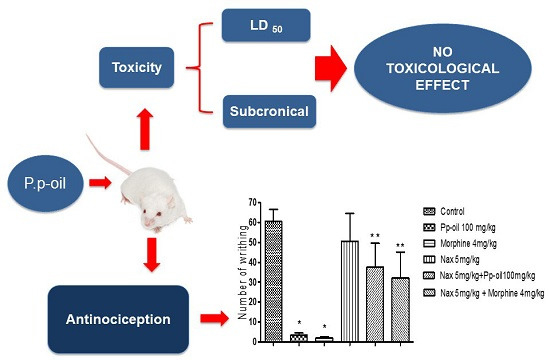
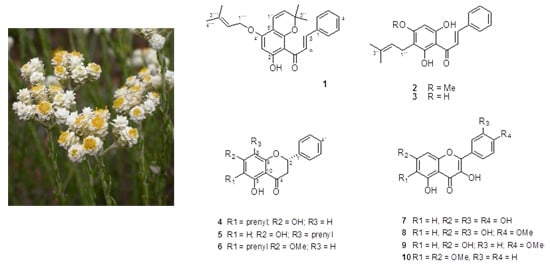
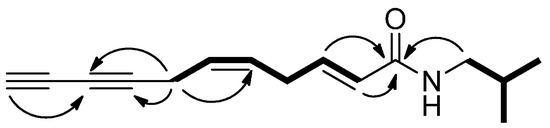
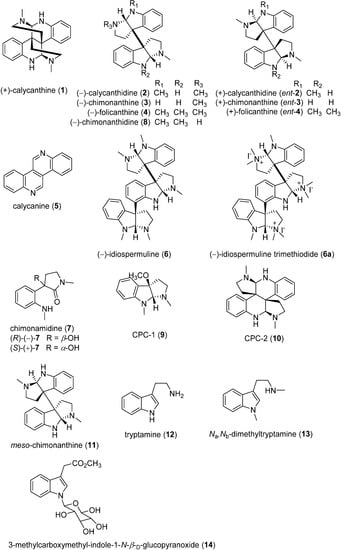
Consumers increasingly believe that foods contribute directly to their health and well-being. In this context, extranutritional constituents that typically occur in small quantities in foods, "Bioactive compounds", play a very significant role. Bioactive compounds are being intensively studied to evaluate their effects on health, including antioxidant, antiallergic, antimicrobial, antithrombotic, antiatherogenic, hypoglycaemic, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, cytostatic, immunosuppressive properties, and hepatoprotective activities. Contributions for this issue, both in form of original research and review articles, may cover all aspects of bioactive compounds with proven activities in various biological screenings and pharmacological models, e.g. quantification, variability and efficacy of bioactive compounds; development of new protocols and methods based on chemical or biological systems for the evaluation of in vivo and in vitro bioactivity; clinical and nutritional trials focused on the bioactive properties of bioactive compounds synthesized or isolated; elucidation of bioactive compounds mechanisms; innovative techniques of bioactive compounds delivery and protocols for the extraction, isolation, structural characterization of new bioactive compounds will be welcomed, on condition that an adequate evaluation of their efficacy is provided. Papers regarding the development of pharmaceuticals from bioactive compounds will be also taken into consideration.
Dr. Roberto Fabiani
Dr. Eliana Pereira
Collection Editors
Prof. Dr. Isabel C.F.R. Ferreira
Dr. Nancy D. Turner
Former Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts for the topical collection can be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All papers will be peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on this website. The topical collection considers regular research articles, short communications and review articles. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The article processing charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Keywords
- bioactivity
- natural products
- synthesised compounds
- isolation techniques
- structure elucidation
- mechanism of action
Related Special Issue
- Bioactive Compounds in Pharmaceuticals (1 article)